| [1] Li X, Han Y, Di Z, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation. J Clin Neurosci. 2016; 33(11):19-27. [2] Kamson S, Trescot AM, Sampson PD, et al. Full-endoscopic assisted lumbar decompressive surgery performed in an outpatient, ambulatory facility: report of 5 years of complications and risk factors. Pain Physician. 2017;20(2):E221-E231. [3] 李建江,楚戈,杨涛,等.经皮椎间孔镜下 TESSYS 技术修复腰椎固定融合后邻近节段退行性变[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(26): 4186-4190.[4] Mahesha K. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: Results of first 100 cases. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51(1):36-42. [5] Eun SS, Lee SH, Sabal LA. Long-term follow-up results of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar dis6cectomy. Pain Physician. 2016;19(8):E1161-E1166. [6] Ruan W, Feng F, Liu Z, et al. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus open lumbar microdiscectomy for lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2016;31:86-92. [7] Jasper GP, Francisco GM, Telfeian AE. Endoscopic transforaminal discectomy for an extruded lumbar disc herniation. Pain Physician. 2013;16(1):E31-35. [8] Fan G, Han R, Gu X, et al. Navigation improves the learning curve of transforamimal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Int Orthop. 2017;41(2):323-332. [9] Zeng Y, Bao J, Su J, et al. Novel targeted puncture technique for percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy reduces X-ray exposure. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):2960-2968. [10] 谭海涛,黄圣斌,谢兆林,等.导航导杆在椎间孔镜穿刺定位的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(4):339-344.[11] Wu R, Liao X, Xia H. Radiation exposure to the surgeon during ultrasound-assisted transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: A prospective study. World Neurosurg. 2017; 101(5):658-665. [12] Hu Z, Li X, Cui J, et al. Significance of preoperative planning software for puncture and channel establishment in percutaneous endoscopic lumbar DISCECTOMY: A study of 40 cases. Int J Surg. 2017;41:97-103. [13] Choi G, Modi HN, Prada N, et al. Clinical results of XMR-assisted percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8(1):14. [14] Moses ZB, Chi JH. Genetic susceptibility for sciatica and lumbar disc herniation. Neurosurgery. 2017;81(1):N13-N14. [15] Heider FC, Mayer HM. Surgical treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2017;29(1):59-85. [16] Wu W, Liang J, Ru N, et al. Microstructural changes in compressed nerve roots are consistent with clinical symptoms and symptom duration in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(11):E661-666. [17] Ahn Y, Lee S H, Park WM, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbardiscectomy for recurrent disc herniation: surgical technique, out?come, and prognostic factors of 43 consecutive cases. Spine. 2004;29(16):E326-E332. [18] Kim MJ, Lee SH, Jung ES, et al. Targeted percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic diskectomy in 295 patients: comparison with results of microscopic discectomy. Surg Neurol. 2007;68(6):623-631. [19] Choi KC, Park CK. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for l5-s1 disc herniation: consideration of the relation between the iliac crest and L5-S1 disc. Pain Physician. 2016;19(2):E301-308. [20] Tezuka F, Sakai T, Abe M, et al. Anatomical considerations of the iliac crest on percutaneous endoscopic discectomy using a transforaminal approach. Spine. 2017;17(12):1875-1880. [21] Ahn SS, Kim SH, Kim DW. Learning curve of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy based on the period (early vs. late) and technique (in-and-out vs. in-and-out-and-in): a retrospective comparative study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(6):539-546. [22] Wang H, Huang B, Li C, et al. Learning curve for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy depending on the surgeon’s training level of minimally invasive spine surgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115 (10):1987-1991. [23] Sclafani JA, Kim CW. Complications associated with the initial learning curve of minimally invasive spine surgery: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(6):1711-1717. [24] Wu XB, Fan GX, Gu X, Learning curves of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy in transforaminal approach at the L4/5 and L5/S1 levels: a comparative study. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(7):553-560. [25] 温冰涛,张西峰,王岩,等.经皮内窥镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症的并发症及其处理[J].中华外科杂志,2017,49(12):1091-1095.[26] Ahn Y, Kim CH, Lee JH, et al. Radiation exposure to the surgeon during percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a prospective study. Spine. 2013;38(7):617-625. [27] Srinivasan D, Than KD, Wang AC, et al. Radiation safety and spine surgery: systematic review of exposure limits and methods to minimize radiation exposure. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(6): 1337-1343. [28] Hadelsberg UP, Harel R. Hazards of Ionizing radiation and its impact on spine surgery. World Neurosurg. 2016;92(8):353-359. [29] Mulconrey DS. Fluoroscopic radiation exposure in spinal surgery: in vivo evaluation for operating room personnel. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(7):E331-335. [30] Iprenburg M, Wagner R, Godschalx A, et al. Patient radiation exposure during transforaminal lumbar endoscopic spine surgery: a prospective study. Neurosurg Focus. 2016;40(2):E7. [31] Fan G, Gu X, Liu Y, et al. Lower learning difficulty and fluoroscopy reduction of transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy with an accurate preoperative location method. Pain Physician. 2016;19(8):E1123-E113. |
.jpg)
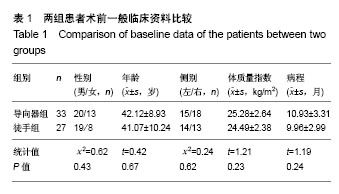
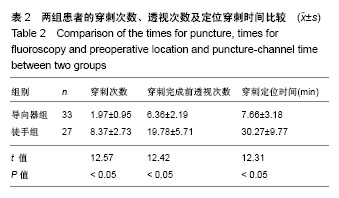
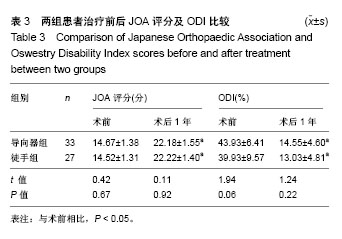
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)