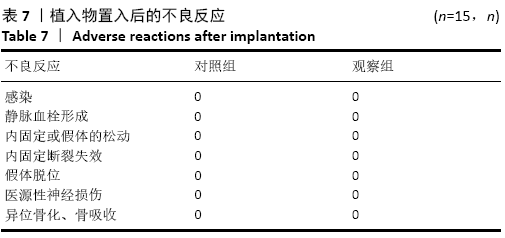
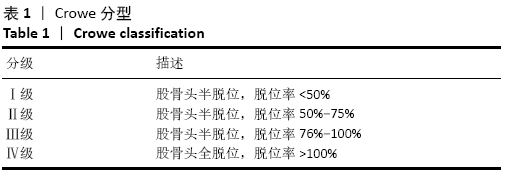
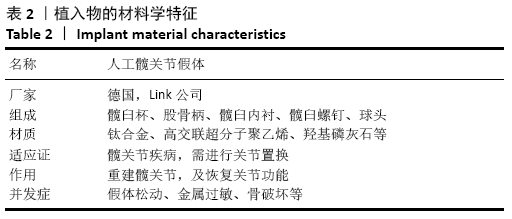
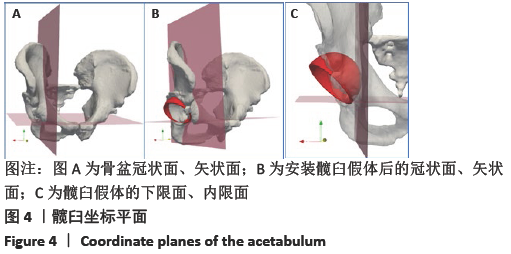
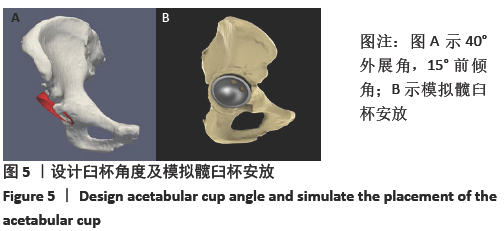
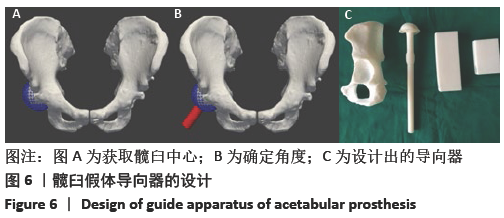
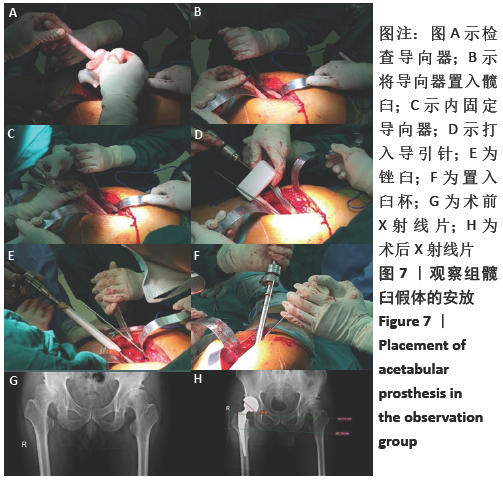
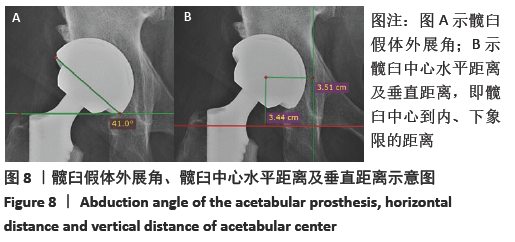
[1] 秦宏敏,刘汉涛,刘典锋.发育性髋关节发育不良(DDH)的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(23):2163-2165.
[2] 李蓉,王雯雯.发育性髋关节发育不良诊断进展及中国筛查模式探讨[J].医学综述,2018,24(14):2817-2822.
[3] 底垚宗,杨建平,王雯雯,等.天津市发育性髋关节异常的早前筛查[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,5(31):463-468.
[4] 杨晓东,莫小联,冯祥,等.西藏日喀则地区发育性髋关节发育不良致病危险因素相关性研究[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2016,6(31):833-835.
[5] BARONCIANI D, ATTI G, ANDILORO F, et al. Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip:from theory to practice.Collaborative group DDH project. Pediatrics. 1997;99(2): E5.
[6] PATEL H. Canadian task force on preventive health care.Preventive health care, 2001 update: Screening and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. CMAJ. 2001;164(12):1669-1677.
[7] 陈述,燕华,吴伟平,等.骨盆截骨术治疗发育性髋关节发育不良的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(3):244-247.
[8] ROGERS BA, GARBEDIAN S, KUCHINAD RA, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for adult hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(19):1809-1821.
[9] 温东栋,梁瑞德.发育性髋关节发育不良治疗进展[J].广西中医药大学学报, 2015,18(2):94-97.
[10] 卢俊雄. 全髋关节置换术治疗成人髋关节发育不良临床疗效分析[D].广西医科大学,2019.
[11] 何忠,梁周.3D打印技术辅助全髋关节置换术治疗Crowe Ⅳ型成人髋关节发育不良[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(2):146-148.
[12] 阿拉木斯,Gonchigsuren D. 3D打印在全髋关节置换术治疗髋关节发育不良的临床研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(85):91-92.
[13] 曹彭凯,王晓猛,白伟侠,等.2018年版《骨关节炎诊疗指南》解读[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(11):1241-1243.
[14] 王雷,尚希福.成人髋关节发育不良治疗新进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(17):3223-3226.
[15] 张政,官建中.3D打印技术在成人发育性髋关节发育不良患者中的应用进展[J].安徽医药,2018,22(8):1437-1440.
[16] 杨清,杨毅,杨柳,等.3D打印技术用于人工全髋关节置换术治疗成人DDH的临床应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(8):693-697.
[17] 王春鹏,杨海娇,张成,等.3D打印技术在骨科领域的应用进展[J].医学综述, 2020,26(1):118-122.
[18] 黎庆钿,林博夫,陈学潘,等.3D技术辅助钽金属块植入修复严重髋臼骨缺损的早期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(3):129-137.
[19] 田书畅,姚庆强,殷信道,等.iASSIST智能导航系统与三维打印个性化膝关节截骨导板技术在人工全膝关节置换中的应用效果比较[J],中华外科杂志, 2017,55(6):423-429.
[20] XING QQ, ZHONG D, PAN YX, et al. A comparative study of patients’ subjective feelings toward total hip arthroplasty with patient‐specific instruments and traditional total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):269-276.
[21] ZHOU F, XUE F, ZHANG S. The application of 3D printing patient specific instrumentation model in total knee arthroplasty. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27(5): 1217-1221.
[22] YANG L, GROTTKAU B, HE Z, et al. Three dimensional printing technology and materials for treatment of elbow fractures. Int Orthop. 2017;41(11):2381-2387.
[23] LIU ZJ, JIA J, ZHANG YG, et al.Internal fixation of complicated acetabular fractures directed by preoperative surgery with 3D printing models. Orthop Surg. 2017; 9(2):257-260.
[24] 李明,孙亮,马腾,等.3D打印快速成型技术在髋臼骨折分型及年轻医生培养中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(2):140-145.
[25] GREBER EM, PELT CE, GILILLAND JM, et al. Challenges in total hip arthroplasty in the setting of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9s): S38-s44.
[26] 王波,余楠生.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版) [J].中华关节外科杂志(电子),2019,13(1):124-130.
[27] 曹彭凯,王晓猛,白伟侠,等.2018年版《骨关节炎诊疗指南》解读[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(11):1241-1243.
[28] 王岩.坎贝尔骨科手术学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2013:148.
[29] 杨育晖,李钊,董航,等. 成人DDH患者保髋手术失败后的THA疗效分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2018,12(2):256-260.
[30] 周金,刘炯,杨砥,等.3D打印技术辅助成人DDH初次THA的髋臼置入[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2017, 25(23): 2182-2186.
[31] 张勇,朱振安,朱明生,等.CroweⅡ/Ⅲ型髋关节发育不良继发重度骨关节炎髋臼解剖旋转中心重建方法及效果[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016,10(4):393-398.
[32] DAPUZZO MR, SIERRA RJ. Acetabular Considerations during total hip arthroplasty for hip dysplasia.Orthop Clin North Am. 2012;43(3):369-375.
[33] 买提库尔班•买吐送,李国庆,汪洋,等.成人DDH患者保髋手术失败后的THA疗效分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(3):200-205+218.
[34] 周涛,肖勋刚,邹康,等.3D打印技术在DDH患者中重建髋臼旋转中心的最新进展[J].中南医学科学杂志,2019,47(1):106-109.
[35] JOHANN H, HOLME TJ, WARWICK R, et al. 3D-printed patient-specific guides for hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(16):1342-1348.
[36] LIU K, LI Z, MA Y, et al. 3D-printed pelvis model is an efficient method of osteotomy simulation for the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(2):1155-1160.
[37] WON SH, LEE YK, HA YC, et al. Improving pre-operative planning for complex total hip replacement with a Rapid Prototype model enabling surgical simulation. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1458-1463.
[38] 李艳捧,杜晓猛,李兴华,等.正常成人髋关节软骨厚度的MRI测量研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2016,14(3):111-112.
[39] 李宏斌,骆剑敏,骆宏伟,等.全髋关节置换术中髋臼位置安放不良的预防[J].临床骨科杂志,2017,20(2):165-168.
[40] 李建有,管国华,李雄峰,等.全髋关节置换术治疗Crowe Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良患者及围手术期并发症分析[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(1):74-77.
|
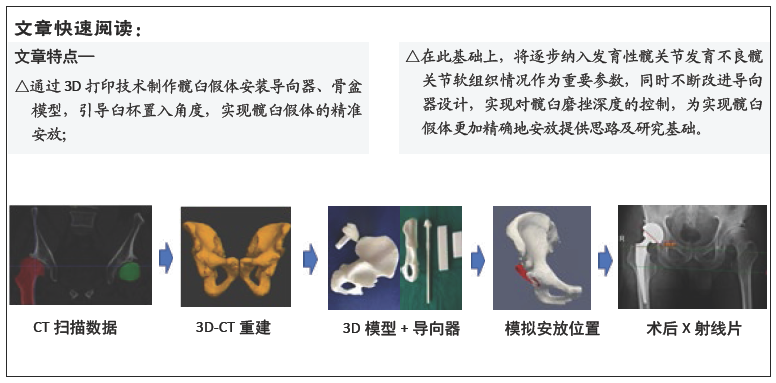 文题释义:
文题释义: