| [1] Craft AM, Ahmed N, Rockel JS, et al. Specification of chondrocytes and cartilage tissues from embryonic stem cells. Development. 2013;140(12):2597-2610.[2] Akkiraju H, Nohe A. Role of Chondrocytes in Cartilage Formation, Progression of Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2015;3(4):177-192.[3] Koh YG, Choi YJ, Kwon SK, et al. Clinical results and second-look arthroscopic findings after treatment with adipose-derived stem cells for knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(5):1308-1316.[4] Marupanthorn K, Tantrawatpan C, Tantikanlayaporn D, et al. The Effects of TNF-α on Osteogenic Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98 Suppl 3:S34-40.[5] Latief N, Raza FA, Bhatti FU, et al. Adipose stem cells differentiated chondrocytes regenerate damaged cartilage in rat model of osteoarthritis. Cell Biol Int. 2016;40(5):579-588.[6] Freitag J, Ford J, Bates D, et al. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the treatment of isolated knee chondral lesions: design of a randomised controlled pilot study comparing arthroscopic microfracture versus arthroscopic microfracture combined with postoperative mesenchymal stem cell injections. BMJ Open. 2015;5(12):e009332.[7] English A, Jones EA, Corscadden D, et al. A comparative assessment of cartilage and joint fat pad as a potential source of cells for autologous therapy development in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(11):1676-1683.[8] Chang YH, Liu HW, Wu KC, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Clinical Applications in Osteoarthritis. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):937-950.[9] Salyutin RV, Zapohlska KM, Palyanytsya SS, et al. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells of adipose tissue. Klin Khir. 2015;(3):61-64.[10] Kessler MW, Ackerman G, Dines JS, et al. Emerging technologies and fourth generation issues in cartilage repair. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2008;16(4):246-254.[11] Zheng B, Li G, Chen WC, et al. Human myogenic endothelial cells exhibit chondrogenic and osteogenic potentials at the clonal level. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7): 1089-1095.[12] Beane OS, Fonseca VC, Cooper LL, et al. Impact of aging on the regenerative properties of bone marrow-, muscle-, and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115963.[13] Matsumoto T, Cooper GM, Gharaibeh B, et al. Cartilage repair in a rat model of osteoarthritis through intraarticular transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells expressing bone morphogenetic protein 4 and soluble Flt-1. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(5):1390-1405.[14] Koga H, Muneta T, Nagase T, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal tissues-derived stem cells for in vivo chondrogenesis: suitable conditions for cell therapy of cartilage defects in rabbit. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;333(2): 207-215.[15] Yoshimura H, Muneta T, Nimura A, et al. Comparison of rat mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovium, periosteum, adipose tissue, and muscle. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;327(3):449-462.[16] Jo CH, Lee YG, Shin WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1254-1266.[17] Sekiya I, Muneta T, Horie M, et al. Arthroscopic Transplantation of Synovial Stem Cells Improves Clinical Outcomes in Knees With Cartilage Defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(7):2316-2326.[18] Henrotin Y, Clutterbuck AL, Allaway D, et al. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(2):141-149.[19] Campbell DD, Pei M. Surface markers for chondrogenic determination: a highlight of synovium-derived stem cells. Cells. 2012;1(4):1107-1120.[20] Jones BA, Pei M. Synovium-derived stem cells: a tissue-specific stem cell for cartilage engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(4):301-311.[21] Campbell DD, Pei M. Surface markers for chondrogenic determination: a highlight of synovium-derived stem cells. Cells. 2012;1(4):1107-1120.[22] Vilar JM, Morales M, Santana A, et al. Controlled, blinded force platform analysis of the effect of intraarticular injection of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells associated to PRGF-Endoret in osteoarthritic dogs. BMC Vet Res. 2013;9:131.[23] Musumeci G, Mobasheri A, Trovato FM, et al. Biosynthesis of collagen I, II, RUNX2 and lubricin at different time points of chondrogenic differentiation in a 3D in vitro model of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(8):1407-1417.[24] Platas J, Guillén MI, del Caz MD, et al. Conditioned media from adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells downregulate degradative mediators induced by interleukin-1β in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:357014.[25] Skalska U, Kontny E. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from infrapatellar fat pad of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis have comparable immunomodulatory properties. Autoimmunity. 2016;49(2): 124-131.[26] Mei L, Shen B, Ling P, et al. Culture-expanded allogenic adipose tissue-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration in an experimental rat osteoarthritis model. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176107.[27] Pagani S, Borsari V, Veronesi F, et al. Increased Chondrogenic Potential of Mesenchymal Cells From Adipose Tissue Versus Bone Marrow-Derived Cells in Osteoarthritic In Vitro Models. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(6): 1478-1488.[28] Manferdini C, Maumus M, Gabusi E, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert antiinflammatory effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes from osteoarthritis patients through prostaglandin E2. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(5): 1271-1281.[29] Ivanova-Todorova E, Bochev I, Dimitrov R, et al. Conditioned medium from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells induces CD4+FOXP3+ cells and increases IL-10 secretion. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012: 295167.[30] Park MJ, Kwok SK, Lee SH, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce expansion of interleukin-10-producing regulatory B cells and ameliorate autoimmunity in a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(11):2367-2377.[31] Nava MM, Zandrini T, Cerullo G, et al. 3D Stem Cell Niche Engineering via Two-Photon Laser Polymerization. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1612:253-266.[32] Payr S, Tichy B, Atteneder C, et al. Redifferentiation of aged human articular chondrocytes by combining bone morphogenetic protein-2 and melanoma inhibitory activity protein in 3D-culture. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0179729.[33] Sieber S, Wirth L, Cavak N, et al. Bone marrow-on-a-chip: Long-term culture of human haematopoietic stem cells in a three-dimensional microfluidic environment. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):479-489. |
.jpg)
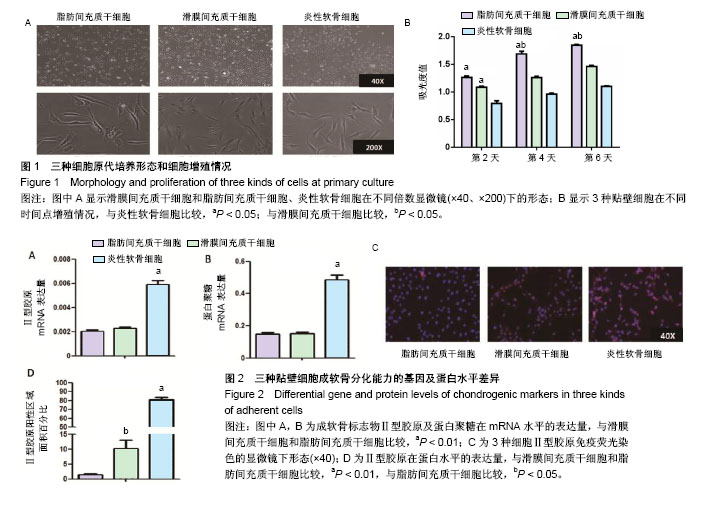
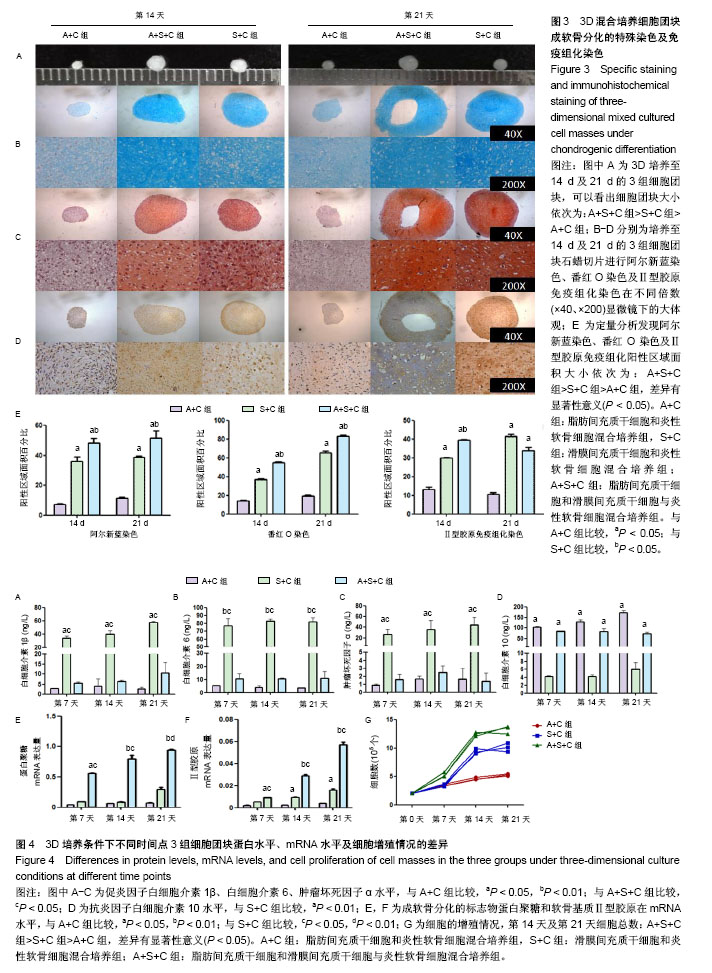
.jpg)
.jpg)