中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (17): 2686-2691.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0525
• 脐带脐血干细胞 umbilical cord blood stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
第2代和第5代人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体miRNA谱的比较
林庆铿1,2,尹德宏2,刘菊芬2,张学娟1,2,白盈盈1,2,宋乙甲1,2,潘兴华2,刘高米洋2
- 1昆明医科大学解放军昆明总医院临床学院,云南省昆明市 650032;2解放军昆明总医院细胞生物治疗中心,干细胞与免疫细胞生物医药技术国家地方联合工程实验室,云南省细胞治疗技术转化医学重点实验室,云南省昆明市 650032
Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells at passage 2 and 5: a comparative study on microRNA profiles
Lin Qing-keng1, 2, Yin De-hong2, Liu Ju-fen2, Zhang Xue-juan1, 2, Bai Ying-ying1, 2, Song Yi-jia1, 2, Pan Xing-hua2, Liu-Gao Mi-yang2
- 1Kunming General Hospital Clinical College of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China; 2Cell Biological Therapy Center of Kunming General Hospital of PLA, Cell Biological Medicine integrated Engineering Laboratory of State and Region of Yunnan Province, the Stem Cell Therapy Key Laboratory of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 外泌体:是一类由某些细胞释放的细胞外囊泡。已有报道认为它们能够调节宿主-病原体的相互作用,参与传染性和炎性疾病、神经疾病和癌症等很多种疾病的病理过程,同时在正常的生理过程中也发挥着介导细胞间通讯等作用。另外细胞外囊泡含有丰富的生物标志物,可用于监测临床状态、治疗反应、疾病进展等,同时它们还有发展成临床药物递送载体的潜力。由于细胞外囊泡的组成成分并不是随机的,每一个细胞外囊泡都会携带特定的分子信息,如携带蛋白质、脂质、核酸和糖等生物活性分子在细胞间传递信号,其有一个复杂的分选系统来决定哪些分子能够进入细胞外囊泡,因而其有望成为进一步了解人体细胞层面调节过程的突破口。 聚类分析:是通过建立各种不同的数学模型,把基于相似数据特征的变量或样本组合在一起。归为一个簇的 miRNA在功能上可能相似或关联,从而找到miRNA的功能信息。聚类分析将表达模式相同或相近的miRNA或样本聚集成类,并使用不同颜色的区域代表不同的聚类分组信息,从而判断不同样品或不同实验条件下的聚类模式。由于同类的miRNA可能具有相似的功能,或是共同参与同一代谢过程或细胞通路,因此有助于筛选潜在的有协同作用或受同样调控的miRNA,从而帮助发掘miRNA的功能。
中图分类号:
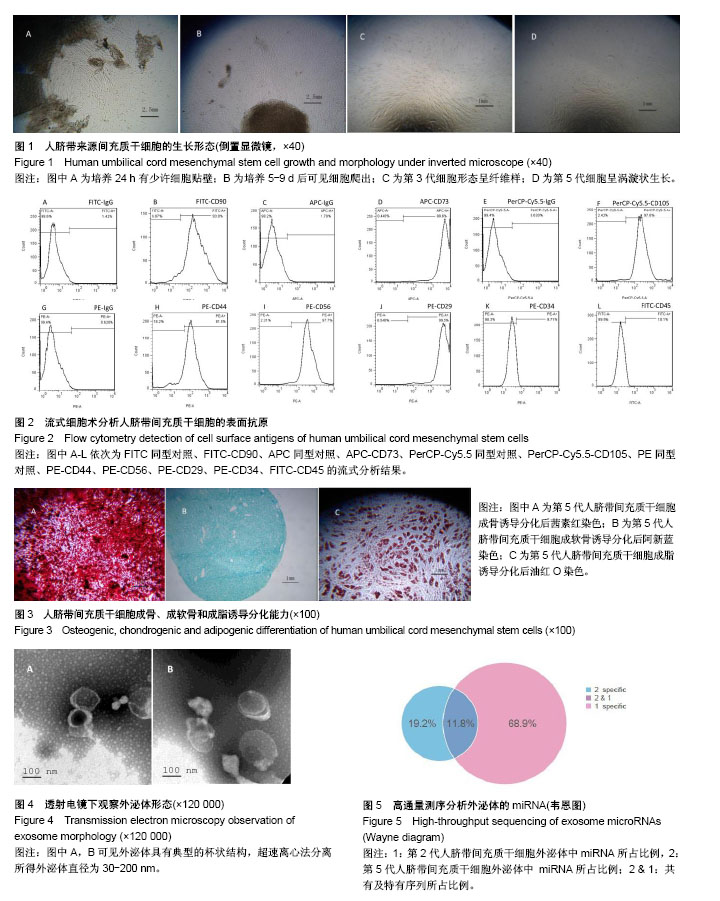
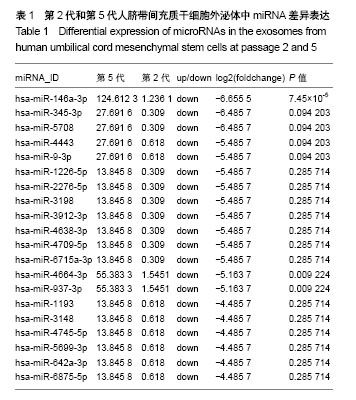
.jpg)