1.1 设计 细胞学体外观察实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2012年6月至2013年9月在暨南大学医学院血液病研究所完成。
1.3 材料 人T淋巴细胞白血病细胞系Molt-4株(生命科学研究院细胞资源中心,上海)。RPMI 1640培养基(GIBCO公司,USA);胎牛血清(PAA公司,奥地利);TRIzol 试剂(Invitrogen公司,USA);兔抗人Smo单抗(CST公司,USA);siRNA由Invitrogen公司进行化学合成。
1.4 方法
1.4.1 实验分组 Smo-siRNA1,2,3组为实验组,分别转染Smo-siRNA1,2,3;对照组分别为转染无关干扰序列RNA的阴性对照组及未予任何处理的空白对照组。
1.4.2 细胞培养 人T淋巴细胞白血病细胞系Molt-4株接种在含体积分数10%新生牛血清、100 U/mL 链霉素的RPMI1640培养基中,在37 ℃,体积分数5%CO2的培养箱连续培养,两三天传代1次。
1.4.3 Smo-siRNA的设计与合成 Smo-siRNA设计遵循Invitrogen 公司(www.invitrogen.com)提供的StealthTMRNAi设计法则由网上在线进行设计而成。
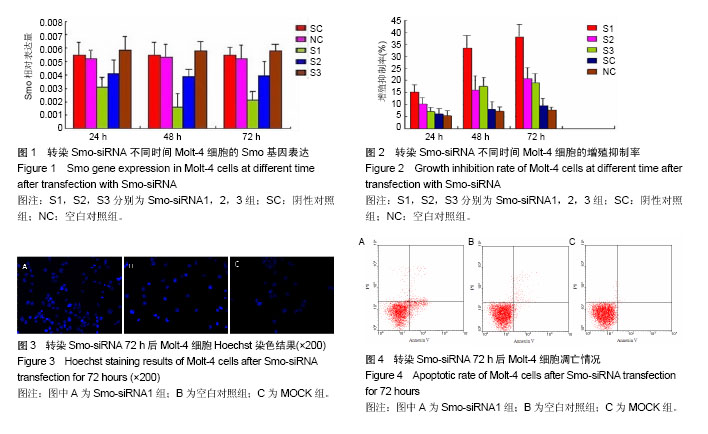
在GenBank(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)查找Smo基因序列(ACCESSION NM_005631.4),通过Invitrogen公司(www.invitrogen.com)提供的StealthTM RNAi设计法则,成功地在线设计出若干条针对Smo基因mRNA上不同序列的siRNA(长度都为21 nt),并从中再根据经验选出3条进行合成,分别将它们命名为Smo-siRNA1,2,3,其靶位点起始于Smo mRNA序列上1 221 bp,1 458 bp,1 851 bp,分别位于Smo序列不同外显子上。
根据siRNA设计原则,还设计出与Smo基因序列无同源性的阴性对照siRNA(SC),BLAST比对后确证它们与人类基因组中的mRNA没有序列同源性。相对以前的设计方法,采用上述方法合成出来的siRNA,稳定性提高的同时还有效去除脱靶效应。设计出来的siRNA交给Invitrogen 公司进行化学合成,所合成的siRNA具有周期短、纯度高特点,对组织或细胞的毒副作用较小;由于其有容易降解的特点,将转染后24-72 h设定为检测指标时间。利用Alexa Red Oligo观察和流式细胞仪检测其荧光值(发射光波长565 nm、激发光波长555 nm),分析细胞活力和转染效率。
1.4.4 核转染 每组单次收集2.5×106个处于对数生长期的Molt-4细胞,1 100 r/min离心10 min,完全去除上清;用100 μL预热至室温的Supplement和NucleofectorTM Solution混合液(二者比例2︰9,现配)悬浮细胞;各组分别用核转染专用的移液管加入无关干扰序列的阴性对照siRNA或1 μL siRNA1,2,3,混匀,加入核转杯,启动核酸转染仪特异性程序,依据常用指南,各组细胞转染时所选择的程序分别为C-005,转染完成后马上用移液管将转染后的细胞液接种在含体积分数10%新生牛血清、100 U/mL链霉素的RPMI1640培养基的培养瓶中,置于37 ℃,含体积分数为5% CO2培养箱中培养。空白对照则直接接种于同样预处理过的培养基中。每组均增设总数为1×107个Molt-4细胞的4个平行杯,转染后接种于终体积为20 mL同一培养瓶中,以保证各项检测指标所需的细胞数。
1.4.5 RNA提取、反转录和RT-PCR 总RNA使用TRIzol从Molt-4细胞中分离,cDNA通过使用Superscript Ⅱ RNA酶反转录酶试剂盒合成。
利用SYBR GreenⅠ实时定量PCR检测各组Molt-4细胞Smo基因表达情况[11],应用于荧光实时定量PCR的引物序列见表1,以β2M基因作为内参照。每一样本分别进行β2M和Smo检测,应用Real Master Mix试剂盒,总反应体积为20 µL,包括终浓度为0.5 mmol/L的上、下游引物1 μL、2.5×Real Master Mix 8 μL、dH2O 9 μL和cDNA 1 μL。经过95 ℃、1 min变性,共进行40个循环扩增后,每一循环包括95 ℃、72 ℃、62 ℃,各15 s。并在81 ℃读板(1 s)。以0.17 ℃/s变化速度从55 ℃到95 ℃,每隔2 s记录一次荧光值,并描绘熔解曲线。在Chromo 4 荧光定量PCR仪中进行反应。每样本检测均重复3次。以β2M为内参照,利用Ct值,计算Molt-4细胞中Smo基因相对mRNA表达量,其计算公式为:相对mRNA表达量=2-?Ct×100%,其中,?Ct= Ct(Smo)-Ct(β2M)[12]。
.jpg)
1.4.6 Smo-siRNA 转染后各组细胞增殖抑制效应 用CCK-8法观察各组Molt-4细胞体外增殖的抑制情况。将各组转染后Molt-4细胞液接种在96孔培养板中,并设空白对照组、阴性对照组,每组设3个平行孔,每孔100 µL(含约5×105 Molt-4细胞或者仅含100 U/mL链霉素、100 U/mL青霉素和体积分数为10%新生牛血清的RPMI1640培养基),置于体积分数为5%CO2、饱和湿度的培养箱,37 ℃条件下,常规培养24,48,72 h,分别向每孔内加入CCK-8 10 µL,37 ℃孵育2 h,然后用酶标仪测定450 nm波长处吸光度值,可间接反映细胞存活数量。每孔均重复测量3次。据此可计算Smo-siRNA1,2,3转染后,各时间点Molt-4细胞的增殖抑制率。
1.4.7 Smo-siRNA转染后各组细胞凋亡效应 转染Smo-siRNA1 72 h后,收集各组Molt-4细胞,进行Hoechst33258染色观察细胞凋亡形态,流式细胞仪AnnexinV/PI双染法检测细胞凋亡率。
流式细胞仪AnnexinV/PI双染法:离心收集每组约5×105个Molt-4细胞(Smo-siRNA1),并设未加任何RNA进行空转染的转染条件对照组(MOCK组),PBS洗涤2次,离心去上清,用Annexinv-FITC结合液195 µL重悬细胞,加入Annexinv-FITC 5 µL,避光孵育10 min,离心后去上清,再用Annexinv-FITC结合液190 µL重悬细胞,加入碘化丙啶染色液10 µL,冰浴、避光放置,进行流式细胞仪检测,用MULTCYCLE软件分析结果。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①Smo-siRNA转染后Smo在Molt-4 T细胞中表达水平;②Smo-siRNA转染后Molt-4 T细胞的增殖抑制效应;③Smo-siRNA转染后Molt-4 T细胞的凋亡效应。
1.6 统计学分析 使用SPSS 13.0统计软件进行配对t 检验和单因素方差分析。检验水准均为α=0.05。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)