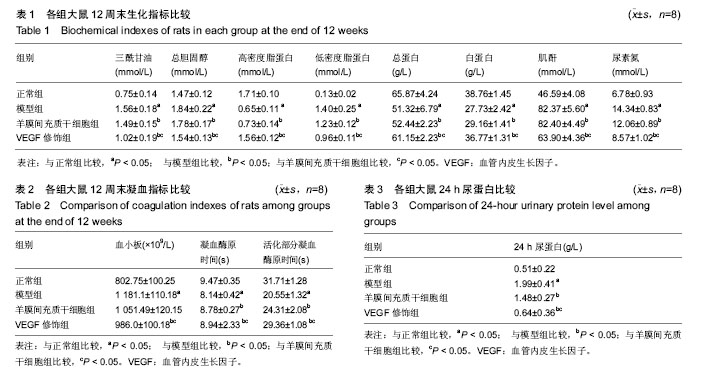
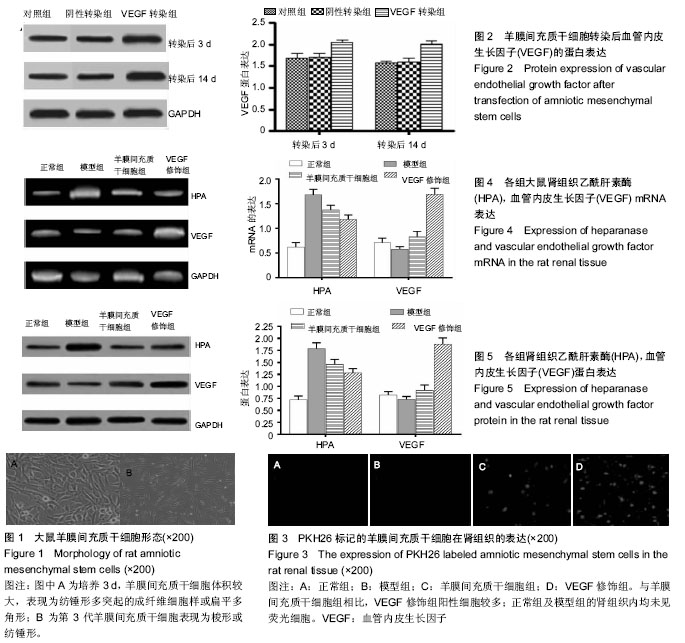
| [1] Ma R, Cui Z, Hu SY, et al. The alternative pathway of complement activation may be involved in the renal damage of human anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. PLoS One. 2014; 9(3):e91250.[2] Jellouli M, Fitouhi S, Abidi K, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil in treatment of childhood steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Tunis Med. 2016;94(3):221-225.[3] 黄义夫.浅析肾病综合症的诊断思路与治疗[J].中国保健营养,2015, 25(17):145-146.[4] Davin JC, Rutjes NW. Nephrotic syndrome in children: from bench to treatment. Int J Nephrol. 2011;2011:372304.[5] Bennett MR. Biomarkers of therapeutic response in primary nephrotic syndrome: response. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28(1):161-162.[6] 徐雁,王时光,赵玉男.益肾通络方对实验性糖尿病大鼠血液流变学指标、血脂及PAI-1 的影响[J].江苏中医药,2013,45(12):73-75.[7] 王佳晶.中医治疗肾病综合症的临床分析[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志,2016,4(16):158.[8] Shakeel S, Mubarak M, I Kazi J, et al. Frequency and clinicopathological characteristics of variants of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults presenting with nephrotic syndrome. J Nephropathol. 2013;2(1):28-35.[9] 李建刚.原发性肾病综合征并发急性肾功能衰竭临床诊治分析[pJ].临床研究, 2017, 25(1) :91-92.[10] 孙宗成.中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征27例的疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2014,7(35):48-49.[11] 李善伟.肾病综合征六经辨证探讨[J].长春中医药大学学报,2013, 29(3):443-444.[12] Ku?ma-Mroczkowska E, Skrzypczyk P, Pańczyk-Tomaszewska M. Levamisole therapy in children with frequently relapsing and steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a single-center experience. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2016;41(3):243-247.[13] 徐丹.激素治疗肾病综合症副作用的观察与护理[J].医药前沿,2013, 3(28):259.[14] Lovric S, Ashraf S, Tan W, et al. Genetic testing in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: when and how. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(11):1802-1813.[15] 王洁敏,尹虹,董彦平,等.缺氧和高糖对大鼠肾成纤维细胞VEGF和PEDF表达的影响[J].甘肃科技,2013,29(18):133-135.[16] 钟建,李夏露.益肾活血通络法对单侧输尿管梗阻大鼠肾脏缺氧诱导因子-血管内皮生长因子信号通路干预作用的实验研究[J].环球中医药,2014,7(1):12-16.[17] 黄娜,赵建刚,侯宁宁,等.糖尿病大鼠肾小球VEGF-NO轴失衡在2型糖尿病早期肾病发生中的作用[J].中华临床医师杂志,2014,8(4): 656-660.[18] 郭燕羽,史丽萍.磷酸西格列汀干预糖尿病大鼠肾脏中VEGF的表达[J].河北联合大学学报:医学版,2013,15(1):10-12.[19] 赵东波,何扬,孙辽,等.厄贝沙坦联合吡格列酮对糖尿病肾病尿VEGF水平的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(24):4714-4717.[20] Ba?enková D, Rosocha J, Tóthová T, et al. Isolation and basic characterization of human term amnion and chorion mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(9):1047-1056.[21] Lu Y, Hui GZ, Wu ZY, et al. Transformation of human amniotic epithelial cells into neuron-like cells in the microenvironment of traumatic brain injury in vivo and in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(10):744-749.[22] 张超,曹洁,张素芳.人端粒酶反转录酶基因修饰人羊膜间充质干细胞移植治疗肺动脉高压[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(6):820-826.[23] 王钰莹,方宁,陈代雄,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞静脉移植后在心肌梗死大鼠体内的定植及分化[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(7):1583-1586.[24] 吕刚,张宏远.人促红细胞生成素修饰人羊膜间充质干细胞蛛网膜下腔移植对脑损伤的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(23):3432-3438.[25] 陈洁,张智,曾慧兰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞预处理脑死亡供鼠对移植肾的保护作用[J].中华器官移植杂志,2015,36(6):362-366.[26] 曲春辉,张玲,武杰,等.大鼠羊膜细胞体外培养及其干细胞标记物的表达[J].中国比较医学杂志,2015,25(4):61-65.[27] 王佳晶.中医治疗肾病综合症的临床分析[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志,2016,4(16):158.[28] Rahman MH, Qader MA, Haque SS, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a 5-year-old boy with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016;27(5):1021-1025.[29] Trachtman H. Biomarkers of therapeutic response in primary nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28(1):159.[30] 曾子文.长期使用糖皮质激素治疗肾病综合症不良反应研究[J].中国卫生产业,2011,8(11):98.[31] Nakagawa T, Shiratori A, Kawaba Y, et al. Efficacy of rituximab therapy against intractable steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Int. 2016;58(10):1003-1008.[32] 栾健,王艳,张杰涛,等.血管内皮生长因子和内抑素在大鼠糖尿病肾病发病中的作用[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2011,19(6):465-468.[33] Al-Husseiny F, Sobh MA, Ashour RH, et al. Amniotic Fluid-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cut Short the Acuteness of Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Int J Stem Cells. 2016;9(1):70-78.[34] Morigi M, De Coppi P. Cell therapy for kidney injury: different options and mechanisms--mesenchymal and amniotic fluid stem cells. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2014;126(2):59.[35] Monteiro Carvalho Mori da Cunha MG, Zia S, Oliveira Arcolino F, et al. Amniotic Fluid Derived Stem Cells with a Renal Progenitor Phenotype Inhibit Interstitial Fibrosis in Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136145.[36] Baulier E, Favreau F, Le Corf A, et al. Amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent fibrosis and preserve renal function in a preclinical porcine model of kidney transplantation. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(7):809-820. |
.jpg)
.jpg)