| [1] 神经病理性疼痛诊疗专家组. 神经病理性疼痛诊疗专家共识[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2013,19(12):705-710.[2] 钱滔来,高崇荣.神经性疼痛的治疗现状及进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2004,10(5):305-307.[3] van Hecke O, Austin SK, Khan RA, et al. Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 2014;155:654-662.[4] Bouhassira D, Lanteri-Minet M, Attal N, et al. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain. 2008;136:380-387.[5] 高永静,张志军,曹德利. 趋化因子介导的神经炎症反应和神经病理性疼痛[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2014,36(3):297-307.[6] Bennett CJ,Xie YK.A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pai. 1988;33:87-107.[7] 史吉胜,张毕,薛超,等. 星形胶质细胞在脊髓损伤中的研究进展[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2015,14(6):567-569.[8] 刘念,臧凯凯,张玉秋. 外周神经损伤小鼠不同脊髓节段小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的激活状态[J]. 生理学报, 2015,67(6): 571-582.[9] 肖霞,丁有权,齐建国. 周围神经损伤后慢性失神经及其对神经再生的影响[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2016,32(3):412-416.[10] 孙彩霞,苏兆亮,许化溪. 神经病理性疼痛中枢敏化的免疫炎症机制研究进展[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2012,33(3):331-333.[11] 彭海英,梁尚栋. 外周神经节卫星胶质细胞的研究进展[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2012,28(6):631-635.[12] 刘迪,唐倩倩,曹君利. 脑源性生长因子参与疼痛-抑郁共病的研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报,2015,31(1):26-30.[13] Yang Y, Wu H, Yan JQ, et al.Tumor narrows factor-alpha inhibits angiotensin II receptor type 1 expression in dorsal root ganglion neuruns via beta-catenin signaling. Neuroscience. 2013;248 C: 383-391.[14] Xu JQ, Deng JL, Wu YS, et al. Construction and Activity Assay of the Activating Transcription Factor 3 Reporter Vector pATF/CRE-luc. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica. 2006;1: 58-62. [15] 李思思,屠文展,钟燕彪,等. 神经胶质细胞在电针治疗神经病理性疼痛中的作用研究进展[J]. 针刺研究,2016,41(4):369-372.[16] 李世城,刘曾旭,王向东,等. p38MAPK激活与神经病理性疼痛关系的研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2016,22(6):458-460.[17] 熊青明,王汉兵,杨承祥,等. 神经肽与神经病理性疼痛研究新进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2016,22(2):137-140+143.[18] 徐江涛,马柯. 神经病理性疼痛中背根神经节交感神经芽生的机制研究[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2015,21(7):481-485.[19] 郑昌健,胡涵,曹红,等. JNK/MCP-1信号通路在姜黄素抗糖尿病神经病理性疼痛中的作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2014,30(11): 1941-1945.[20] 高永静,张志军,曹德利. 趋化因子介导的神经炎症反应和神经病理性疼痛[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2014,36(3):297-307.[21] 郭张华,陈建平. NMDA受体在神经病理性疼痛中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2013,19(3):173-176.[22] Anand U, Facer P, Yiangou Y, et al. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) localization and antagonist-mediated inhibition of capsaicin responses and neurite outgrowth in human and rat sensory neurons.Eur J Pain. 2013; 17(7): 1012-1026. [23] Khan N, Muralidharan A, Smith MT. Attenuation of the Infiltration of Angiotensin II Expressing CD3+ T-Cells and the Modulation of Nerve Growth Factor in Lumbar Dorsal Root Ganglia – A Possible Mechanism Underpinning Analgesia Produced by EMA300, An Angiotensin II Type 2 (AT2) Receptor Antagonist. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017; 10: 389.[24] 王新梅,杨莹,薛霞. 神经病理性疼痛的小胶质细胞机制[J]. 科技创新导报,2012,(19):233-234.[25] 刘健,李伟彦. 神经胶质细胞与神经病理性疼痛[J]. 医学研究生学报,2009,22(2):209-212.[26] 虞雪融,黄宇光,许力. 神经病理性疼痛大鼠脊髓NMDA受体NR2B亚基的表达[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2007,23(3):215-217.[27] Saijilafu, Zhang BY, Zhou FQ. Signaling pathways that regulate axon regeneration. Neurosci Bull. 2013; 4:411-420.[28] 肖韩艳,张本卓,韩丽萍,等. 血管紧张素Ⅱ2型受体拮抗剂EMA401对神经性疼痛模型大鼠的镇痛效应及机制研究[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(1):110-115.[29] Miyamoto S, Nakamura J, Ohtori S, et al.Pain-related behavior and the characteristics of dorsal-root ganglia in a rat model of hip osteoarthritis induced by mono-iodoacetate. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(7):1424-1430. [30] Medici T, Shortland PJ. Effects of peripheral nerve injury on parvalbumin expression in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. BMC Neurosci. 2015;16:93. [31] McCarthy CJ, Tomasella E, Malet M, et al. Axotomy of tributaries of the pelvic and pudendal nerves induces changes in the neurochemistry of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons and the spinal cord. Brain Struct Funct. 2016;221(4): 1985-2004.[32] Su J, Gao T, Shi T, et al. Phenotypic changes in dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord in the collagen antibody-induced arthritis mouse model. J Comp Neurol. 2015;523(10): 1505-1528. [33] Boateng EK, Novejarque A, Pheby T, et al. Heterogeneous responses of dorsal root ganglion neurons in neuropathies induced by peripheral nerve trauma and the antiretroviral drug stavudine. Eur J Pain. 2015;19(2):236-245. [34] Ogawa N, Kawai H, Terashima T, et al. Gene therapy for neuropathic pain by silencing of TNF-α expression with lentiviral vectors targeting the dorsal root ganglion in mice. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92073.[35] Matsuura Y, Ohtori S, Iwakura N, et al. Expression of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons in a lower trunk avulsion pain model in rats. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(8):1794-1799.[36] Cachemaille M, Laedermann CJ, Pertin M, et al. Neuronal expression of the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2 in rat dorsal root ganglia: modulation in the spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience. 2012;227:370-380. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
中枢神经系统敏化:在慢性神经病理性疼痛中发挥重要作用,其特征为神经元和胶质细胞的活化,并且在慢性神经病理性疼痛发生和长期持续状态中都能发现中枢神经系统敏化的存在。
脑源性神经营养因子:可能是联系神经病理性疼痛和神经修复的纽带,目前研究发现脑源性神经营养因子通过刺激脊髓中枢活化参与神经病理性疼痛的发生,同时脑源性神经营养因子促进神经元存活和轴突的生长,有利于神经修复。
文题释义:
中枢神经系统敏化:在慢性神经病理性疼痛中发挥重要作用,其特征为神经元和胶质细胞的活化,并且在慢性神经病理性疼痛发生和长期持续状态中都能发现中枢神经系统敏化的存在。
脑源性神经营养因子:可能是联系神经病理性疼痛和神经修复的纽带,目前研究发现脑源性神经营养因子通过刺激脊髓中枢活化参与神经病理性疼痛的发生,同时脑源性神经营养因子促进神经元存活和轴突的生长,有利于神经修复。.jpg) 文题释义:
中枢神经系统敏化:在慢性神经病理性疼痛中发挥重要作用,其特征为神经元和胶质细胞的活化,并且在慢性神经病理性疼痛发生和长期持续状态中都能发现中枢神经系统敏化的存在。
脑源性神经营养因子:可能是联系神经病理性疼痛和神经修复的纽带,目前研究发现脑源性神经营养因子通过刺激脊髓中枢活化参与神经病理性疼痛的发生,同时脑源性神经营养因子促进神经元存活和轴突的生长,有利于神经修复。
文题释义:
中枢神经系统敏化:在慢性神经病理性疼痛中发挥重要作用,其特征为神经元和胶质细胞的活化,并且在慢性神经病理性疼痛发生和长期持续状态中都能发现中枢神经系统敏化的存在。
脑源性神经营养因子:可能是联系神经病理性疼痛和神经修复的纽带,目前研究发现脑源性神经营养因子通过刺激脊髓中枢活化参与神经病理性疼痛的发生,同时脑源性神经营养因子促进神经元存活和轴突的生长,有利于神经修复。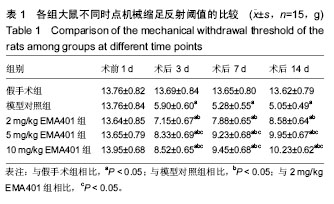
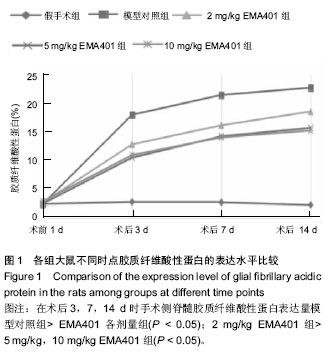
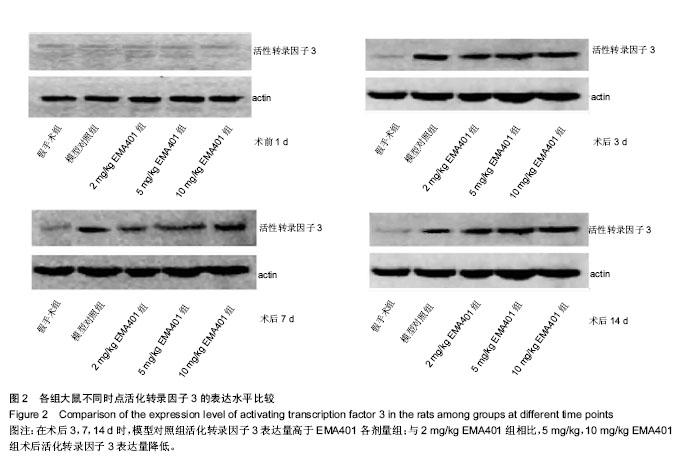
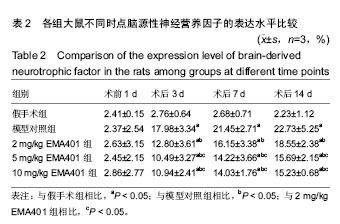
.jpg) 文题释义:
中枢神经系统敏化:在慢性神经病理性疼痛中发挥重要作用,其特征为神经元和胶质细胞的活化,并且在慢性神经病理性疼痛发生和长期持续状态中都能发现中枢神经系统敏化的存在。
脑源性神经营养因子:可能是联系神经病理性疼痛和神经修复的纽带,目前研究发现脑源性神经营养因子通过刺激脊髓中枢活化参与神经病理性疼痛的发生,同时脑源性神经营养因子促进神经元存活和轴突的生长,有利于神经修复。
文题释义:
中枢神经系统敏化:在慢性神经病理性疼痛中发挥重要作用,其特征为神经元和胶质细胞的活化,并且在慢性神经病理性疼痛发生和长期持续状态中都能发现中枢神经系统敏化的存在。
脑源性神经营养因子:可能是联系神经病理性疼痛和神经修复的纽带,目前研究发现脑源性神经营养因子通过刺激脊髓中枢活化参与神经病理性疼痛的发生,同时脑源性神经营养因子促进神经元存活和轴突的生长,有利于神经修复。