中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (8): 1190-1195.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0136
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
泸州地区成年人鼻部形态与颅面结构的关系
龙 杨,费 露,袁小平
- 西南医科大学附属口腔医院口腔正畸科,四川省泸州市 646000
Relationship between nose morphology and craniofacial structures in Luzhou adults
Long Yang, Fei Lu, Yuan Xiao-ping
- Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
软组织面突度:是过软组织额点、鼻下点、软组织颏前点所形成的锐角,代表鼻底软组织轮廓的突度。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中软组织面突度依次减小,表明Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类错颌中鼻底软组织的突度依次减小,这与错颌畸形的颅面结构特征一致,Ⅱ类错颌多表现为凸面型,Ⅲ类错颌则多表现为凹面型,提示侧面软组织轮廓可以一定程度上反映骨骼轮廓。
鼻颏角:是鼻背长轴与过鼻尖点与软组织颏前点连线的交角。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中鼻颏角依次增大,与Robison和Gulsen等的研究结果相似。研究发现鼻背长轴、鼻尖点与矢状骨面型未见明显相关性,提示三类骨面型中鼻颏角的差异主要由颏部位置不同造成。
文题释义:
软组织面突度:是过软组织额点、鼻下点、软组织颏前点所形成的锐角,代表鼻底软组织轮廓的突度。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中软组织面突度依次减小,表明Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类错颌中鼻底软组织的突度依次减小,这与错颌畸形的颅面结构特征一致,Ⅱ类错颌多表现为凸面型,Ⅲ类错颌则多表现为凹面型,提示侧面软组织轮廓可以一定程度上反映骨骼轮廓。
鼻颏角:是鼻背长轴与过鼻尖点与软组织颏前点连线的交角。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中鼻颏角依次增大,与Robison和Gulsen等的研究结果相似。研究发现鼻背长轴、鼻尖点与矢状骨面型未见明显相关性,提示三类骨面型中鼻颏角的差异主要由颏部位置不同造成。
.jpg) 文题释义:
软组织面突度:是过软组织额点、鼻下点、软组织颏前点所形成的锐角,代表鼻底软组织轮廓的突度。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中软组织面突度依次减小,表明Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类错颌中鼻底软组织的突度依次减小,这与错颌畸形的颅面结构特征一致,Ⅱ类错颌多表现为凸面型,Ⅲ类错颌则多表现为凹面型,提示侧面软组织轮廓可以一定程度上反映骨骼轮廓。
鼻颏角:是鼻背长轴与过鼻尖点与软组织颏前点连线的交角。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中鼻颏角依次增大,与Robison和Gulsen等的研究结果相似。研究发现鼻背长轴、鼻尖点与矢状骨面型未见明显相关性,提示三类骨面型中鼻颏角的差异主要由颏部位置不同造成。
文题释义:
软组织面突度:是过软组织额点、鼻下点、软组织颏前点所形成的锐角,代表鼻底软组织轮廓的突度。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中软组织面突度依次减小,表明Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类错颌中鼻底软组织的突度依次减小,这与错颌畸形的颅面结构特征一致,Ⅱ类错颌多表现为凸面型,Ⅲ类错颌则多表现为凹面型,提示侧面软组织轮廓可以一定程度上反映骨骼轮廓。
鼻颏角:是鼻背长轴与过鼻尖点与软组织颏前点连线的交角。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中鼻颏角依次增大,与Robison和Gulsen等的研究结果相似。研究发现鼻背长轴、鼻尖点与矢状骨面型未见明显相关性,提示三类骨面型中鼻颏角的差异主要由颏部位置不同造成。摘要
背景:研究表明正畸治疗可以改变鼻部与颏部的形态位置,从而对面部美观产生重大影响。因此正畸治疗设计需将鼻形态与颅颌面各结构之间的关系作为重要参考,避免因矫治而带来或加重颜面部的不协调。
目的:研究泸州地区成年人鼻形态指标与性别、矢状骨面型、垂直骨面型三因素的相关性及差异性,以及鼻形态指标与颅面结构形态指标的相关性,为正畸临床诊断与治疗设计提供一些参考。
方法:选择2014至2016年于西南医科大学附属口腔医院正畸科就诊的患者240例,进行头影测量分析,测量软硬组织指标共计27项。
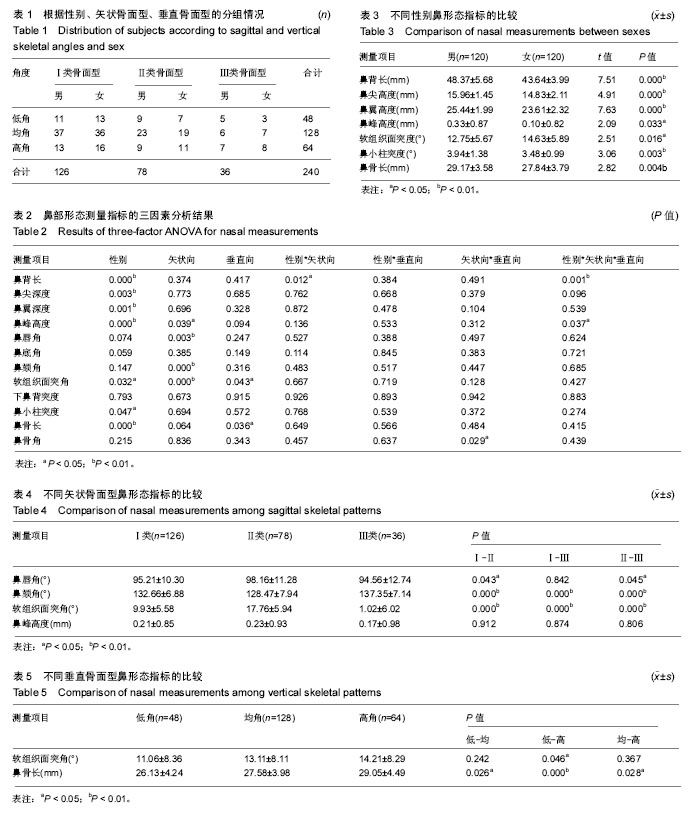
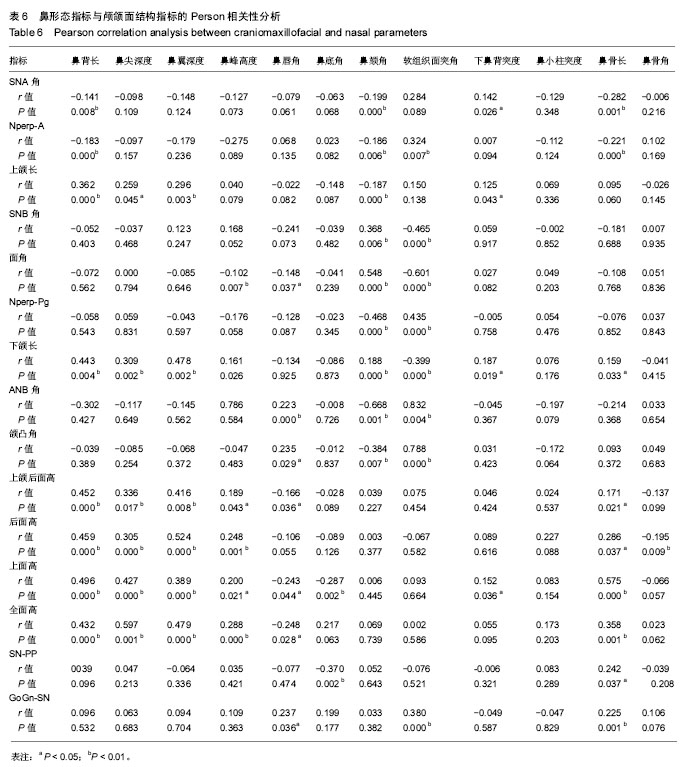
结果与结论:①三因素方差分析结果显示:与性别有关的鼻形态指标有鼻背长、鼻尖深度、鼻翼深度、鼻峰高度、软组织面突角、鼻小柱突度、鼻骨长(P < 0.05),与矢状骨面型有关的鼻形态指标有鼻峰高度、鼻唇角、鼻颏角、软组织面突角(P < 0.05),与垂直骨面型有关的鼻形态指标有鼻骨长、软组织面突角(P < 0.05);②不同性别之间鼻形态存在差异,男性鼻部大小、突度均大于女性;③不同矢状骨面型的鼻部大小无显著差异,但反映鼻形态与面部结构关系的指标在三类骨面型中有显著差异;④不同垂直骨面型与软组织面突度、鼻骨长有显著相关性;⑤鼻部的大小、突度及形态与颌骨的长度、高度以及颌骨在矢状/垂直向的位置有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-9022-0805(龙杨)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
软组织面突度:是过软组织额点、鼻下点、软组织颏前点所形成的锐角,代表鼻底软组织轮廓的突度。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中软组织面突度依次减小,表明Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类错颌中鼻底软组织的突度依次减小,这与错颌畸形的颅面结构特征一致,Ⅱ类错颌多表现为凸面型,Ⅲ类错颌则多表现为凹面型,提示侧面软组织轮廓可以一定程度上反映骨骼轮廓。
鼻颏角:是鼻背长轴与过鼻尖点与软组织颏前点连线的交角。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中鼻颏角依次增大,与Robison和Gulsen等的研究结果相似。研究发现鼻背长轴、鼻尖点与矢状骨面型未见明显相关性,提示三类骨面型中鼻颏角的差异主要由颏部位置不同造成。
文题释义:
软组织面突度:是过软组织额点、鼻下点、软组织颏前点所形成的锐角,代表鼻底软组织轮廓的突度。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中软组织面突度依次减小,表明Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类错颌中鼻底软组织的突度依次减小,这与错颌畸形的颅面结构特征一致,Ⅱ类错颌多表现为凸面型,Ⅲ类错颌则多表现为凹面型,提示侧面软组织轮廓可以一定程度上反映骨骼轮廓。
鼻颏角:是鼻背长轴与过鼻尖点与软组织颏前点连线的交角。研究中Ⅱ、Ⅰ、Ⅲ类骨面型中鼻颏角依次增大,与Robison和Gulsen等的研究结果相似。研究发现鼻背长轴、鼻尖点与矢状骨面型未见明显相关性,提示三类骨面型中鼻颏角的差异主要由颏部位置不同造成。