中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1659-1665.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2487
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
颅底曲度与后牙牙合平面倾斜度对矢状骨面型形成的影响
余星月1,吕冬梅1,田姗璨1,袁小平2,程 钎2
- 1西南医科大学口腔医学院,四川省泸州市 646000;2西南医科大学附属口腔医院正畸科,四川省泸州市 646000
Influence of cranial base angle and posterior occlusal plane inclination on sagittal dentoskeletal types
Yu Xingyue1, Lü Dongmei1, Tian Shancan1, Yuan Xiaoping2, Cheng Qian2
- 1School of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
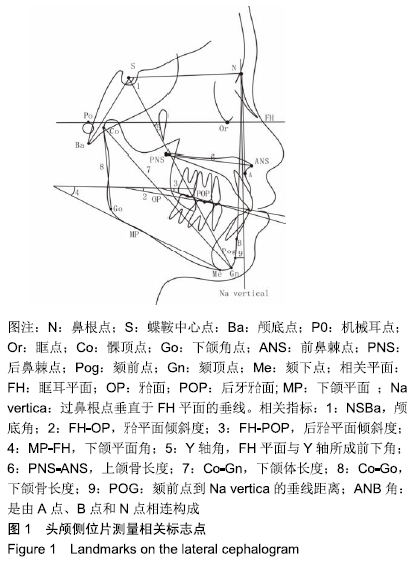
矢状骨面型:矢状向上,上下颌骨的位置关系及其所导致的错牙合畸形类型。
牙合 平面:由连接上下颌切牙覆牙合中点、上下颌第1磨牙覆牙合中点确定的假想平面。
后牙牙合平面:由连接上颌第2前磨牙颊尖和上颌第2磨牙或第3磨牙(如果萌出)颊尖的假想平面。
背景:研究表明颅底角与矢状骨面型的形成有关,牙合平面或后牙牙合平面对矢状骨面型形成的影响也存在一定的争议。
目的:比较牙合平面倾斜度与后牙牙合平面倾斜度在决定矢状骨面型形成中的重要性,探讨颅底曲度、后牙牙合平面倾斜度对矢状骨面型形成的综合效应,及两者之间的相关性。
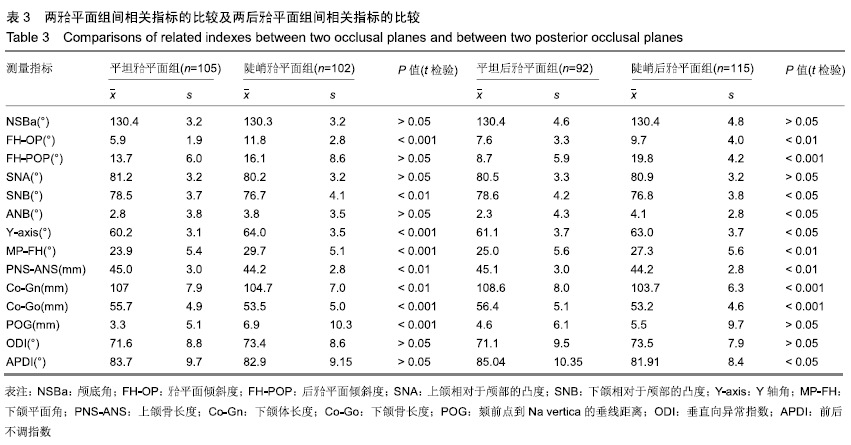
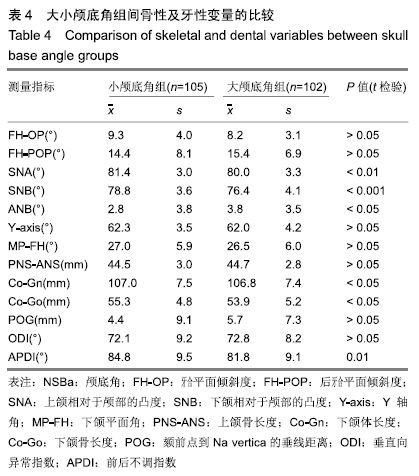
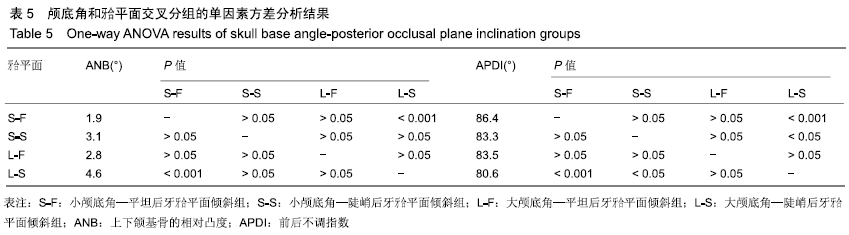
方法:研究方案的实施符合西南医科大学附属口腔医院的相关伦理要求,患者及监护人对测量过程均知情同意,并签署了知情同意书。选择符合纳入标准的207名个体的头颅侧位片(男100例,女107例,年龄12-20岁),利用Uceph 软件、SPSS软件(版本17.0)进行相关指标的测量和分析。按照前后不调指数(APDI)值将样本的矢状骨面型分为3组:Ⅱ类组、Ⅰ类组、Ⅲ类组。SNK、LSD 法比较各项相关指标在3组之间的差异。运用Pearson积矩相关系数分析法对颅底角(NSBa角)、牙合平面(FH-OP)、后牙牙合平面(FH-POP)与其他相关测量指标的相关性进行分析。根据牙合平面倾斜度、后牙牙合平面倾斜度及颅底角进行分组,并运用成组t检验法分别对相关骨性与牙性指标的进行比较。根据后牙牙合平面角度和颅底角度建立4个牙齿骨骼型组:小颅底角-平坦后牙合平面组(S-F),小颅底角-陡峭后牙合平面组(S-S),大颅底角-平坦后牙合平面组(L-F),大颅底角-陡峭后牙合平面组(L-S)。应用交叉单因素方差分析法进行各组间差异的比较。
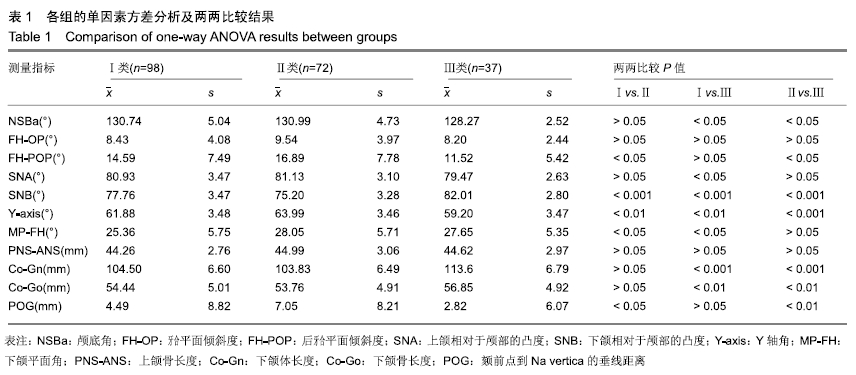
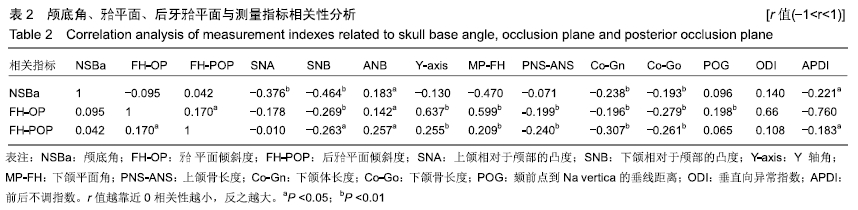
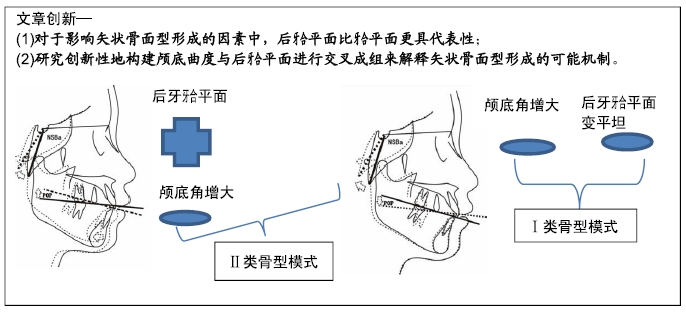
结果与结论:①Ⅲ类错牙合畸形患者的颅底角明显小于Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类,而Ⅱ类错牙合患者的后牙牙合平面明显大于Ⅲ类和Ⅰ类;②代表矢状骨面型分类的指标(APDI及ANB角)在牙合平面倾斜组之间并未发现差异;③颅底角和后牙牙合平面交叉分组的比较中,只有小颅底角-平坦后牙牙合平面组和大颅底角-陡峭后牙牙合平面组间的比较结果显示ANB角和APDI值存在显著差异;④结果说明,对于影响矢状骨面型的形成的因素中,后牙合平面比牙合平面更具代表性;颅底角度和牙合平面倾斜度作为单独的指标在确立前后骨骼畸形方面存在局限性;颅底曲度和后牙合平面倾斜共同影响矢状骨面型的形成;在矢状骨面型形成过程中,颅底曲度及后牙合平面之间可能存在一定的补偿机制。
ORCID: 0000-0002-1930-6566(余星月);0000-0002-2386-6515(程钎)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: