中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (8): 1209-1214.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.08.011
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者上气道生长发育的特点
祁祎喆,张亚秋,刘 珂,李永明
- 解放军第四军医大学口腔医院正畸科,陕西省口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心,军事口腔医学国家重点实验室,陕西省西安市 710032
Characteristics of the upper airway growth in class III malocclusion patients
Qi Yi-zhe, Zhang Ya-qiu, Liu Ke, Li Yong-ming
- Department of Orthodontics, School of Stomatology of the Fourth
Military Medical University, Shaanxi Provincial Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Military Stomatology, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合:安氏Ⅲ类错牙合在国内青少年中的发病率12.81%,其中有一部分是骨性Ⅲ类错牙合,主要是上下颌骨发育不协调,从而引起面部形态及功能障碍。许多骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者均有家族背景,并且会对患者的心理、社会造成负面影响。
骨龄评价:常用手腕骨,与手腕骨相比,颈椎的骨化中心较少,但生长发育过程中的变化明显,且容易观察,与颅面的关系较手腕骨更为密切,而且通过常规头颅侧位片即可观察。基于X射线头颅侧位片的第2-4颈椎的颈椎骨龄定量分期法不仅可以定性,而且可以定量获得个体生长发育所处的具体阶段。
文题释义:
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合:安氏Ⅲ类错牙合在国内青少年中的发病率12.81%,其中有一部分是骨性Ⅲ类错牙合,主要是上下颌骨发育不协调,从而引起面部形态及功能障碍。许多骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者均有家族背景,并且会对患者的心理、社会造成负面影响。
骨龄评价:常用手腕骨,与手腕骨相比,颈椎的骨化中心较少,但生长发育过程中的变化明显,且容易观察,与颅面的关系较手腕骨更为密切,而且通过常规头颅侧位片即可观察。基于X射线头颅侧位片的第2-4颈椎的颈椎骨龄定量分期法不仅可以定性,而且可以定量获得个体生长发育所处的具体阶段。
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合:安氏Ⅲ类错牙合在国内青少年中的发病率12.81%,其中有一部分是骨性Ⅲ类错牙合,主要是上下颌骨发育不协调,从而引起面部形态及功能障碍。许多骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者均有家族背景,并且会对患者的心理、社会造成负面影响。
骨龄评价:常用手腕骨,与手腕骨相比,颈椎的骨化中心较少,但生长发育过程中的变化明显,且容易观察,与颅面的关系较手腕骨更为密切,而且通过常规头颅侧位片即可观察。基于X射线头颅侧位片的第2-4颈椎的颈椎骨龄定量分期法不仅可以定性,而且可以定量获得个体生长发育所处的具体阶段。
文题释义:
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合:安氏Ⅲ类错牙合在国内青少年中的发病率12.81%,其中有一部分是骨性Ⅲ类错牙合,主要是上下颌骨发育不协调,从而引起面部形态及功能障碍。许多骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者均有家族背景,并且会对患者的心理、社会造成负面影响。
骨龄评价:常用手腕骨,与手腕骨相比,颈椎的骨化中心较少,但生长发育过程中的变化明显,且容易观察,与颅面的关系较手腕骨更为密切,而且通过常规头颅侧位片即可观察。基于X射线头颅侧位片的第2-4颈椎的颈椎骨龄定量分期法不仅可以定性,而且可以定量获得个体生长发育所处的具体阶段。摘要
背景:很多研究表明骨性Ⅱ类错牙合与上气道的形态存在一定的关系,但未见关于骨性Ⅲ类患者上气道生长发育及其与颅面部形态结构之间关系的相关研究。
目的:基于颈椎骨龄定量分期法,探讨骨性Ⅲ类错牙合畸形患者上气道生长发育的特点,为不同骨龄上气道参考值的建立和颅面部生长发育的研究提供一定的参考。
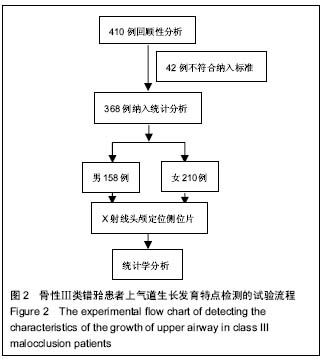
方法:将收集的368例骨性Ⅲ类错牙合畸形患者(4-39岁)根据颈椎骨龄定量分期法分为4期:Ⅰ期(加速期)、Ⅱ期(高峰期)、Ⅲ期(减速期)、Ⅳ期(结束期),对其X射线头颅侧位片进行测量,并对上气道矢状径的测量值进行分析。
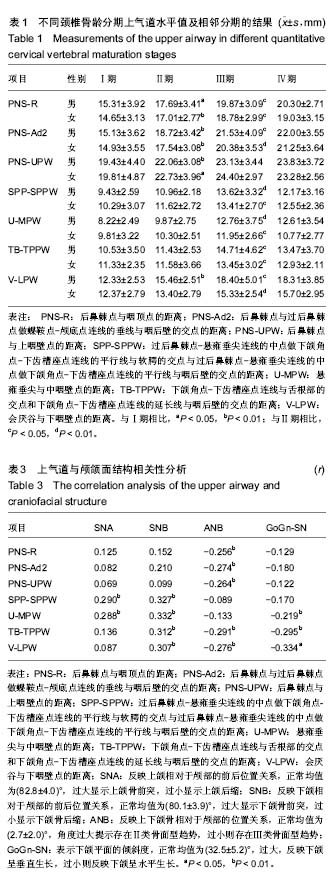
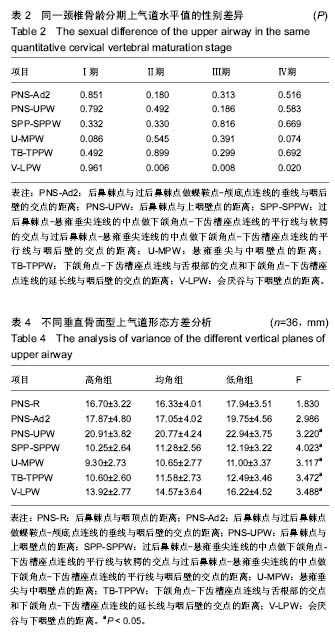
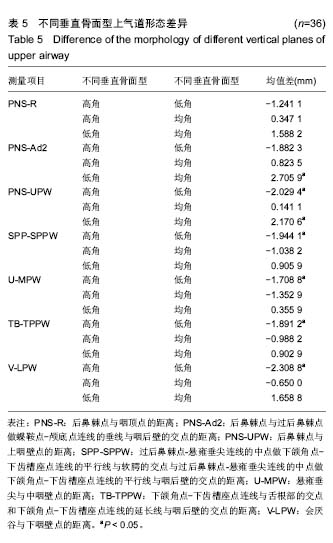
结果与结论:Ⅰ期各水平测量值无显著性别差异,Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ期上气道各段除会厌谷与下咽壁点的距离外也无性别差异。从Ⅰ期到Ⅲ期,男性上气道后鼻棘点与咽顶点的距离、后鼻棘点与过后鼻棘点做蝶鞍点-颅底点连线的垂线与咽后壁的交点的距离、会厌谷与下咽壁点的距离有显著增长,过后鼻棘点-悬雍垂尖连线的中点做下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线的平行线与软腭的交点与过后鼻棘点-悬雍垂尖连线的中点做下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线的平行线与咽后壁的交点的距离、悬雍垂尖与中咽壁点的距离、下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线与舌根部的交点和下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线的延长线与咽后壁的交点的距离从Ⅱ期开始逐渐增大,后鼻棘点与上咽壁点的距离在Ⅰ期到Ⅱ期增长显著;从Ⅰ期到Ⅲ期,女性上气道后鼻棘点与咽顶点的距离、后鼻棘点与过后鼻棘点做蝶鞍点-颅底点连线的垂线与咽后壁的交点的距离显著增长,过后鼻棘点-悬雍垂尖连线的中点做下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线的平行线与软腭的交点与过后鼻棘点-悬雍垂尖连线的中点做下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线的平行线与咽后壁的交点的距离、悬雍垂尖与中咽壁点的距离、下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线与舌根部的交点和下颌角点-下齿槽座点连线的延长线与咽后壁的交点的距离、会厌谷与下咽壁点的距离从Ⅱ期开始逐渐增大,后鼻棘点与上咽壁点的距离在Ⅰ期到Ⅱ期增长显著;从Ⅲ期到Ⅳ期,各测量值基本无变化。上气道矢状径与颅颌面结构存在相关性。垂直骨面型对上气道口咽、喉咽水平有影响。提示骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者上气道与颅颌面部生长发育相关,并为骨性Ⅲ类错牙合的发生与上气道关系的研究提供了实验依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-1152-3926(李永明)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合:安氏Ⅲ类错牙合在国内青少年中的发病率12.81%,其中有一部分是骨性Ⅲ类错牙合,主要是上下颌骨发育不协调,从而引起面部形态及功能障碍。许多骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者均有家族背景,并且会对患者的心理、社会造成负面影响。
骨龄评价:常用手腕骨,与手腕骨相比,颈椎的骨化中心较少,但生长发育过程中的变化明显,且容易观察,与颅面的关系较手腕骨更为密切,而且通过常规头颅侧位片即可观察。基于X射线头颅侧位片的第2-4颈椎的颈椎骨龄定量分期法不仅可以定性,而且可以定量获得个体生长发育所处的具体阶段。
文题释义:
骨性Ⅲ类错牙合:安氏Ⅲ类错牙合在国内青少年中的发病率12.81%,其中有一部分是骨性Ⅲ类错牙合,主要是上下颌骨发育不协调,从而引起面部形态及功能障碍。许多骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者均有家族背景,并且会对患者的心理、社会造成负面影响。
骨龄评价:常用手腕骨,与手腕骨相比,颈椎的骨化中心较少,但生长发育过程中的变化明显,且容易观察,与颅面的关系较手腕骨更为密切,而且通过常规头颅侧位片即可观察。基于X射线头颅侧位片的第2-4颈椎的颈椎骨龄定量分期法不仅可以定性,而且可以定量获得个体生长发育所处的具体阶段。