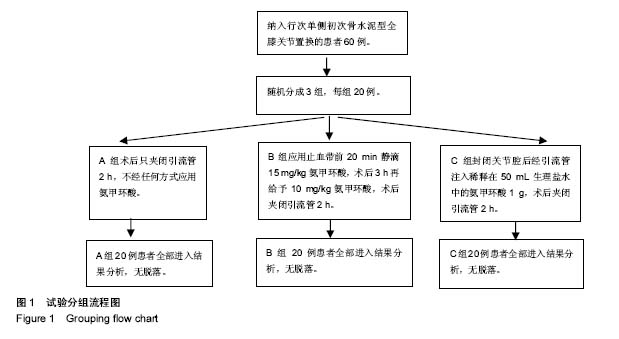
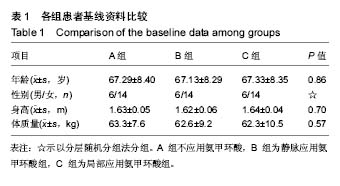
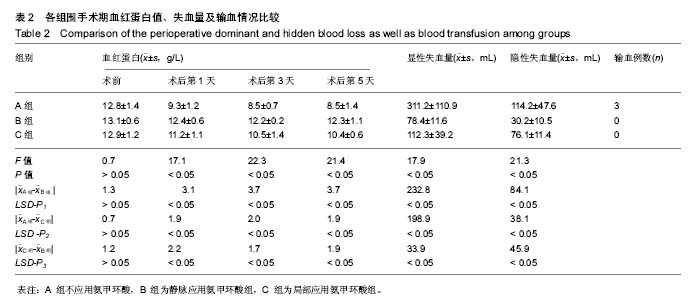
| [1] Panteli M, Papakostidis C, Dahabreh Z, et al. Topical tranexamicacid in total knee replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2013;20:300-309.[2] Eubanks JD. Antifibrinolytics in major orthopaedic surgery. Jam Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18:132-138.[3] Ker K, Edwards P, Perel P, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on surgical bleeding: systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;344: e3054.[4] Barwell J, Anderson G, Hassan A, et al. The effects of early tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79: 265-268.[5] Fahmy NR, Patel DG. Hemostatic changes and postoperative deep-vein thrombosis associated with use of a pneumatic tourniquet. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1981;63: 461-465.[6] Katsumata S, Nagashima M, Kato K, et al. Changes in coagulation-fibrinolysis marker and neutrophil elastase following the use of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty and the influence of neutrophil elastase on thromboembolism. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49:510-516.[7] Hiippala S, Strid L, Wennerstrand M, et al. Tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron ) reduces perioperative blood loss associated with total knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 1995;74: 534-537.[8] Benoni G, Fredin H. Fibrinolytic inhibition with tranexamic acidreduces blood loss and blood transfusion after knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study of 86 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78: 434-440.[9] Akizuki S, Yasukawa Y, Takizawa T. A new method of hemostasis for cementless total knee arthroplasty. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1997;56:222-224.[10] Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003;90:596-599.[11] Benoni G, Lethagen S, Fredin H. The effect of tranexamic acid on local and plasma fibrinolysis during total knee arthroplasty. Thromb Res. 1997;85:195-206.[12] Jansen AJ, Andreica S, Claeys M, et al. Use of tranexamic acid for an effective blood conservation strategy after total knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 1999;83: 596-601.[13] Ido K, Neo M, Asada Y, et al. Reduction of blood loss using tranexamic acid in total knee and hip arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2000;120: 518-520.[14] Tanaka N, Sakahashi H, Sato E, et al. Timing of the administration of tranexamic acid for maximum reduction in blood loss in arthroplasty of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83: 702-705.[15] Ellis MH, Fredman B, Zohar E, et al. The effect of tourniquet application, tranexamic acid, and desmopressin on the procoagulant and fibrinolytic systems during total knee replacement. J Clin Anesth. 2001;13: 509-513.[16] Cid J, Lozano M. Tranexamic acid reduces allogeneic red cell transfusions in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Transfusion. 2005;45: 1302-1307.[17] Ishida K, Tsumura N, Kitagawa A, et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop.2011;35: 1639-1645.[18] Yang ZG,Chen WP,Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94: 1153 -1159.[19] Gandhi R, Evans HM, Mahomed SR, et al. Tranexamic acid and the reduction of blood loss in total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6: 184.[20] 张阳,钱齐荣,吴海山,等. 氨甲环酸减少全膝关节置换术失血量的Meta 分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2009,29(6): 524-529.[21] Zhang H,Chen J,Chen F,et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and use of blood products in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20: 1742-1752.[22] 傅德杰,陈凯宁,杨柳. 氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术失血量影响的系统评价[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(13): 1172 -1177.[23] Howes JP,Sharma V,Cohen AT. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss after knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78:995-996.[24] Endo Y,Nishimura S,Miura A. Deep-vein thrombosis induced by tranexamic acid in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. JAMA. 1988;259: 3561-3562.[25] Upadhyay SP,Mallick PN,Jagia M,et al. Acute arterial thrombosis associated with inadvertent high dose of tranexamic acid. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2013;17: 237-239.[26] Astedt B,Liedholm P,Wingerup L. The effect of tranexamic acid on the fibrinolytic activity of vein walls. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1978;67: 203-205.[27] 张福江,高志国,于建华. 氨甲环酸减少全膝关节置换术出血量的临床对比研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(12): 1302-1304.[28] 苗兵,毕晓扬,任凯晶,等.氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术围手术期失血量的影响及安全性评估[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(9): 864-867.[29] 邱贵兴.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华关节外科志(电子版),2009,3(3):380-383.[30] Ralley FE, Berta D, Binns V, et al. One intraoperative dose of tranexamic Acid for patients having primary hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:1905-1911.[31] Lin PC, Hsu CH, Huang CC, et al. The blood-saving effect of tranexamic acid in minimally invasive total knee replacement: is an additional pre-operative injection effective. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94: 932-936.[32] Panteli M, Papakostidis C, Dahabreh Z, et al. Topical tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: A systematic review and meta -analysis. Knee. 2013;20:300-309.[33] 傅德杰,陈凯宁,杨柳.氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术失血量影响的系统评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(13):1172-1177.[34] Faris PM, Ritter MA, Keating EM, et al. Unwashed filtered shed blood collected after knee and hip arthroplasties: a source of autologous red blood cells. J Bone Joint Surg. 1991;73(8):1169-1178.[35] McManus KT, Velchik MCP, Alavi A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of postoperative bleeding in TKA patients with Tc-99m RNCs. J Nuclear Med.1987;28:565-567.[36] 张瑜哲,金毅,苏礼,等.氨甲环酸减少初次单侧全膝关节置换术后失血量的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(8):762-765.[37] Ker K, Edwards P, Perel P, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on surgical bleeding: systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. BMJ.2012;344:e3054. |
.jpg)
.jpg)