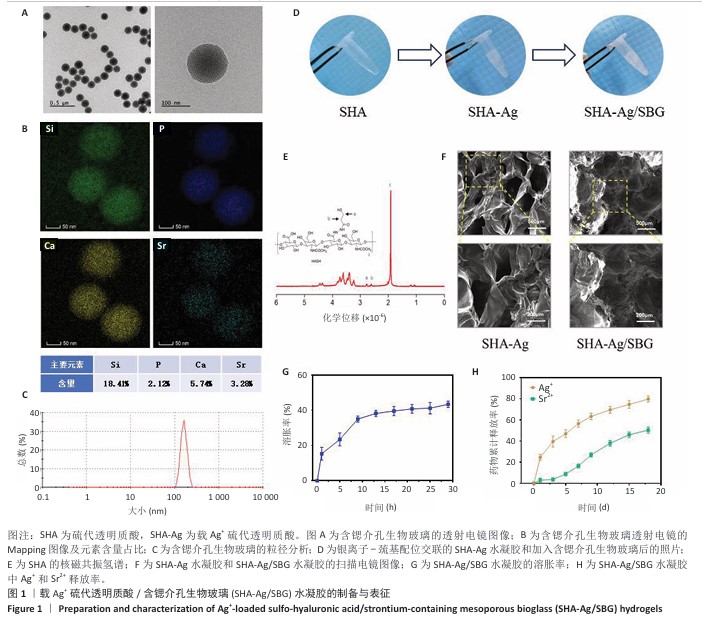
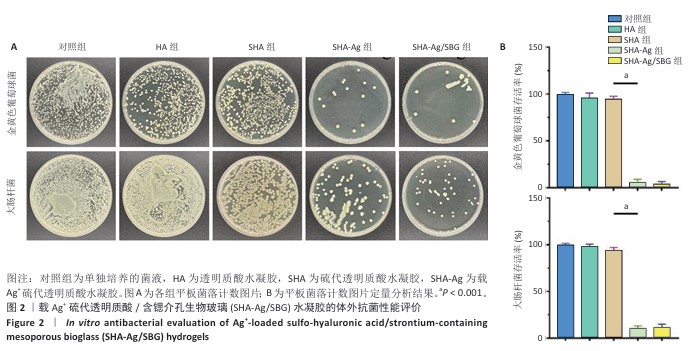
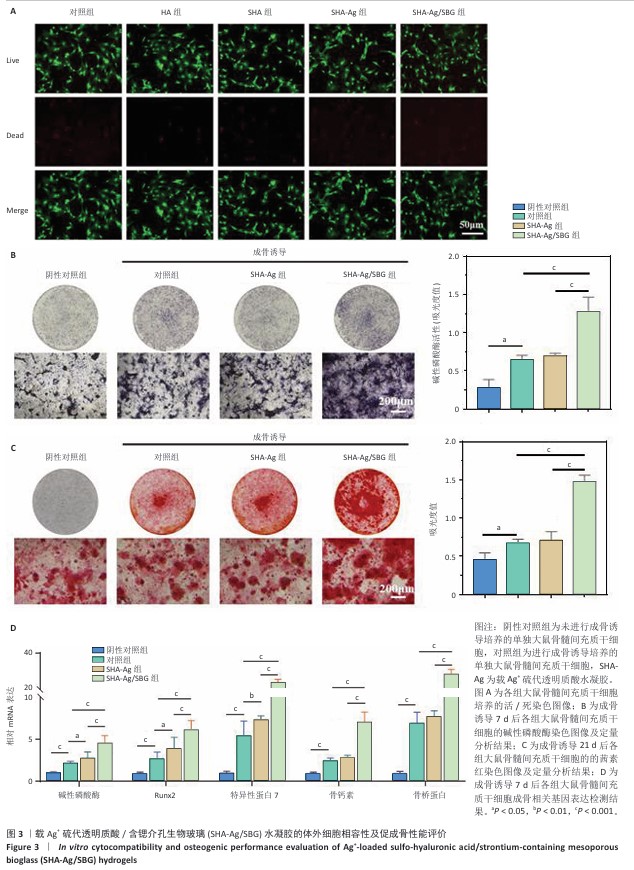
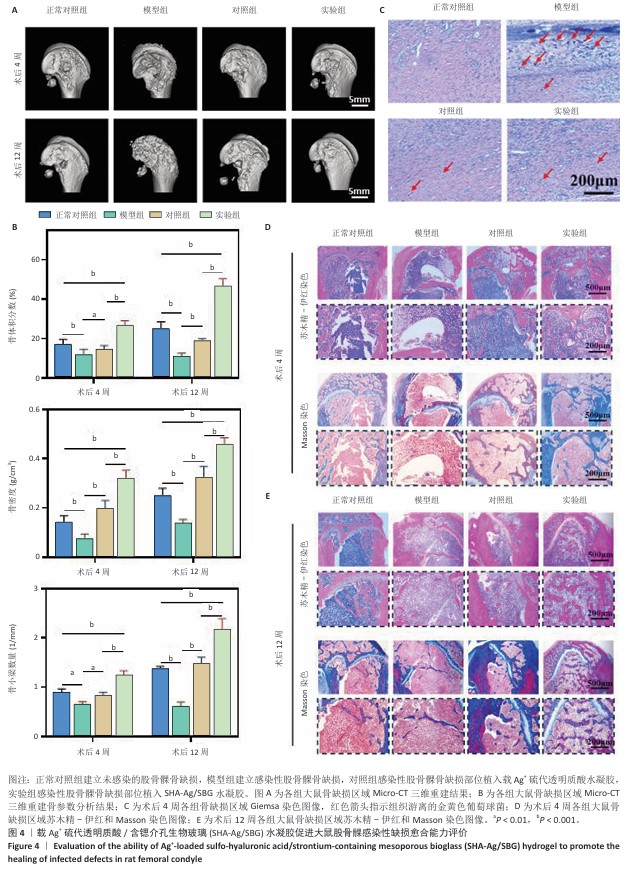
[1] 唐国柯,文根,刘彦斌,等.骨缺损修复生物材料的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(2):185-192.
[2] MATHIEU L, MOURTIALON R, DURAND M, et al. Masquelet technique in military practice: specificities and future directions for combat-related bone defect reconstruction. Mil Med Res. 2022;9(1):48.
[3] MORIARTY TF, METSEMAKERS WJ, MORGENSTERN M, et al. Fracture-related infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8(1):67.
[4] WIESE A, PAPE HC. Bone defects caused by high-energy injuries, bone loss, infected nonunions, and nonunions. Orthop Clin North Am. 2010;41(1):1-4.
[5] GARMANY A, TERZIC A. Global healthspan-lifespan gaps among 183 World Health Organization member states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(12):e2450241.
[6] 张宇,尹庆水,张余,等.载银珊瑚羟基磷灰石人工骨的机械性能及修复桡骨大段污染性骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(47): 7567-7574.
[7] THABIT AK, FATANI DF, BAMAKHRAMA MS, et al. Antibiotic penetration into bone and joints: an updated review. Int J Infect Dis. 2019;81: 128-136.
[8] SAINT-PASTOU TERRIER C, GASQUE P. Bone responses in health and infectious diseases: a focus on osteoblasts. J Infect. 2017;75(4):281-292.
[9] DONG Q, ZHOU J, FENG M, et al. A review of bacterial and osteoclast differentiation in bone infection. Microb Pathog. 2024;197:107102.
[10] TANG R, WU S, JING Y, et al. Application of platelet-rich plasma in traumatic bone infections. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021;19(7): 867-875.
[11] QIN L, YANG S, ZHAO C, et al. Prospects and challenges for the application of tissue engineering technologies in the treatment of bone infections. Bone Res. 2024;12(1):28.
[12] 朱礼威,王江玥,白丁,等.纳米复合甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶在不同骨缺损环境中应用的价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(5): 753-758.
[13] CHERNOUSOVA S, EPPLE M. Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52(6): 1636-1653.
[14] PARK HJ, KIM JY, KIM J, et al. Silver-ion-mediated reactive oxygen species generation affecting bactericidal activity. Water Res. 2009; 43(4):1027-1032.
[15] 张骏,尤奇,邹刚,等.锶元素在骨组织工程研究中的应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2936-2940.
[16] CHUANG EY, LIN YC, HUANG YM, et al. Biofunctionalized hydrogel for segmental bone defect repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;339:122174.
[17] SZEWCZYK A, SKWIRA A, KONOPACKA A, et al. Mesoporous silica-bioglass composite pellets for bone drug delivery system. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4708.
[18] 王想福,张万乾,郑卉卉,等.感染性骨缺损的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(6):469-472.
[19] OU Z, WEI J, LEI J, et al. Biodegradable Janus sonozyme for infected critical-sized bone defects. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):10525.
[20] ZHANG H, QIAO W, LIU Y, et al. Addressing the challenges of infectious bone defects: a review of recent advances in bifunctional biomaterials. J Nanobiotechnol. 2025;23:257.
[21] MASTERS E, RICCIARDI B, BENTLEY K, et al. Skeletal infections: microbial pathogenesis, immunity and clinical management. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20:385-400.
[22] WU S, WU B, LIU Y, et al. Mini Review Therapeutic Strategies Targeting for Biofilm and Bone Infections. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:936285.
[23] JIAN G, LI D, YING Q, et al. Dual photo‐enhanced interpenetrating network hydrogel for infected bone defect healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(25):e2300469.
[24] MA L, CHENG Y, FENG X, et al. A Janus-ROS healing system promoting infectious bone regeneration. Adv Mater. 2024;36(2):2307846.
[25] HOU S, NIU X, LI L, et al. Injectable hydrogels via nanofibrous protein microparticles for tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;223:119458.
[26] SHAO N, GUO J, GUAN Y, et al. Organic/inorganic composites for bone regeneration. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(9):3637-3648.
[27] SUN X, MA Z, ZHAO X, et al. 3D bioprinting of multicell-laden scaffolds with BMP-4 for bone repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(3):757-769.
[28] GENG B, LI P, FANG F, et al. Carbon quantum dots for regeneration of infected bone defects. Carbon. 2021;184:375-385.
[29] JING X, XU C, SU W, et al. Photosensitive and conductive hydrogel for innerved bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(3):2201349.
[30] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):278-314.
[31] DE PACE R, MOLINARI S, MAZZONI E, et al. Bone Regeneration: A Review of Current Treatment Strategies. J Clin Med. 2025;14(6):1838.
[32] 焦振华,刘飞,范文浩,等.胫腓骨感染性骨缺损治疗的研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(6):541-546.
[33] SAAVEDRA PHV, TRZECIAK AJ, LIPSHUTZ A, et al. Broad-spectrum antibiotics disrupt homeostatic efferocytosis. Nat Metab. 2024;6(9): 1682-1694.
[34] ZHAO Q, NI Y, WEI H, et al. Ion incorporation into bone grafting materials. Periodontol 2000. 2024;94(1):213-230.
[35] AMENDOLA V, ESTEBAN-GÓMEZ D, FABBRIZZI L, et al. Metal-enhanced H-bond donor tendencies of urea and thiourea. Inorg Chem. 2005;44(24):8690-8698.
[36] KHANSA I, SCHOENBRUNNER AR, KRAFT CT, et al. Silver in wound care—friend or foe? A comprehensive review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7(8):e2390.
[37] PERCIVAL SL, MCCARTY SM. Silver and alginates: role in wound healing and biofilm control. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015;4(7): 407-414.
[38] DOHERTY C, BYRNE CV, BAQADER S, et al. Anti-biofilm effects and healing promotion by silver oxynitrate-based dressings. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):2014.
[39] SHEN Z, MA N, XU J, et al. Metal-ion-controlled hydrogel dressing with enhanced adhesive and antibacterial properties for accelerated wound healing. Mater Today Bio. 2024;26:101039.
[40] ALEKSANDRA H, PAULINA K, KAROLINA K, et al. Ag+ complexes as potential therapeutic agents. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(4):624-647.
[41] WANG L, JIANG S, ZHOU J, et al. Strontium-containing biomaterials in regenerative medicine. Bioact Mater. 2025;49:85-120.
[42] MARX D, RAHIMNEJAD YAZDI A, PAPINI M, et al. Mechanism of action of strontium in bone. Bone Rep. 2020;12:100273.
[43] LODE A, HEISS C, KNAPP G, et al. Strontium-modified calcium phosphate cements for osteoporotic defects. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:475-485.
[44] LI J, ZHAO X, XIA Y, et al. Strontium-containing piezoelectric biofilm promotes dentin regeneration. Adv Mater. 2024;36(21):2313419.
[45] LIU J, SHI Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Metal–phenolic nanocoating for enhanced osseointegration. Adv Sci. 2024;11(18):2307269.
[46] YU Z, WANG Z, CHEN Y, et al. Programmed surface platform for anti-bacterial and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2025;313:122772.
[47] YU L, QIAO Y, GE G, et al. Engineered bionic periosteum for bone regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(41):2401109.
[48] WANG J, ZHANG Q, WANG H, et al. Sr@Ag-based scaffold against chronic osteomyelitis. Biomaterials. 2025;314:122899.
[49] YANG SC, IN Y, ALSHAMMARI SM, et al. Rapid bone destruction caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa septic arthritis: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(36):e39462.
[50] 周子墨,柳达,陈森相,等.3D细胞培养和类器官在骨髓源性间充质干细胞成骨分化中的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022, 28(9):1400-1404.
[51] DE WILDT BWM, CUYPERS LAB, CRAMER EEA, et al. The impact of culture variables on a 3D human in vitro bone remodeling model: a design of experiments approach. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(27): e2301205.
[52] REMMERS S, MAYER D, MELKE J, et al. Measuring mineralised tissue formation and resorption in a human 3D osteoblast-osteoclast co-culture model. Eur Cell Mater. 2020;40:189-202.
[53] BORCIANI G, MONTALBANO G, BALDINI N, et al. Co-culture systems of osteoblasts and osteoclasts: simulating in vitro bone remodeling in regenerative approaches. Acta Biomater. 2020;108:22-45.
[54] TOMIZAWA T, NISHITANI K, ITO H, et al. The limitations of mono- and combination antibiotic therapies on immature biofilms in a murine model of implant-associated osteomyelitis. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(2):449-457.
[55] MA L, CHENG Y, FENG X, et al. A Janus-ROS healing system promoting infectious bone regeneration via sono-epigenetic modulation. Adv Mater. 2024;36(2):e2307846.
[56] WANG L, WU Z, CHEN X, et al. A multifunctional self-assembled hydrogel with bactericidal activity and macrophage metabolic reprogramming for diabetic bone defect repair. Mater Today Bio. 2025;34:102162.
|