中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (20): 5270-5281.doi: 10.12307/2026.149
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
生物募集组织修复材料:调控细胞和因子的迁移及改善组织整合的优势
刁有录,高 佳,潘国庆
- 江苏大学材料科学与工程学院,新材料研究院,江苏省镇江市 212013
-
接受日期:2025-04-07出版日期:2026-07-18发布日期:2025-12-02 -
通讯作者:潘国庆,博士生导师,江苏大学材料科学与工程学院,新材料研究院,江苏省镇江市 212013 -
作者简介:刁有录,男,2000年生,吉林省通化市人,汉族,江苏大学在读硕士,主要从事生物医用高分子领域研究。 -
基金资助:江苏省研究生科研与实践创新计划项目(KYCX24_3950),项目负责人:刁有录;国家自然科学基金项目(32401113,32222041),项目负责人:高佳、潘国庆;中国博士后科学基金面上资助项目(2024M751193),项目负责人:高佳;国家资助博士后研究人员计划项目(GZC20240617),项目负责人:高佳;江苏省卓越博士后资助计划项目(2024ZB698),项目负责人:高佳;江苏省高等学校基础科学(自然科学)研究面上项目(24KJB430013),项目负责人:高佳
Recruitable tissue repair biomaterials: advantages of regulating cell and factor migration and improving tissue integration
Diao Youlu, Gao Jia, Pan Guoqing
- Institue for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-04-07Online:2026-07-18Published:2025-12-02 -
Contact:Pan Guoqing, Doctoral supervisor, Institue for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Diao Youlu, Master candidate, Institue for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, No. KYCX24_3950 (to DYL); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32401113 and 32222041 (to GJ, PGQ); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2024M751193, (to GJ); National Funding for Postdoctoral Researchers Program, No. GZC20240617 (to GJ); Jiangsu Funding Program for Excellent Postdoctoral Talent, No. 2024ZB698 (to GJ); Natural Science Research Project of Higher Education Institutions in Jiangsu Province, No. 24KJB430013 (to GJ)
摘要:
文题释义:
生物募集组织修复材料:是一类能够主动诱导特定细胞或生长因子向受损组织部位迁移并促进组织修复的智能生物材料,通过对材料的特殊分子修饰实现对生长因子或细胞的识别以及对生理微环境的调控,可在创伤愈合、骨再生、血管生成等组织修复领域发挥重要作用。
细胞迁移调控:是生物募集组织修复材料实现组织修复和再生的核心机制。材料可通过释放趋化因子、构建仿生微环境或调控生物物理信号引导干细胞、免疫细胞或内皮细胞向损伤部位定向迁移,这一策略在促进创面愈合、减少炎症反应及改善组织整合方面具有广泛应用前景。
背景:生物募集组织修复材料通过精准调控细胞迁移、分化,促进组织修复与再生,从而推动再生医学应用。
目的:总结生物募集组织修复材料在再生医学领域中的研究现状。
方法:由第一作者检索中国知网、PubMed数据库中收录的文章,文献检索时限为2010年1月至2025年3月,以“生物材料,募集,修复,成骨,软骨,血管”为中文检索词,以“biomaterials,recruitment, repair,osteogenesis,cartilage,vascularization”为英文检索词,最终选取符合标准的90篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:在组织修复领域内,生物募集组织修复材料的核心优势在于精确控制细胞迁移、增殖行为及生长因子活性,这类材料优化生长因子的时空释放模式与信号通路激活效率,以及创面定向迁移的速度,相比传统材料可显著提升组织再生速率。在设计层面,调整材料的亲疏水性、降解速率及力学模量,可确保植入物与组织的力学适配性及安全降解。在功能化方面,采用精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽、肝素等亲和分子进行表面修饰,赋予材料特异性结合整合素受体或固定生长因子的能力,直接增强靶细胞黏附效率并延长生长因子局部作用时间。凭借可控的降解-再生匹配性、高效的空间引导能力及低免疫原性,生物募集组织修复材料为骨缺损、血管再生等难题提供了新工具,并拓展至神经、软骨等复杂组织再生领域。
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-2532-9600 (刁有录)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
刁有录, 高 佳, 潘国庆. 生物募集组织修复材料:调控细胞和因子的迁移及改善组织整合的优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5270-5281.
Diao Youlu, Gao Jia, Pan Guoqing. Recruitable tissue repair biomaterials: advantages of regulating cell and factor migration and improving tissue integration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5270-5281.
2.2 生物募集组织修复材料的材料类型 2.2.1 天然基生物募集组织修复材料 作为细胞外基质的核心蛋白组分,胶原蛋白广泛分布于皮肤、骨骼、肌腱等多种组织,对维持组织结构稳定和调控细胞活动至关重要。胶原蛋白通过其固有的精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸等细胞黏附序列直接介导细胞附着,引导特定细胞(如成骨细胞、成纤维细胞)定向迁移,并影响干细胞向特定谱系(如成骨细胞、软骨细胞)分化。优异的生物相容性和可加工性,奠定了胶原蛋白在组织工程及再生医学中的基石地位[3]。胶原分子侧链富含的赖氨酸、羟脯氨酸残基提供了非共价修饰(如与生长因子、肽段偶联)的关键活性位点,显著增强材料的生物活性。在骨缺损修复中,胶原基支架不仅模拟天然骨细胞外基质的纳米纤维结构,更能通过表面修饰提升间充质干细胞募集效率,加速矿化基质沉积速率。然而,胶原材料固有的低力学强度和快速降解性,严重制约了它在承重部位(如膝关节软骨、大段骨缺损)的应用[4]。研究表明,通过化学交联(如戊二醛、活化羧基等方式)或物理交联(如紫外光照等)可提升胶原支架的压缩模量、延长酶解稳定性,从而拓展胶原蛋白在需承受生理载荷环境的适用性。
透明质酸是由重复的N-乙酰葡糖胺和D-葡糖醛酸二糖单元构成的天然线性糖胺聚糖。透明质酸通过结合细胞膜表面的受体,从而调控细胞迁移、增殖、分化等行为,加速组织修复与再生[5]。透明质酸分子质量的大小决定了不同的生物学功能:高分子质量透明质酸被证实可减轻炎症反应(如降低白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子水平);相反,低分子质量透明质酸则诱导血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及血管内皮生长因子的表达,促进血管生成。透明质酸材料具有优异亲水性、流变学性能和可修饰性,可制备出孔径均匀、力学性能较好的稳定三维网络支架,提升细胞的黏附效果及定向迁移能力。基于卓越的生物相容性、可降解性和对微环境的动态响应能力,透明质酸支架已成为关节软骨缺损修复和深度烧伤/慢性创面皮肤再生的核心材料之一[6]。在临床转化中,Cartistem是全球首款治疗骨关节炎的干细胞药物,其中包含脐血间充质干细胞与4%透明质酸,可见透明质酸具有稳定细胞外源环境、提供营养物质、协同组织修复等功能。
壳聚糖是一种天然来源的阳离子多糖,化学结构由葡萄糖胺取代透明质酸中的D-葡萄糖醛酸组成,这种独特的分子构型使壳聚糖兼具生物相容性与可降解性。壳聚糖的生物学功能高度依赖于分子质量与脱乙酰度的调控,脱乙酰度的增加会增强正电荷密度,从而优化材料与细胞膜表面受体的相互作用[7]。BOUDEMAGH等[8]利用溶剂浇铸和冷冻染色技术将壳聚糖加工成膜,制备的膜比用商业壳聚糖覆盖的膜疏水性更低。根据查找的数据,壳聚糖材料有多个临床研究,如使用壳聚糖海绵支架用于伤口愈合治疗(NCT02668055)、壳聚糖补充剂Kiomedine CM-300对膝关节骨关节炎的Ⅱ期临床研究(NCT05214807)、壳聚糖与三氯化磷酸钙的骨再生剂治疗下颌骨折Ⅱ期临床研究(NCT02081885)等。
海藻酸盐作为一种天然存在的阴离子多糖,它的显著特性是在二价阳离子(如钙离子、锌离子、铜离子)存在下能发生交联反应,形成具有三维网络结构的水凝胶,不仅为细胞生长提供三维微环境,还对细胞的生物学行为产生调节作用。决定海藻酸盐物理化学性质的关键因素是其组成单元α-L-古洛糖醛酸与β-D-甘露糖醛酸的相对含量,当材料中古洛糖醛酸单元占比较高时,形成的凝胶通常表现出更高的刚性,同时伴随着脆性的增加;反之,若甘露糖醛酸的单元比例更多,则材料的延展性增强,更适配软组织修复的需求[9]。在组织工程的实际应用中,海藻酸盐水凝胶因独特的性质常被用作生长因子的递送载体,旨在模拟并维持细胞生长所需的适宜微环境。典型的研究是基于钙离子交联的海藻酸盐水凝胶,不仅增强了材料本身的机械稳定性,还有助于维持细胞外环境的离子动态平衡,进而可能激活相关的细胞信号通路。例如在构建血管化支架材料时,采用海藻酸盐水凝胶能够有效促进血管内皮细胞的迁移活动以及新生血管的生成,这为缺血性组织的修复提供了一种颇具前景的干预方案[10]。
2.2.2 合成生物募集组织修复材料 聚乳酸是一种具备可降解性的高分子材料,这种材料源自玉米、甘蔗等可再生资源,经化学合成而来,具体为乳酸单体聚合而成。聚乳酸具有良好的生物相容性,在人体内降解后产生的乳酸可参与代谢,不会引发炎症或干扰组织修复[11]。但聚乳酸的分子结构存在酯键(R-COO-R’),导致材料表面呈现很强的疏水性,不利于细胞黏附与增殖。为解决这个问题,研究者采用了多种方法,比如在聚乳酸材料中接枝精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽段,提升材料与整合素受体的结合力,增强细胞黏附和募集;在合成聚乳酸时混入聚乙二醇,增加材料亲水性,优化生物相容性;其他的策略,如凭借支化改性的方式改变聚乳酸的线性结构,借助这样的方式来提升材料的机械强度以及降解速率的可调控性。
聚乙二醇作为典型的两亲性线性聚合物,分子链末端含有高反应活性的伯羟基(-OH),可作为功能化修饰的关键位点。通过精确控制聚合度,可合成分子质量范围从几百道尔顿至几万道尔顿的聚乙二醇衍生物,理论上可制备出100 kD以上的衍生物,显著影响材料的流体力学半径、溶液黏度及胶束临界浓度。聚乙二醇的核心优势在于超亲水性:分子链中重复的醚键(-C-O-C-)与水分子形成氢键网络,在材料表面构建动态水合层,该水合层通过熵排斥效应有效抑制血浆蛋白的非特异性吸附,大幅提升材料的抗污性能与血液相容性,同时增强内源性细胞在支架内的定向迁移与归巢能力[12],这种模块化修饰策略使聚乙二醇成为构建功能化生物界面的理想平台。值得注意的是,通过调控拓扑结构可突破线性聚乙二醇的力学局限,如四臂、八臂结构的聚乙二醇,因分子链缠结密度增加,聚乙二醇水凝胶的压缩模量提升,为组织工程提供更稳定的三维微环境。
聚己内酯作为脂肪族聚酯类材料的代表,分子主链中重复的己内酯单元通过酯键连接。在生理环境中,聚己内酯经历分步酶解/水解过程,首先酯键断裂生成低聚物,最终代谢为水和二氧化碳,这种无毒性代谢途径使聚己内酯获得美国食品药品管理局认证为植入材料。聚己内酯的生物相容性体现为双重机制,免疫惰性与细胞亲和性[13-14]。为突破疏水性与细胞识别位点缺失的限制,当前改性策略聚焦于共聚增溶,聚己内酯-聚乙二醇嵌段共聚物使接触角度数降低;表面仿生手段,即接枝明胶/精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽,提升细胞黏附密度[15-16]。
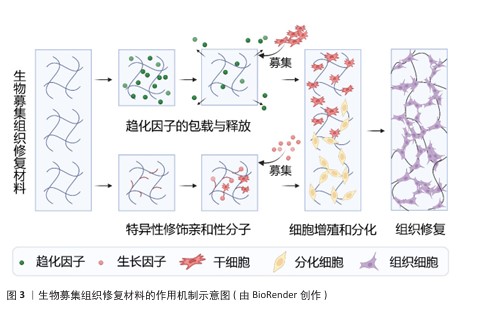
2.3 生物募集组织修复材料的作用机制 生物募集组织修复材料的作用机制示意图,见图3。
2.3.1 细胞招募机制
(1)干细胞归巢:间充质干细胞因高度分化潜能和良好的安全性,在疾病治疗研究领域展现出广阔前景。其中,间充质干细胞能够实现精准治疗的关键之一在于其“归巢效应”,即干细胞可通过血液循环自发迁移至受损组织[17-18]。作为干细胞发挥作用的重要机制之一,自体或外源性的间充质干细胞均可趋向具损伤部位,在这一定向募集过程中,各类生长因子和趋化因子协同作用,共同促进间充质干细胞的迁移和定植[19]。通过引入生物募集组织修复材料可为间充质干细胞提供迁移引导,增强细胞归巢能力,从而提高组织修复效率[20]。随着研究的深入,间充质干细胞在骨科、心血管疾病等多个领域被视为理想的“种子细胞”,细胞归巢机制的进一步优化将为再生医学带来更广阔的应用前景。
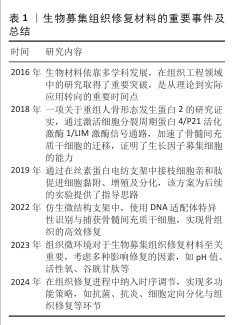
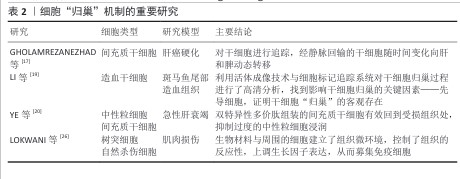
此外,除了通过简单包覆释放趋化因子以促进干细胞归巢外,近年来研究也逐渐聚焦于通过支架表面修饰细胞识别分子来增强细胞的原位识别和募集能力。CHEN等[21]在四面体框架核酸(tFNA)表面修饰了具有募集间充质干细胞能力的适配体(Apt19S),并将其化学连接至透明质酸水凝胶中,构建了高效的间充质干细胞募集系统。这种特异性修饰亲和性分子的策略已在多个领域得到应用,例如,有研究人员受贻贝足蛋白结构的启发,设计了两种多巴胺-聚乙二醇-生长因子结构的多肽,并将其结合在钛基螺钉表面,依靠多巴胺的非共价相互作用、金属配位以及氢键相互作用,使螺钉表面具有优异的细胞募集能力,在骨科领域显示出广泛的应用前景[22]。在血管修复领域,利用点击化学结合将靶向肽与支架材料结合,亦展现出强大的细胞捕获能力[23]。此外在神经组织修复中,PARK及其同事[24]采用P物质修饰神经引导导管,在神经缺损区域构建微通道以原位招募间充质干细胞,募集的细胞可在通道内向神经细胞方向分化。总体而言,在组织修复过程中,合理调节组织支架材料以促进干细胞归巢至关重要,无论是通过趋化因子释放还是通过表面分子修饰来提高细胞识别与募集效率,这些策略不仅影响细胞后续的增殖与分化进程,更是推动组织修复策略迈向临床应用的关键[25]。细胞“归巢”机制的重要研究见表2。
2.3.2 生长因子识别募集机制 在组织损伤后,快速而有效的细胞募集是启动再生修复过程的关键步骤。生长因子作为由多种细胞分泌的信号分子,能够通过与靶向细胞表面受体特异性结合激活一系列信号通路,从而实现对靶细胞的精准识别与高效募集。这些生物活性分子不仅能引导干细胞向损伤区域迁移,还能诱导干细胞在局部微环境中增殖与分化,加速组织结构与功能的恢复。
转化生长因子β是生长因子家族中的代表性成员,在生物系统中广泛调节细胞生长、分化及发育[28]。转化生长因子β通过与其受体结合,激活包括Smad、磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶等在内的多条信号通路,调节干细胞的运动性和分化潜能。研究表明,转化生长因子β可促进间充质干细胞骨架重构与迁移,从而调节干细胞的运动性和分化潜能;与此同时,Smad2/3信号通路的激活可诱导SOX9的表达促进间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化,同时上调Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白多糖的合成,抑制基质金属酶的表达,从而维持细胞外基质稳定性[29-30]。GUO等[31]构建了能够靶向内源转化生长因子β1的亲和肽水凝胶,结果显示水凝胶可在局部高效富集转化生长因子β1,并显著提高Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白多糖的mRNA表达水平,在关节软骨修复中表现出显著的干细胞募集能力。另一项研究制备负载转化生长因子β3的甲基丙烯酸酯丝素蛋白仿生支架,该支架在紫外光固化后不仅具备良好的止血性与力学性能,还能促进软骨细胞在材料表面的黏附与迁移,并且在8周的软骨工程实验中,实验组ICRS宏观修复评分较对照组提升了约7倍[32]。此外,转化生长因子β在血管组织工程中同样具有重要作用。募集的转化生长因子β可通过Smad信号通路诱导血管平滑肌细胞表达Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,并增强细胞的迁移和增殖能力;在成纤维细胞生长因子2和表皮细胞生长因子等的协同作用下DNA合成进一步加快,整体推动血管化过程与组织修复效率的提升[33]。综上所述,转化生长因子β作为典型的识别与募集型生长因子,在多种组织修复策略中发挥着核心调控作用,它与靶细胞间的精准互作及下游信号调控机制,为生长因子介导的组织工程研究提供了重要理论基础和应用价值。
骨形态发生蛋白属于转化生长因子β超家族中的一员,在临床应用中广泛使用。骨形态发生蛋白2是骨和软骨形成的关键调控因子,在组织修复过程中不可或缺,当骨形态发生蛋白2被敲除后,成骨相关基因(Osterix、Runt相关转录因子2、Ⅰ型胶原等)表达水平显著降低,影响骨骼修复能力。骨形态发生蛋白2通过特异性识别机制调控细胞行为,低浓度骨形态发生蛋白2可促进间充质干细胞向骨形成区域募集,中等浓度骨形态发生蛋白2诱导间充质干细胞向软骨细胞和成骨细胞分化,高浓度骨形态发生蛋白2则主要促进细胞增殖[34]。此外,负载骨形态发生蛋白2的多糖材料能够凭借识别机制特异性地与骨形态发生蛋白2相结合,并将骨形态发生蛋白2递送到损伤的部位,诱导巨噬细胞向抗炎表型极化,在降低炎症反应的同时还可以提高组织的修复能力[35]。LLOPIS-HERNáNDEZ等[36]研发了一种基于细胞外基质的聚(丙烯酸乙酯)材料,这种材料能够让纤连蛋白自发地形成纤维状纳米网络,并特异性地结合骨形态发生蛋白2,展示出整合素结合位点,提高骨形态发生蛋白2的生物活性;在体内实验中,低剂量的骨形态发生蛋白2也能够实现骨缺损的完全再生。这种研究策略充分发挥了生长因子的潜力,还为控制生长因子递送提供了一种有效的替代方案,凸显出借助材料设计提高生长因子与细胞相互作用的意义。
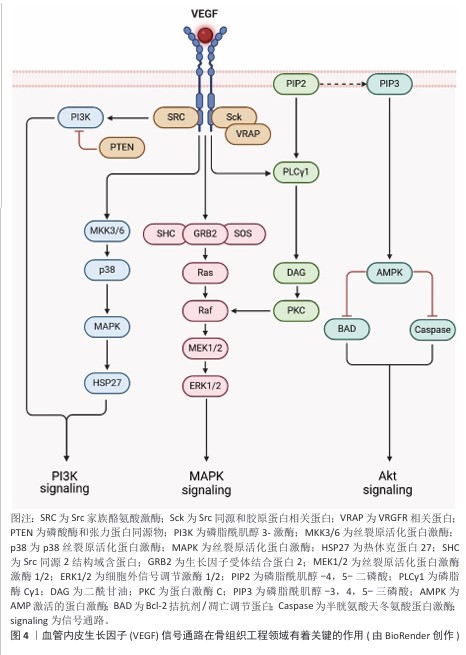
血管内皮生长因子在骨组织工程领域有着关键的作用,它主要通过促进内皮细胞进行增殖、迁移以及血管生成实现骨修复的重要作用[37],见图4。
血管内皮生长因子选择性地作用于血管内皮细胞,激活磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B与丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路,进而促进细胞进行迁移和增殖。GARCIA等[38]将血管内皮生长因子偶联到整合素受体的聚乙二醇水凝胶中,相较于游离的血管内皮生长因子、精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽支架,偶联的血管内皮生长因子-精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽水凝胶有效促进血管形成。在骨组织工程领域,血管内皮生长因子能够促进血管生成,为骨组织提供必需的氧气和营养物质,而且还可以凭借募集内皮细胞对骨修复的进程产生间接的影响;除此之外,血管内皮生长因子还可以对软骨细胞凋亡、软骨重塑以及成骨细胞的迁移进行调节,从而推动骨组织的再生和重塑。血管内皮生长因子的多种生物学效应让它成为了骨组织工程里不可缺少的关键因子[39]。
胰岛素样生长因子是一类调节组织生长、修复及代谢的多肽因子,在成骨分化过程中发挥重要作用。胰岛素样生长因子通过激活磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路抑制间充质干细胞的凋亡,并通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路促进细胞增殖[40-41]。在软骨修复过程中,胰岛素样生长因子能够调控细胞外基质成分(如蛋白多糖)的合成,增强修复效果;此外,在肌肉损伤修复中,胰岛素样生长因子通过促进肌卫星细胞的增殖和激活,加速肌肉组织再生。以上研究结果表明,胰岛素样生长因子在组织修复过程中通过募集细胞和调控细胞行为,发挥关键的修复功能[42]。
神经纤毛蛋白1作为一种多功能细胞受体可与多种生长因子结合,广泛参与骨组织、血管生成及肾脏功能调控。在骨折修复中,神经纤毛蛋白1通过与细胞膜表面的血管内皮生长因子A结合募集细胞迁移,并促进血管生成及成骨细胞活化。ZHANG等[43]研究证实,在小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞MC3T3-E1中补充外源性Sema3A可增强成骨分化,并抑制破骨细胞活化;此外,神经纤毛蛋白1还可降低多糖诱导的ATDC5软骨细胞凋亡。这些研究表明,神经纤毛蛋白1通过识别和募集关键生长因子及细胞,调控骨修复过程中的细胞行为和组织再生[44]。
除上述提到的生长因子外,多种胞外基质活性组分已被证实深度参与组织再生进程,例如狭缝同源物蛋白[45]、乳铁蛋白[46]、血小板衍生生长因子[47]、肝细胞生长因子等在骨骼、血管等领域同样发挥重要作用[48]。这些生长因子在生理浓度下通过配体-受体特异性结合触发胞内级联反应,可以实现核心功能:细胞命运编程,定向诱导干细胞向骨分化;微环境重塑,调控细胞外基质代谢平衡;再生时序协调,建立炎症-增殖-重塑期的分子开关。
2.4 影响生物募集组织修复材料性能的因素
2.4.1 材料的力学性能 当生物募集组织修复材料与细胞直接接触时,材料力学特性(如弹性模量、孔隙拓扑、表面能)通过整合素-黏着斑信号轴调控细胞行为。尤其在骨组织工程中,替代材料的力学仿生设计直接决定干细胞募集效率与分化命运。材料孔径尺度影响细胞铺展,例如XIA 等[49]采用溶胶-凝胶法制备了介孔生物活性玻璃,20 nm孔径支架(介孔生物活性玻璃-20)因比表面积优势接种细胞的铺展面积超过介孔生物活性玻璃-3、介孔生物活性玻璃-8支架6倍以上,介孔生物活性玻璃-20的介孔通道延缓了钙离子/磷酸根离子释放速率,规避了离子浓度骤升导致的细胞毒性。KONG团队[50]利用力学性能的仿生适配策略,结合有限元应力云图分析、纳米压痕,通过多重优化制备的杆板状小梁仿生结构材料总孔隙率为83.1%,在Z轴的弹性模量达到798.1 MPa,载荷值为8719.8 N,能够有效契合骨组织对于模量以及孔隙率的要求。
通过交联技术构建分子间多节点网络结构,为调控材料力学性能提供技术手段[51]。以实验室中广泛研究的甲基丙烯酰化明胶和巯基明胶为例,甲基丙烯酰化明胶在光引发聚合时具有高效性,双键的取代度直接决定交联效率;巯基明胶主要是凭借配位作用或者迈克尔加成反应来实现交联的[52]。然而,取代度过高会降低材料的生物相容性;取代度过低,会减弱细胞的黏附能力,并且交联点过少,无法形成稳定的水凝胶结构[53]。为了优化材料的性能,研究者们会添加辅助交联剂,包括甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸和羧甲基壳聚糖等。例如,DING等[54]将甲基丙烯酰化明胶和羧甲基壳聚糖进行双交联,所制备出来的水凝胶可以借助氨基和羟基等官能团,与细胞膜发生分子间的相互作用,水凝胶中还负载了血管内皮生长因子,显著提高了伤口微环境中细胞的募集能力。

2.4.2 生长因子的有效呈现 生长因子的负载与释放策略对于提高材料的募集能力至关重要。将生长因子直接负载到生物募集组织修复材料中,是最直接且有效的方法之一,可确保生长因子在特定区域稳定释放。然而,由于生长因子的浓度直接影响其生理作用,因此精准调控释放过程成为关键。CHENG等[55]制备了一种核壳纳米纤维垫,通过调控物料比例使骨形态发生蛋白2可在30 d内稳定释放,同时结合快速释放的结缔组织生长因子,协同促进碱性磷酸酶的表达,从而增强成骨效果。
外界环境(如光、热、磁、声等)也可用于控制生长因子的释放,以避免突释效应对细胞的不利影响。例如,研究人员开发了一种由超短肽SESSE与自组装肽CFF结合形成的纳米纤维,通过超声响应性海藻酸钙水凝胶调控肽的释放,骨缺损实验表明,实验组骨小梁相对体积显著高于空白组(0.2% vs. 0.02%),骨小梁厚度也显著增加[56-57]。磁场控制亦可实现生长因子的精准释放,例如在磁性双室水凝胶系统中,外室明胶负载基质细胞衍生因子1α,内室海藻酸盐亚铁凝胶负载骨形态发生蛋白2,磁场作用下可在不同时间点精准释放骨形态发生蛋白2,从而高效募集间充质干细胞,为控释系统提供新思路[58]。
近红外光技术因穿透能力强、不良反应小等特点,在生物募集组织修复材料调控中亦具有潜力。研究表明,将甲基丙烯酰化明胶/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯/聚多巴胺水凝胶用于颅骨缺损修复,在40-43℃近红外光照射下能够显著促进成骨分化与组织修复[59]。此外,温敏性材料(如聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)因低临界溶解温度接近人体温度,温度变化可引发材料的亲疏水性和结构转变,进而用于智能化调控生长因子释放[60-64]。
在基因工程策略方面,生长因子的表达调控可通过mRNA递送实现,而非直接负载至材料中。例如,YANG等[65]将骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA富集至外泌体,RT-qPCR检测结果表明成骨基因(骨桥蛋白、碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原)表达水平显著提高,8周后颅骨修复效果优异,表明细胞吞噬外泌体后可有效诱导成骨分化。

2.4.3 特定的生物功能化 特定的生物功能化表面修饰是增强生物募集组织修复材料活性的重要手段之一。通过物理吸附或化学偶联方式固定,可提高生长因子的稳定性,延长其作用时间,并减少释放过程中的浓度波动,从而更有效地调控细胞行为[66]。例如,精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽作为一种常见的整合素识别序列,已广泛应用于促进细胞黏附和募集能力。在骨关节炎治疗中,精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸修饰的水凝胶微球可有效增强细胞募集能力,促进组织修复[67]。此外,通过化学结合方式还可控制生长因子的释放速率,例如成骨生长肽的末端五肽片段YGFGG被证实具有良好的促细胞增殖和诱导分化能力[68],功能化修饰还可优化生长因子的释放特性,例如,QIAO等[69]将成骨生长肽的YGFGG肽段修饰到甲基丙烯酰化明胶上,使成骨生长肽随水凝胶降解逐步释放,有效诱导MC3T3-E1细胞的募集与成骨分化。
为了在复杂微环境中更精准地发挥生长因子的生物学效应,近年来研究者开始关注如何设计能够特异性识别生长因子的分子,以实现对生长因子的靶向捕获和可控释放。通过筛选与目标生长因子具有高亲和力的肽序列或构建互补识别结构,可以显著提高其在局部环境中的浓度和稳定性。例如,研究者基于骨形态发生蛋白2结合肽开发了一种两亲性纳米纤维凝胶支架,在支架表面修饰骨形态发生蛋白2结合肽后可实现对内源骨形态发生蛋白2的高效捕获与持续释放,增强材料诱导成骨的能力[70]。类似的,另一项实验通过将特异性识别血管内皮生长因子的结合肽修饰至微球表面,实现了对血管内皮生长因子的靶向捕获和可控释放,有效激活细胞微环境中血管内皮生长因子相关信号通路,从而促进血管生成和组织修复[71]。
TEIXEIRA团队[72]通过表位印迹反相微乳液聚合法,以转化生长因子β3的特征肽段为模板,在功能单体交联过程中构建了空间拓扑与静电势互补的三维结合腔,这种分子印迹纳米颗粒对转化生长因子β3的识别选择性达毫摩尔级别,其机制基于模板分子与印迹位点的特异性结合;在RT-qPCR检测结果中,分子印迹纳米颗粒激活了转化生长因子β3信号通路,软骨基因盒转录因子9、硬化蛋白的表达水平升高;另一方面,编码脂肪酸结合蛋白4出现降低的趋势。该策略通过定向调控转化生长因子β3的局部浓度梯度,显著抑制了转化生长因子β3在非靶向组织中的扩散,从而提升生物效应的精准性。
众所周知,身体在损伤后极易存在感染的风险,若将抗菌功能整合到修饰策略中便能实现更好的修复效果[73]。例如,骨折后常用的钛钉材料,在其表面进行抗菌肽、多巴胺或万古霉素的接枝可降低感染的概率,并保持良好的生物相容性[74]。LIU等[75]延续了这种策略,将镁/锶离子掺杂的细菌纤维素涂层钛基植入到体内,涂层降解过程中会释放促成骨离子,实现良好的骨修复效果。
综上所述,通过对材料修饰靶向识别生长因子的分子,如高亲和力的肽序列、分子印迹技术或利用智能释放系统等方式,成功实现了对生长因子的特异性捕获与靶向释放,增强了材料在组织修复中的生物活性,降低了生长因子在非靶组织中的不良反应。以上策略为生物募集组织修复材料的功能化提供了全新思路。在未来的研究中将持续探索更多生长因子的识别机制,并且开发出新一代高效、精准的功能化材料体系,以契合临床组织修复与再生过程中的多样化需求。
2.4.4 微环境的适配调控 组织微环境发生的动态变化会直接且明显地影响生物募集组织修复材料的修复进程。在受损组织的周边,材料的理化状态是动态变化的,例如微环境的pH值、一氧化氮含量以及活性氧水平等,如此复杂的实际情况对生物募集组织修复材料的功能适配性提出了更高要求。生物募集组织修复材料不仅要具备良好的生物相容性,还需要根据不同组织类型的微环境特征,提供有针对性的支持功能,例如血管化能力、神经再生能力,甚至抗氧化能力、抗菌等多重调控能力,才能与目标组织微环境实现精准的匹配[76-77]。这种基于“适配”理念进行的功能设计提高了组织修复的效率、促进多组织再生整合,正逐渐成为一种关键的策略[78]。
在多种影响微环境变化的因素中,pH值波动表现得特别敏感且反应迅速。健康的组织会维持在接近中性的pH值环境中,但是炎症、感染、缺血等病理状态会导致机体的pH值向酸性微环境发生转变[79],因此,开发pH值响应型生物募集组织修复材料成为一种适配病灶环境的有效办法。例如,以席夫碱键构建的水凝胶在酸性条件下会加速降解和药物释放,能够对炎症部位做出精准的响应,提高局部的治疗效果[80]。在感染性骨折模型中,实验员研制出了一种掺杂镓离子的pH值响应型透明质酸水凝胶,这种水凝胶在酸性微环境下表现出了优异的成骨和抗菌功能,证明了pH值适配型材料在骨修复方面的临床潜力[81]。
除了pH值之外,活性氧是在组织损伤以及修复过程中呈现出高度活跃状态的另一种信号因子,适量的活性氧能够促进细胞进行迁移,还可以促进组织再生,而过量的活性氧则会导致细胞受到损伤,并抑制组织的修复,因此,对活性氧的含量进行调控是实现组织微环境适配的关键环节[82-83]。
有研究表明,活性氧水平与新生骨组织的形成密切的关联,适时调控活性氧的浓度可有效抑制破骨细胞的生成,促进成骨细胞的相关活性[84-85]。鉴于上述情况,开发出对活性氧具有响应特性的生物募集组织修复材料成为了研究热点。研究人员已开发了一系列活性氧响应型材料,如二氧化锰、硼酸酯、碳纳米管及花青素等[86]。例如,SUN等[87]制备了一种含铜涂层的二氧化锰纳米颗粒,二氧化锰可以特异性响应过氧化氢,并与甲状旁腺激素共同负载于明胶基质中,构建出具有优异抗氧化性能的生物募集组织修复材料;体外实验表明,这种水凝胶复合材料在成骨及成血管过程中表现出良好的适应性与修复能力。
谷胱甘肽作为内源性抗氧化系统的核心组分,通过还原性巯基直接中和活性氧自由基(如羟基自由基、过氧化氢),动态调节细胞内氧化还原稳态[88],这种生理特性使谷胱甘肽成为材料设计的靶向调控枢纽。基于二硫键(-S-S-)构建的响应性材料(如四臂聚乙二醇-巯基水凝胶)可在谷胱甘肽浓度梯度驱动下发生特异性断裂,实现降解速率从0.5 h至22 d的精准调控[89-90]。值得注意的是,病灶微环境的异质性决定了修复过程的动态需求。这种基于微环境自适应调控的策略,通过整合材料降解动力学与生物分子通路为再生医学提供了兼具组织特异性和个性化的精准治疗方案。
骨组织结构修复示意图,见图5。
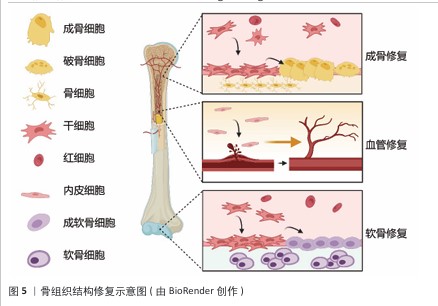
2.5 挑战与未来
2.5.1 现存挑战 在组织修复的生物医学应用中,生物募集材料历经多轮技术迭代,它驱动细胞定向迁移与缺损组织再生能力已获实证突破,然而临床转化面临三重核心障碍:①在免疫识别屏障方面,当异质材料(如长期植入的金属合金、合成聚合物)与宿主细胞直接接触时,固有免疫系统可能启动异物识别通路,诱发级联炎症反应。这种免疫激活不仅导致局部组织微环境失衡,更可能引发植入物周围纤维化包裹,显著降低材料-组织整合效率。当前亟需通过表面拓扑工程或免疫调节因子的原位负载,重塑材料的生物界面特性。②生长因子递送存在困境:其一维持活性功能困境,当血管内皮生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白2等关键因子通过物理吸附或化学偶联方式固载于材料基质时,材料三级结构易受微环境扰动而失活;其二是代谢动力学困境,生理环境下生长因子半衰期普遍小于30 min,流经肝脏后生物利用度骤降,这直接削弱了其在修复及再生等场景的治疗窗口。③监管转化瓶颈则体现在从实验室原型到Ⅲ类医疗器械的转化路径中,需通过生物相容性多项测试,并证明材料在体内动态环境下的长期结构稳定性。特别在可降解材料领域,降解速率与组织再生时序的匹配度成为审批关键指标。
2.5.2 前沿方向 生物医学领域的组织修复材料研发正经历智能化转型,多种前沿技术的协同创新正在重塑该领域的发展轨迹。当前研究表明,通过整合基因编辑与动态支架技术,材料-生物界面的相互作用机制获得突破性优化:①基因编辑技术革新:基于CRISPR-Cas9的细胞功能编程技术实现了对细胞表面受体的精确调控,这种靶向修饰显著增强了细胞在材料界面的黏附与分化行为,为组织再生提供了分子级精度控制工具;②动态支架技术演进:水凝胶支架体系正从静态3D构建转向环境响应型4D体系,相较于传统增材制造,4D打印通过引入温敏型聚合物(如聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)和光响应交联剂,可构建具有形状记忆效应的智能支架;③人工智能驱动研发:机器学习算法,例如,图神经网络正深度介入材料研发全流程。AlphaFold2预测蛋白的结合域、生成对抗网络优化聚合物的设计、迁移学习整合多源实验数据减少了动物实验量。随着人工智能与器官芯片技术的深度整合,个性化组织修复方案有望突破临床转化瓶颈,为精准医疗建立新的技术范式。

| [1] SHAN BH, WU FG. Hydrogel-based growth factor delivery platforms: Strategies and recent advances. Adv Mater. 2024;36(5): e2210707. [2] OLIVEIRA ÉR, NIE L, PODSTAWCZYK D, et al. Advances in growth factor delivery for bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(2):903. [3] GAO Y, WANG J, DAI W, et al. Collagen-based hydrogels induce hyaline cartilage regeneration by immunomodulation and homeostasis maintenance. Acta Biomater. 2024;186:108-124. [4] LIU T, HAO J, LEI H, et al. Recombinant collagen for the repair of skin wounds and photo-aging damage. Regen Biomater. 2024;11:rbae108. [5] SIMIŃSKA-STANNY J, PODSTAWCZYK D, DELPORTE C, et al. Hyaluronic acid role in biomaterials prevascularization. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(30):e2402045. [6] QIN S, WANG M, WEI H, et al. Self-healing hyaluronic acid/polylysine hydrogel prepared by dual-click chemistry from polyrotaxane slidable crosslinkers. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025;680(Pt B):157-172. [7] PAN P, HU Y, WANG C, et al. Abalone shells bioenhanced carboxymethyl chitosan/collagen/PLGA bionic hybrid scaffolds achieving biomineralization and osteogenesis for bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;279(Pt 2):135018. [8] BOUDEMAGH D, VENTURINI P, FLEUTOT S, et al. Elaboration of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and chitosan/hydroxyapatite composites: a present status. Polym Bull. 2019;76(5):2621-2653. [9] JIANG S, JING H, ZHUANG Y, et al. BMSCs-laden mechanically reinforced bioactive sodium alginate composite hydrogel microspheres for minimally invasive bone repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;332:121933. [10] DONG Z, ZHAO J, XU J, et al. Strongly adhesive, self-healing, hemostatic hydrogel for the repair of traumatic brain injury. Biomacromolecules. 2024;25(4):2462-2475. [11] WU L, XU T, LI S, et al. Sequential activation of osteogenic microenvironment via composite peptide-modified microfluidic microspheres for promoting bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2025;316:122974. [12] ZAUCHNER D, MÜLLER MZ, HORRER M, et al. Synthetic biodegradable microporous hydrogels for in vitro 3D culture of functional human bone cell networks. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):5027. [13] HAN Y, SUN LH, CAI B, et al. 3D-printed Ti(3)C(2)/polycaprolactone composite scaffold with a DOPA-SDF1 surface modified for bone repair. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025;248:114470. [14] YUN JH, LEE HY, YEOU SH, et al. Electrostatic attachment of exosome onto a 3D-fabricated calcium silicate/polycaprolactone for enhanced bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2024;29:101283. [15] EVLASHIN S, DYAKONOV P, TARKHOV M, et al. Flexible polycaprolactone and polycaprolactone/graphene scaffolds for tissue engineering. Materials. 2019; 12(18):2991. [16] REMYA KR, JOSEPH J, MANI S, et al. Nanohydroxyapatite incorporated electrospun polycaprolactone/polycaprolactone-polyethyleneglycol-polycaprolactone blend scaffold for bone tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(9):1483-1494. [17] GHOLAMREZANEZHAD A, MIRPOUR S, BAGHERI M, et al. In vivo tracking of 111In-oxine labeled mesenchymal stem cells following infusion in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Nucl Med Biol. 2011;38(7):961-967. [18] YIN Y, HAO H, CHENG Y, et al. The homing of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and the subsequent modulation of macrophage polarization in type 2 diabetic mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018; 60:235-245. [19] LI D, XUE W, LI M, et al. VCAM-1+ macrophages guide the homing of HSPCs to a vascular niche. Nature. 2018; 564(7734):119-124. [20] YE T, WU Z, LIU X, et al. Engineered mesenchymal stromal cells with bispecific polyvalent peptides suppress excessive neutrophil infiltration and boost therapy. Sci Adv. 2025;11(10):eadt7387. [21] CHEN X, XU Z, GAO Y, et al. Framework nucleic acid-based selective cell catcher for endogenous stem cell recruitment. Adv Mater. 2024;36(50):2406118. [22] BAI J, GE G, WANG Q, et al. Engineering stem cell recruitment and osteoinduction via bioadhesive molecular mimics to improve osteoporotic bone-implant integration. Research. 2022;2022:9823784. [23] YANG Z, ZHAO X, HAO R, et al. Bioclickable and mussel adhesive peptide mimics for engineering vascular stent surfaces. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2020;117(28):16127-16137. [24] PARK D, KIM D, PARK SJ, et al. Micropattern-based nerve guidance conduit with hundreds of microchannels and stem cell recruitment for nerve regeneration. NPJ Regen Med. 2022;7(1):62. [25] PACELLI S, BASU S, WHITLOW J, et al. Strategies to develop endogenous stem cell-recruiting bioactive materials for tissue repair and regeneration. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2017;120:50-70. [26] LOKWANI R, JOSYULA A, NGO TB, et al. Pro-regenerative biomaterials recruit immunoregulatory dendritic cells after traumatic injury. Nat Mater. 2024;23(1):147-157. [27] OUYANG L, LIN Z, HE X, et al. Conductive hydrogel inspires neutrophil extracellular traps to combat bacterial infections in wounds. ACS Nano. 2025;19(10):9868-9884. [28] WU M, WU S, CHEN W, et al. The roles and regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β and BMP signaling in bone and cartilage development, homeostasis and disease. Cell Res. 2024;34(2):101-123. [29] DENG Z, FAN T, XIAO C, et al. TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):61. [30] HU HH, CHEN DQ, WANG YN, et al. New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;292:76-83. [31] GUO Q, YIN W, WANG H, et al. Dynamic proteinaceous hydrogel enables in-situ recruitment of endogenous TGF-β1 and stem cells for cartilage regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(39):2403055. [32] WU X, ZHOU M, JIANG F, et al. Marginal sealing around integral bilayer scaffolds for repairing osteochondral defects based on photocurable silk hydrogels. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):3976-3986. [33] QUELQUEJAY H, AL-RIFAI R, SILVESTRO M, et al. L-Wnk1 deletion in smooth muscle cells causes aortitis and inflammatory shift. Circ Res. 2024;135(4):488-502. [34] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711. [35] ZHU F, JI L, DAI K, et al. In situ licensing of mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulatory function via BMP-2 induced developmental process. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2024;121(48):e2410579121. [36] LLOPIS-HERNÁNDEZ V, CANTINI M, GONZÁLEZ-GARCÍA C, et al. Material-driven fibronectin assembly for high-efficiency presentation of growth factors. Sci Adv. 2016;2(8):e1600188. [37] RATTNER A, WANG Y, NATHANS J. Signaling pathways in neurovascular development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2022;45:87-108. [38] GARCÍA JR, CLARK AY, GARCÍA AJ. Integrin-specific hydrogels functionalized with VEGF for vascularization and bone regeneration of critical-size bone defects. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2016;104(4): 889-900. [39] QIN Q, LEE S, PATEL N, et al. Neurovascular coupling in bone regeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(11):1844-1849. [40] WANG JJ, XUE Q, WANG YJ, et al. Engineered chimeric peptides with IGF-1 and titanium-binding functions to enhance osteogenic differentiation in vitro under T2DM condition. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(9):3134. [41] WANG J, ZHU Q, CAO D, et al. Bone marrow-derived IGF-1 orchestrates maintenance and regeneration of the adult skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(1):e2203779120. [42] AHMAD SS, AHMAD K, LEE EJ, et al. Implications of insulin-like growth factor-1 in skeletal muscle and various diseases. Cells. 2020;9(8):1773. [43] ZHANG L, ZHENG L, LI C, et al. Sema3a as a novel therapeutic option for high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation in diabetic osteopathy. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:562. [44] ZHANG H, LU Y, WU B, et al. Semaphorin 3A mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced chondrocyte inflammation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation by binding to Neuropilin-1. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):9641-9654. [45] LI J, WU G, XU C, et al. Slit guidance ligand 3 (SLIT3) loaded in hydrogel microparticles enhances the tendon-bone healing through promotion of type-H vessel formation: An experimental study in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13638. [46] CORNISH J, NAOT D. Lactoferrin as an effector molecule in the skeleton. BioMetals. 2010;23(3):425-430. [47] WANG J, FANG C L, NOLLER K, et al. Bone-derived PDGF-BB drives brain vascular calcification in male mice. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(23):e168447. [48] LI S, QIAN ZM, XU G, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor protects PC12 cells against OGD/R-induced injury by reducing iron. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(4):BSR20200287. [49] XIA D, WANG Y, WU R, et al. The effect of pore size on cell behavior in mesoporous bioglass scaffolds for bone regeneration. Appl Mater Today. 2022;29:101607. [50] KONG D, WANG Q, HUANG J, et al. A biomimetic structural material with adjustable mechanical property for bone tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 2024; 34(8):2305412. [51] TANG S, RICHARDSON BM, ANSETH KS. Dynamic covalent hydrogels as biomaterials to mimic the viscoelasticity of soft tissues. Prog Mater Sci. 2021;120: 100738. [52] LIN Z, LI Q, HAN X, et al. An injectable and degradable heterogeneous microgel assembly capable of forming a “micro-nest group” for cell condensation and cartilage regeneration. Mater Horiz. 2024; 11(21):5438-5450. [53] WANG M, LI W, HAO J, et al. Molecularly cleavable bioinks facilitate high-performance digital light processing-based bioprinting of functional volumetric soft tissues. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3317. [54] DING S, HE S, YE K, et al. Photopolymerizable, immunomodulatory hydrogels of gelatin methacryloyl and carboxymethyl chitosan as all-in-one strategic dressing for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253:127151. [55] CHENG G, YIN C, TU H, et al. Controlled co-delivery of growth factors through layer-by-layer assembly of core-shell nanofibers for improving bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2019;13(6):6372-6382. [56] ZHANG F, LV M, WANG S, et al. Ultrasound-triggered biomimetic ultrashort peptide nanofiber hydrogels promote bone regeneration by modulating macrophage and the osteogenic immune microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 2024;31: 231-246. [57] WANG Y, LI B, XU F, et al. Tough magnetic chitosan hydrogel nanocomposites for remotely stimulated drug release. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(8):3351-3360. [58] MADANI SZM, REISCH A, ROXBURY D, et al. A magnetically responsive hydrogel system for controlling the timing of bone progenitor recruitment and differentiation factor deliveries. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1522-1534. [59] WU Y, ZHANG X, TAN B, et al. Near-infrared light control of GelMA/PMMA/PDA hydrogel with mild photothermal therapy for skull regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112641. [60] TANG L, WANG L, YANG X, et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based smart hydrogels: Design, properties and applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2021;115:100702. [61] LIM H L, HWANG Y, KAR M, et al. Smart hydrogels as functional biomimetic systems. Biomater Sci. 2014;2(5):603-618. [62] AZNAR E, OROVAL M, PASCUAL L, et al. Gated materials for on-command release of guest molecules. Chem Rev. 2016;116(2): 561-718. [63] CHEN J, WU M, VERONIAINA H, et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) derived nanogels demonstrated thermosensitive self-assembly and GSH-triggered drug release for efficient tumor Therapy. Polym Chem. 2019;10(29):4031-4041. [64] WEI W, QI X, LIU Y, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel pH-thermo dual responsive hydrogel based on salecan and poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid). Colloid Surface B. 2015;136:1182-1192. [65] YANG Z, LI X, GAN X, et al. Hydrogel armed with Bmp2 mRNA-enriched exosomes enhances bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21(1):119. [66] HAO H, SUN L, CHEN J, et al. Hydrogel-supported poly(L-lactic acid) and polystyrene microsphere-based three-dimensional culture systems for in vitro cell expansion. Front Mater Sci. 2024;18(2):240682. [67] ZHOU Y, HE X, ZHANG W, et al. Cell-recruited microspheres for OA treatment by dual-modulating inflammatory and chondrocyte metabolism. Mater Today Bio. 2024;27:101127. [68] ZHAO ZY, SHAO L, ZHAO HM, et al. Osteogenic growth peptide accelerates bone healing during distraction osteogenesis in rabbit tibia. J Int Med Res. 2011;39(2):456-463. [69] QIAO Y, LIU X, ZHOU X, et al. Gelatin templated polypeptide co-cross-linked hydrogel for bone regeneration. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2020;9(1):1901239. [70] LEE SS, HSU EL, MENDOZA M, et al. Gel scaffolds of BMP-2-binding peptide amphiphile nanofibers for spinal arthrodesis. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2015;4(1):131-141. [71] IMPELLITTERI NA, TOEPKE MW, LAN LEVENGOOD SK, et al. Specific VEGF sequestering and release using peptide-functionalized hydrogel microspheres. Biomaterials. 2012;33(12):3475-3484. [72] TEIXEIRA SPB, DOMINGUES RMA, BABO PS, et al. Epitope-imprinted nanoparticles as transforming growth factor-β3 sequestering ligands to modulate stem cell fate. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(4):2003934. [73] ZENG Q, ZHU Y, YU B, et al. Antimicrobial and antifouling polymeric agents for surface functionalization of medical implants. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(7):2805-2811. [74] SI H, XING T, DING Y, et al. 3D bioprinting of the sustained drug release wound dressing with double-crosslinked hyaluronic-acid-based hydrogels. Polymers. 2019;11(10):1584. [75] LIU X, WANG D, WANG S, et al. Promoting osseointegration by in situ biosynthesis of metal ion-loaded bacterial cellulose coating on titanium surface. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;297:120022. [76] LI H, LI B, LV D, et al. Biomaterials releasing drug responsively to promote wound healing via regulation of pathological microenvironment. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2023;196:114778. [77] CHEN W, ZHANG H, ZHOU Q, et al. Smart hydrogels for bone reconstruction via modulating the microenvironment. Research (Wash D C). 2023;6:0089. [78] LIN Z, SHEN D, ZHOU W, et al. Regulation of extracellular bioactive cations in bone tissue microenvironment induces favorable osteoimmune conditions to accelerate in situ bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2315-2330. [79] SU H, LI Q, LI D, et al. A versatile strategy to construct free-standing multi-furcated vessels and a complicated vascular network in heterogeneous porous scaffolds via combination of 3D printing and stimuli-responsive hydrogels. Mater Horiz. 2022; 9(9):2393-2407. [80] YAO Q, LIU Y, PAN Y, et al. Long-term induction of endogenous BMPs growth factor from antibacterial dual network hydrogels for fast large bone defect repair. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;607:1500-1515. [81] ZHA K, HU W, XIONG Y, et al. Nanoarchitecture-integrated hydrogel boosts angiogenesis–osteogenesis–neurogenesis tripling for infected bone fracture healing. Adv Sci. 2024;11(43): 2406439. [82] YAO Y, ZHANG H, WANG Z, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive biomaterials mediate tissue microenvironments and tissue regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(33):5019-5037. [83] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 129:110452. [84] KIM YE, KIM J. ROS-scavenging therapeutic hydrogels for modulation of the inflammatory response. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(20):23002-23021. [85] YANG W, YUE H, LU G, et al. Advances in delivering oxidative modulators for disease therapy. Research (Wash D C). 2022;2022: 9897464. [86] LIU J, HAN X, ZHANG T, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: from mechanism to therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2023;16(1):116. [87] SUN J, ZHU H, WANG H, et al. A multifunctional composite scaffold responds to microenvironment and guides osteogenesis for the repair of infected bone defects. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024;22(1):577. [88] FERREIRA MJ, RODRIGUES TA, PEDROSA AG, et al. Glutathione and peroxisome redox homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2023;67: 102917. [89] WANG S, LIU X, WEI D, et al. Polyvalent aptamer nanodrug conjugates enable efficient tumor cuproptosis therapy through copper overload and glutathione depletion. J Am Chem Soc. 2024;146(44): 30033-30045. [90] YANG F, WANG J, HOU J, et al. Bone regeneration using cell-mediated responsive degradable PEG-based scaffolds incorporating with rhBMP-2. Biomaterials. 2013;34(5):1514-1528. |
| [1] | 陈伟飞, 梅远东, 巨积辉. 双离子时序释放多功能水凝胶修复感染性骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5188-5200. |
| [2] | 许艺璇, 姚 俊, 刘旭璐, 李新莲, 刘志雄, 张志红. 含万古霉素的猪皮脱细胞外基质水凝胶促进皮肤感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5214-5228. |
| [3] | 陈 颖, 孙盱衡, 刘 青, 肖 聪, 蒋虹婧, 林展翼. 促进组织工程血管移植物早期阶段形成的无血清培养基[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5093-5102. |
| [4] | 周孝辉, 王思怡, 周启云, 何 钊, 贾玉娟, 王元斌, 马建武, 陈 刚, 郑 峰, 褚耿磊. 纳米羟基磷灰石-聚醚碳酸酯脲静电纺丝膜促进骨缺损修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5134-5142. |
| [5] | 曹雨晴, 郭美玲, 刘 峰, 魏俊超. 多糖基水凝胶的制备、分类及在皮肤损伤修复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5257-5269. |
| [6] | 徐亚伟, 孟世龙, 张 徐, 汪成杰, 袁一峰, 史晓林, 王 娇, 刘 康. 中药有效成分结合水凝胶修复骨缺损:成功与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5295-5303. |
| [7] | 何贞贞, 黄汉记, 王嘉伟, 谢庆条, 江献芳. 生物支架在炎症驱动颞下颌关节骨及软骨破坏及结构性损伤修复中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5312-5320. |
| [8] | 王梓桐, 吴子健, 杨傲飞, 毛 田, 方 楠, 王志刚. 生物材料调控微环境失衡治疗脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5321-5330. |
| [9] | 王洁燕, 姚佳沂, 辛颖童 , 张馨文, 李日旺, 刘大海. 壳聚糖水凝胶载药系统治疗口腔溃疡更安全有效的解决方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5331-5340. |
| [10] | 张其娅, 童伊翔, 杨世姣, 张宇梦, 邓 凌, 吴 玮, 解 瑶, 廖 健, 毛 岭. 梯度玻璃分级超透氧化锆的体外生物相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 443-450. |
| [11] | 刘晓红, 赵 天, 穆云萍, 冯文金, 吕存声, 张智永, 赵子建, 李芳红. 脱细胞真皮基质水凝胶促进大鼠皮肤创面的愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [12] | 姜 侃, 阿力木江·阿不都肉苏力, 沙拉依丁·艾尔西丁, 艾克拜尔江·艾赛提, 库提鲁克·守克尔, 艾克热木江·木合热木. 生物材料与骨再生:研究热点及有影响力的500篇文献分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [13] | 俞 磊, 张 巍, 秦 毅, 葛高然, 柏家祥, 耿德春. 贻贝启发接枝骨形态发生蛋白2成骨活性肽的介孔生物玻璃修复股骨髁缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(22): 4629-4638. |
| [14] | 肖 辉, 李冬妍, 汲 婧, 王丽珍. 生物材料促进角膜碱烧伤修复的作用机制和应用途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2162-2170. |
| [15] | 伍志鑫, 蒋雯雯, 詹健辉, 李杨书润, 任文燕, 王一宇. 水凝胶:口腔颌面部组织缺损修复中的作用与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2178-2188. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2025年2-3月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2010年1月至2025年3月,同时纳入少数远期经典及特别相关文献,重点检索近5年的英文文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 主题词检索、关键词检索、摘要检索等。
1.1.5 检索词 以“生物材料,募集,修复,成骨,软骨,血管”为中文检索词,以“biomaterials,recruitment,repair,osteogenesis,cartilage,vascularization”为英文检索词。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检测到文献590余篇。
1.1.8 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.2 入选标准
纳入标准:有关生物募集组织修复材料方面的文章;文献质量、相关性、可靠性高,或创新性较为突出的文献;优先选择最近5年内发表的文献。
排除标准:与该文研究内容不相关的文献;内容重复的文献;年代久远且观点陈旧、质量较差的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 依据中国知网和PubMed数据库的检索策略,优先汇总含有检索关键词、摘要内容相符、标题相符的文献,对文献的研究领域进行分类,在此过程中排除重复文献、排除相关性较差的文献;根据纳入与排除标准再次进行筛选,最终纳入符合标准的研究原著和综述共90篇。文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 在以往的研究中,学者们深入地研究了组织工程领域,尤其是关注生物募集组织修复材料在组织修复中的应用,这些成果为再生医学提供了理论和实践指导。与其他综述不同的是,该文从天然和合成生物募集组织修复材料的角度出发,重点分析了骨科及血管再生等领域中部分生长因子的作用机制,对影响生物募集组织修复材料性能的因素进行了探究;强调了组织微环境对细胞、生长因子和支架材料相互作用的关系,从募集机制角度揭示了生物募集组织修复材料的应用前景,为后续研究提供了新
思路。
3.3 该综述的局限性 尽管该文对生物募集组织修复材料的研究进行了详细总结,但仍存在一定的局限性,并需要通过以下方向实现突破:需结合医学行业与实际材料的发展,开发兼具生物活性与力学性能的仿生复合材料;针对各种报告、研讨会中提出的临床瓶颈,应加强生长因子修饰与智能响应材料的工艺研究;组织修复过程与再生细胞、分子之间的结合机制尚未能清晰阐释,未来需通过跨学科协作实现材料性能的精准化定制。
3.4 该综述的重要意义 该综述旨在归纳和总结生物募集组织修复材料在医学领域的研究现状,为相关领域组织工程的修复提供新的见解;系统地梳理了生物募集组织修复材料的募集机制与其在组织微环境中发挥的作用,不仅有助于推动相关领域的基础研究,还可为未来的材料设计和临床转化提供参考案例。
组织工程技术在生物医学领域中发挥出重要的作用,围绕“材料-细胞-生长因子”之间的紧密关系,生物募集组织修复材料依靠其独特的生物学机制,在各个研究领域内均得到了重视。与传统生物材料相比,生物募集组织修复材料以细胞招募机制、生长因子识别募集机制为出发点,分别对细胞与生长因子进行定向募集、加速组织修复进程。进一步地,探究影响募集能力的四种关键因素:材料的力学性能、生长因子的有效呈现、特定的生物功能化及微环境的适配调控。系统地梳理了生物医学领域内,最新的研究进展与未来趋势,为实现定向组织修复及临床转化提供了参考依据。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||