中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (20): 5257-5269.doi: 10.12307/2026.671
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
多糖基水凝胶的制备、分类及在皮肤损伤修复中的应用
曹雨晴1,2,郭美玲1,刘 峰2,魏俊超1,2,3,4
- 1南昌大学江西医学院,口腔医学院,江西省南昌市 330006;2南昌大学化学化工学院,江西省南昌市 330031;3口腔疾病江西省重点实验室,江西省南昌市 330006;4江西省口腔临床医学研究中心,江西省南昌市 330006
-
接受日期:2025-06-16出版日期:2026-07-18发布日期:2025-12-01 -
通讯作者:魏俊超,教授,博士生导师,南昌大学江西医学院,口腔医学院,江西省南昌市 330006;南昌大学化学化工学院,江西省南昌市 330031;口腔疾病江西省重点实验室,江西省南昌市 330006;江西省口腔临床医学研究中心,江西省南昌市 330006 -
作者简介:曹雨晴,女,2001年生,江西省上饶市人,汉族,南昌大学在读硕士,主要从事高分子水凝胶及其生物性能研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(52163016,52463017),项目负责人:魏俊超;江西省主要学科学术和技术带头人培养项目(20213BCJL22051),项目负责人:魏俊超;江西省自然科学基金委重点项目(20242BAB26161),项目负责人:魏俊超
Preparation, classification and application of polysaccharide-based hydrogels in skin damage repair
Cao Yuqing1, 2, Guo Meiling1, Liu Feng2, Wei Junchao1, 2, 3, 4
- 1School of Stomatology, College of Jiangxi Medicine, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Disease, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 4Jiangxi Province Clinical Research Center for Oral Disease, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-06-16Online:2026-07-18Published:2025-12-01 -
Contact:Wei Junchao, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Stomatology, College of Jiangxi Medicine, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, Jiangxi Province, China; Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Disease, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; Jiangxi Province Clinical Research Center for Oral Disease, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Cao Yuqing, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, College of Jiangxi Medicine, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 52163016, 52463017 (to WJC); Jiangxi Provincial Key Discipline Academic and Technical Leader Training Project, No. 20213BCJL22051 (to WJC); Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Key Project), No. 20242BAB26161 (to WJC)
摘要:
文题释义:
多糖:是一类由多个单糖通过糖苷键连接而成的高分子化合物,通常由十几个甚至上千个单糖单元聚合而成,结构和功能具有多样性,广泛存在于植物、动物和微生物中,具有良好的生物相容性、可降解性、亲水性等,在生物医学领域应用广泛。
水凝胶:是一类具有三维网络结构的高分子材料,能够吸收并保持大量的水分,而不溶解于水。
背景:根据伤口微环境开发出多功能生物活性智能敷料用于实时监测创面微环境,是一种加速伤口愈合的重要策略。多糖基水凝胶因独特的优势在伤口敷料领域获得了广泛关注。
目的:综述多糖基水凝胶的合成方法、功能特性及在皮肤损伤修复中的应用进展。
方法:以“水凝胶,多糖,可逆共价键,伤口敷料,创面修复”为中文检索词,检索万方数据库和中国知网,以“Hydrogels,polysaccharide,reversible covalent bonds,Wound dressings,wound repair”为英文检索词,检索PubMed和Web of Science数据库,根据纳入与排除标准,最终纳入125篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:多糖基水凝胶的交联方式可以分为物理交联、化学交联两种,其中动态的化学键由于能够对某些刺激做出响应,对于开发生物活性智能敷料具有重要意义。多糖富含羧基、羟基、胺基等官能团,可以很容易进行接枝改性,从而满足临床应用的功能需要,例如智能抗菌、消炎、促愈合且无不良反应。随着临床需求的不断多元化和精细化,水凝胶敷料的功能也从先前单一的覆盖保护功能转变为现在的多种功能集合,包括黏附和止血、抗菌、抗炎和抗氧化、物质输送、自我修复、刺激响应和伤口监测等。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-8648-3746(曹雨晴)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
曹雨晴, 郭美玲, 刘 峰, 魏俊超. 多糖基水凝胶的制备、分类及在皮肤损伤修复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5257-5269.
Cao Yuqing, Guo Meiling, Liu Feng, Wei Junchao. Preparation, classification and application of polysaccharide-based hydrogels in skin damage repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5257-5269.
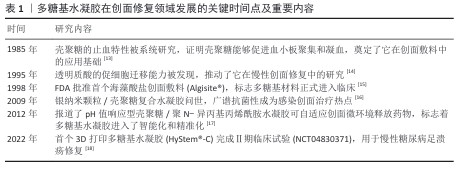
2.2 水凝胶的制备方法 多糖基水凝胶的制备方法多种多样,包括物理交联和化学交联[19]。物理交联法通常利用多糖分子间的非共价相互作用,这种方法操作简单,无需引入额外的交联剂,具有良好的生物相容性[20]。化学交联法通过引入交联剂或利用多糖分子上的活性基团进行化学反应,形成共价键网络,这种方法制备的水凝胶机械强度较高,但可能引入一定的毒性[21]。除此之外,将物理交联与化学交联引入同一凝胶网络从而形成混合交联的水凝胶,兼具了两者的优势,展现出独特的性能和应用潜力[22]。总之,混合交联水凝胶结合了物理交联的动态性和化学交联的稳定性,为开发高性能、多功能的水凝胶材料提供了新的思路。水凝胶创面敷料的主要交联方法总结于表2中。
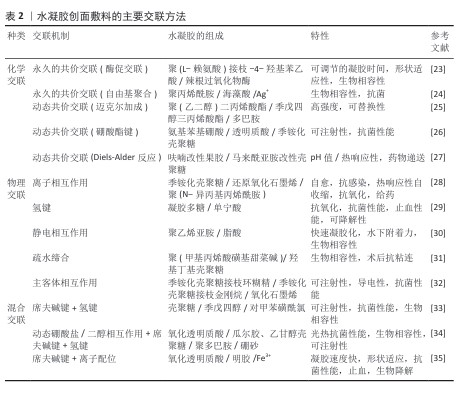
2.2.1 化学交联法 完全化学交联网络中的分子链通过不可逆的共价键相互连接。化学交联法主要包括自由基聚合法[36-37]、缩合反应法[38]、酶促反应法以及使用交联剂(如戊二醛、京尼平)等[39]。化学交联法制备的水凝胶通常具有较好的机械性能和更强的稳定性。WANG等[37]以甲基丙烯酸化透明质酸和甲基丙烯酰化羧基甜菜碱为原料,在紫外光下通过共聚获得水凝胶敷料,该水凝胶具有高压缩弹性以及良好的拉伸强度、黏结性、强防污性、高吸水性和可生物降解性(图7A)。ZHU等[39]通过辣根过氧化物酶介导的过氧化氢(H2O2)与儿茶酚修饰的肽树状大分子发生酶促反应进行交联(图7B)。然而,外界刺激(例如机械压力、温度、pH值改变)会破坏大部分共价交联水凝胶的内部结构,进而影响水凝胶的性能,严重限制了水凝胶的应用,因此,研发出具有自愈合能力的水凝胶材料很有必要。其中,动态可逆共价键是一种能响应外界刺激自发断裂与形成的化学键,与其他机制相比,动态可逆共价键具有更强的可逆性与稳定性,因此常被用于制备多功能水凝胶[40-41]。考虑到人体内任何特定区域都有特定的pH值,以及由于血液和细胞内基质的还原和氧化性质,pH值和氧化还原响应性水凝胶在生物工程领域具有较好的应用前景[42]。含有pH值可解离键(如亚胺、肟、腙、硼酸酯)的水凝胶以及由二硫键、硼酸酯键和二硒键制备的氧化还原响应性水凝胶,引起了广泛关注。CHEN等[43]利用席夫碱反应设计了含有壳聚糖和氧化魔芋葡甘露聚糖的可注射自修复水凝胶,由于壳聚糖富含胺基,除了可注射、自愈特性外,水凝胶还具有黏合、抗菌、生物相容特性,从而促进伤口的愈合。SHAO等[44]通过3-羧基-4-氟苯硼酸接枝季铵化壳聚糖的苯硼酸基团和聚乙烯醇的羟基,制备了一种具有自修复性能和可注射性的自适应多功能水凝胶,其中促血管生成药物去铁胺以明胶微球的形式加载,水凝胶的硼酸酯键可以与高血糖和过氧化氢反应,以减轻创面愈合早期的氧化应激并释放明胶微球。BO等[45]以二硫代二丙酸二酰肼为交联剂,由季铵化的 N-[3-(二甲氨基)丙基]甲基丙烯酰胺共聚物制备了一系列抗菌水凝胶,基于动态酰腙键和二硫键的特点,该水凝胶表现出有效的自修复能力以及 pH值和氧化还原触发的凝胶-溶胶-凝胶过渡特性。
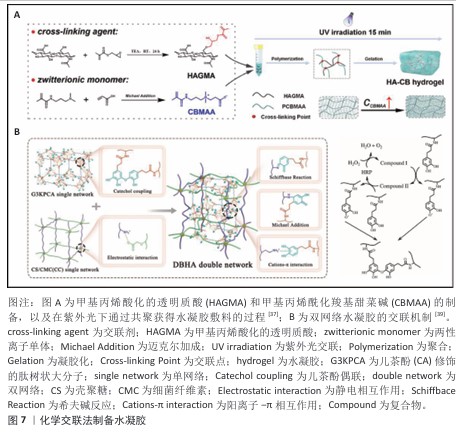
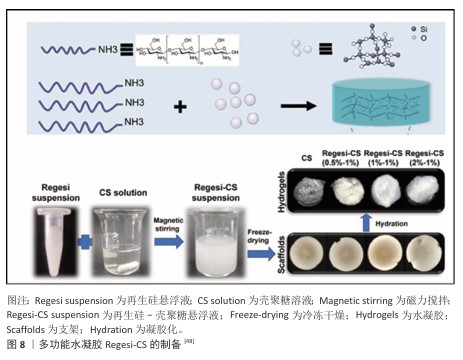
2.2.2 物理交联法 物理交联法制备的水凝胶主要由分子间作用力形成,主要包括氢键、离子相互作用、静电相互作用、疏水缔合、主客体相互作用,可以通过冷冻干燥、离子交联等方法进行,不涉及化学反应,避免了有毒副产物的产生[46]。WANG等[47]基于多糖阳离子瓜尔胶和甘草酸衍生物与Cu2+之间的弱氢键和静电相互作用,制备了一种具有双控释药特性的水凝胶创面敷料,甘草酸衍生物和Cu2+独特的释放能力促使它们在创面愈合的炎症期、增殖期和重塑期发挥重要作用。XU等[48]在非交联壳聚糖溶液中加载再生硅,然后进行冷冻干燥和水化制备了多功能水凝胶(Regesi-CS)(图8),在耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染的糖尿病创面模型中,该水凝胶通过消除细菌感染、促进肉芽组织形成、促进胶原沉积、促进血管生成等方式有效促进创面愈合。
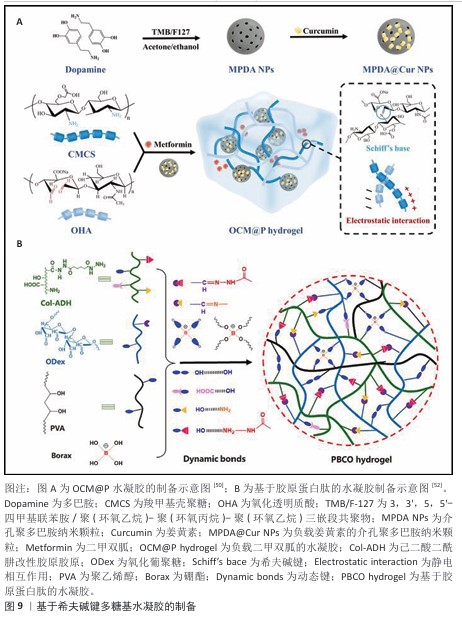
2.2.3 混合交联法 物理交联赋予材料自愈合性和可逆性,而化学交联则提供了稳定的网络结构和更高的强度,两者结合法制备的水凝胶机械性能显著提升,使水凝胶在承受外力时既能保持结构完整性,又能在损伤后实现一定程度的自我修复[49]。TAN等[50] 将载有姜黄素的介孔聚多巴胺纳米颗粒和二甲双胍引入由羧甲基壳聚糖和氧化透明质酸之间动态亚胺键和静电相互作用形成的聚合物基质中,制备了OCM@P水凝胶(图9A)。XIA等[51] 提出了一种使用由己二酸二酰肼改性透明质酸、氧化透明质酸和含锶离子的多巴胺改性聚(6-氨基己酸)组成的糖肽基水凝胶敷料,用于调节糖尿病创面部位pH值微环境,这种水凝胶通过席夫碱相互作用和金属络合形成网络,从而抑制炎症并加速创面愈合过程中的血管生成。水凝胶不仅具有足够的机械性能和自愈能力,还可以支持组织黏附,促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化。LI等[52]开发了一种基于胶原蛋白肽的水凝胶作为创面敷料,该敷料由己二酸二酰肼官能化胶原蛋白肽、氧化葡聚糖、聚乙烯醇和硼砂通过多重动态可逆键(酰腙、硼酸酯和氢键)组成,如图9B所示。可注射水凝胶表现出令人满意的自修复能力、抗菌活性、机械强度以及良好的生物相容性和生物降解性。
2.3 功能化水凝胶的分类
2.3.1 止血水凝胶 止血是创面愈合的最开始阶段,水凝胶创面敷料的止血功能可以更好地加速创面愈合。壳聚糖止血剂在损伤部位应用时可有效控制出血[53]。当壳聚糖的-NH2质子化后,在与血液接触时这些基团有助于聚集血细胞并在出血部位形成塞子[54]。结合黏附性水凝胶的生物黏附特性,通过密封创面以止血,避免创面和外部环境接触导致感染[55]。LI等[56]报道了基于苯硼酸二醇酯交联的单一聚合物组分透明质酸-3-氨基苯硼酸盐酸盐水凝胶,该水凝胶网络的苯硼酸可以与组织表面细胞膜上的糖脂或糖蛋白结合,提供强大且可逆的组织黏附,从而更好地加速创面愈合。受贻贝启发的水凝胶组织胶黏剂,因在潮湿环境中的强大黏合力和内聚强度也受到了广泛关注。CHEN等[57]制备了由聚(γ-谷氨酸)和多巴胺组成的新型贻贝启发的组织黏附水凝胶,它可以很好地黏合组织并在潮湿环境中止血,该水凝胶的湿组织黏附强度(58.2 kPa)显著强于临床使用的纤维蛋白胶,并且在肝脏穿刺动物模型中具有更有效的止血能力。

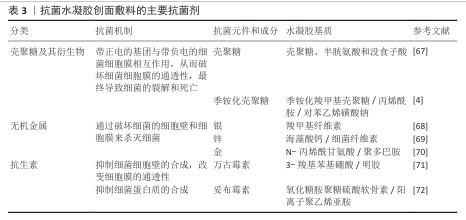
2.3.2 抗菌水凝胶 严重的细菌感染会导致创面一直停滞在炎症阶段无法过渡,从而阻碍创面愈合[58],因此赋予水凝胶创面敷料抗菌特性具有重要意义。为了防止创面感染,通常在水凝胶中加入各种抗菌剂[59],按照抗菌材料的不同,抗菌水凝胶创面敷料可分为以壳聚糖为代表的多糖类水凝胶创面敷料[60-61]、负载无机抗菌剂(银、锌等)的水凝胶创面敷料[62-64]、载有有机抗菌剂的水凝胶创面敷料[65-66]。表3为具有代表性的抗菌剂在水凝胶创面敷料中的应用。
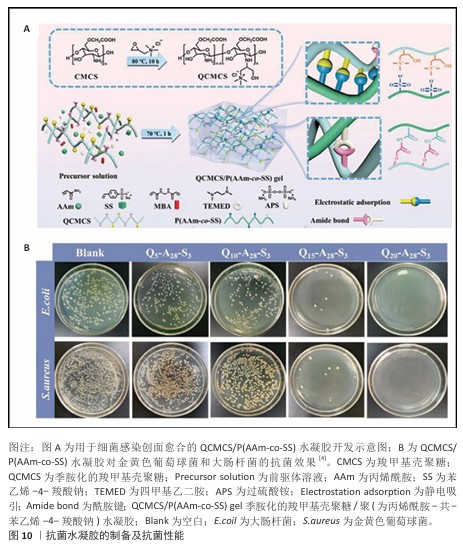
(1) 多糖类抗菌水凝胶:部分天然高分子兼具抗菌性能和独特生物学性能,这些特点使它们在制备抗菌水凝胶敷料中颇具优势[73]。壳聚糖及其衍生物由于含有特定的功能基团,赋予了它抗菌性能。壳聚糖的抗菌机制是通过它结构中带正电的基团与带负电的细菌细胞膜相互作用,从而破坏细菌细胞膜的通透性,最终导致细菌的裂解和死亡。WANG等[74]通过动态席夫碱反应将壳聚糖与双醛壳聚糖交联制成水凝胶,从而得到自愈和可注射系统,该体系避免使用了毒性和高成本的水凝胶交联剂(如甲醛、戊二醛和京尼平),因此表现出优异的生物相容性、抗菌活性。然而,由于壳聚糖的抗菌性能、力学性能有限,要制备具有多种特性(包括柔韧性、可拉伸性、黏附性和抗菌活性)的壳聚糖基水凝胶仍然是一项关键挑战,因此,常常通过复合、接枝或交联以提高壳聚糖基水凝胶的利用率。DU等[4]在季铵化羧甲基壳聚糖存在下,通过丙烯酰胺、对苯乙烯磺酸钠以及交联剂N,N’亚甲基双丙烯酰胺的溶液热引发聚合,轻松制备了一种具有集成功能的壳聚糖基水凝胶QCMCS/P (AAm-co-SS)(图10A),该水凝胶表现出坚韧的机械性能(0.767 MPa拉伸应力和1 100%断裂应变)和较好的组织黏附性;此外,体外生物学评价表明,该水凝胶具有令人满意的生物相容性、血液相容性和优异的抗菌能力(对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抗菌率分别为 98.8%和97.3%),如图10B。
(2)负载无机抗菌剂的多糖基水凝胶:银、金、锌、铜和其它金属纳米颗粒已被广泛用于抗菌水凝胶创面敷料的制备[75]。其中,金属纳米颗粒的抗菌机制主要包括以下几种主要方式[76-79]:①细胞膜破坏:金属纳米颗粒可以通过沉积在细菌细胞膜上破坏细胞膜结构,导致细胞内容物泄露,从而杀死细菌;②电子传递链破坏:金属纳米颗粒可以通过干扰细菌的电子传递链从而破坏细菌的能量代谢,导致细菌死亡;③产生自由基:一些金属纳米颗粒(如金纳米颗粒)可以产生自由基,通过自由基攻击细菌细胞导致细菌死亡;④生物膜破坏:金属纳米颗粒在细菌表面形成一层破坏细菌的生物膜,从而杀死细菌。例如,银纳米颗粒可以通过破坏细菌的细胞壁和细胞膜来杀灭细菌。由于潮湿、透气、抗菌的微环境可促进细胞增殖和迁移,有利于创面愈合,ZHANG等[80]利用氧化海藻酸钠、壳聚糖低聚糖和氧化锌纳米颗粒,通过自发席夫碱反应制备了一种新型复合水凝胶,为创面愈合提供湿润抗菌的环境,并且该复合水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性,能够持续地释放Zn2+,对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、白色念珠菌和枯草芽孢杆菌均具有显著的抑菌活性抑制作用。LONG等[81]制备了一种基于多巴胺接枝透明质酸和苯硼酸接枝甲基纤维素的可注射多功能水凝胶,用于促进糖尿病创面修复,该水凝胶具有多功能特性,包括快速凝胶化时间(小于10 s)、自修复、高吸水性、组织黏附性和优异的抗氧化活性,在加载具有广谱抗菌特性的银纳米颗粒和对细胞具有高亲和力的重组人源Ⅲ型胶原蛋白后表现出pH值/H2O2响应特性,能够更好地促进细胞增殖,并且具有更高的抗菌活性。DONG等[82]设计了一种超小金纳米颗粒(UsAuNPs)和羧甲基壳聚糖(UsAuNPs@CMCS)的复合材料,因为超小金纳米颗粒容易自聚集导致抗菌效果降低,临床应用有限,因此作者采用羧甲基壳聚糖将金纳米颗粒的自聚集限制在 1-3 nm,使复合材料具有很高的抗菌功效。
尽管使用金属作为抗菌材料存在的一些生物毒性问题和潜在风险尚未得到解决,但金属仍然是除抗生素之外最常用的抗菌剂之一[83-84]。为了限制金属粒子的毒性,可以从以下几个方面入手[85-87]:①表面修饰:通过聚合物涂层或其他材料的包覆减少金属离子的释放速度,降低毒性;②纳米复合材料:将金属离子与无毒材料结合形成复合材料,从而降低金属离子的生物活性;③浓度控制:优化金属离子浓度,确保在有效抗菌的同时避免对细胞造成伤害;④靶向释放:设计智能释放系统,使金属离子仅在特定条件下释放,降低对正常细胞的影响。这些方法都可以有效减少金属离子的毒性,提高金属离子的安全性和应用潜力。例如,ZHANG等[88]以苯硼酸接枝壳聚糖(CS-PBA)、对醛基苯甲酸接枝聚乙二醇(PEG-DA)和单宁酸(TA)为基础,通过席夫碱和硼酸酯交联制备了水凝胶,苯基硼酸修饰的氧化锌纳米颗粒在凝胶化之前被嵌入到水凝胶中,抑菌实验表明,由于Zn2+和单宁酸的pH值响应性释放,水凝胶能够有效地消除耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌,并且基本不会产生细胞毒性。
(3)负载有机抗菌剂的多糖基水凝胶:水凝胶作为一种良好的3D材料,可与多种抗菌剂配合使用,实现抗菌治疗[89]。水凝胶在制备抗菌材料中具有显著优势,它能够高效地装载、有效释放药物和抗菌剂,从而显著提高抗菌剂的利用率[90]。例如,水凝胶可以通过负载光热剂在使用过程中将光能转化成热能,从而达到抗菌的目的[91]。常见的光热剂有碳纳米管复合材料[92]、氧化石墨烯等碳基材料以及最近报道的聚多巴胺等[93-94]。除此之外,单宁酸、没食子酸及其衍生物也有一定的抗菌性能,抗菌机制是酚羟基与细菌的细胞膜成分结合从而改变膜的通透性,导致细胞内物质泄漏,从而使细菌失去生存能力;还能与细菌的蛋白质结合形成不溶性复合物,从而干扰细胞的正常代谢和功能[95-97]。例如,CHENG等[98]采用带有醛基和硼酸基的甲酰基苯硼酸作为双功能接头,整合妥布霉素和单宁酸,制备具有多刺激响应性和抗菌活性的全小分子动态共价水凝胶,细菌定植和代谢产生的酸性微环境可以触发妥布霉素的酸响应性释放以杀死细菌;此外,通过对凝胶进行局部加热可以促进妥布霉素的释放和凝胶的抗菌作用,后续也对凝胶进行了针对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制区研究,发现抑制区与加热时间呈正比。HE等[99]使用聚乙烯醇、聚多巴胺和单宁酸制备了一种高性能、多功能的聚乙烯醇基水凝胶敷料,该敷料具有双重黏合、抗菌和抗氧化性能。WANG等[100]开发了一种可注射的、具有三重响应的水凝胶,该水凝胶对糖尿病创面微环境中的酸性条件、活性氧和高葡萄糖水平有响应,可持续地输送单宁酸以增强抗菌性能。
2.3.3 抗炎性能水凝胶 炎症阶段是创面愈合过程中不可或缺的一部分,通过清除感染、促进细胞迁移和修复机制的激活以及调节愈合过程等方式,促进了创面愈合[101]。然而,过度炎症会导致高氧化应激、活性氧急剧增加,从而对脂质、蛋白质和DNA等细胞大分子造成氧化损伤,导致炎症相关疾病的发展和恶化[102-104]。因此,具有抗炎性能的多糖已被广泛研究,其中透明质酸作为细胞外基质的主要成分,已被证明可以促进细胞增殖和迁移、调节炎症反应[105]。除此之外,葡甘露聚糖的抗炎作用也被广泛研究,它能够调节创面微环境中的巨噬细胞表型,从而起到抗炎和免疫调节作用[106]。然而,仅仅使用天然多糖本身的抗炎作用难以满足促进创面愈合的需要,急切开发出新型具有抗炎性能的创面敷料。因此,具有抗氧化、抗炎性能的小分子被广泛研究,其中包含天然多酚类(茶多酚、姜黄素、黄酮类化合物、花青素和白藜芦醇等)的抗氧化剂以及具有抗氧化性能的内源性小分子(超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶)等[107]。通过复合抗炎小分子,能够显著提高天然多糖材料的抗炎性能,从而赋予多糖基水凝胶作为创面敷料更好的抗炎效果。
SU等[108]基于羧甲基壳聚糖、2-甲酰基苯硼酸和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯的双重动态(席夫碱和硼酸酯键)交联构建了一种新型黏合水凝胶,该水凝胶具有良好的pH值响应性、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯释放和光热性能,表现出抗氧化、抗炎活性,有望作为糖尿病创面愈合的多功能敷料。GUO等[109]开发了一种具有光热特性的新型动态硼酸酯键交联杂化多功能水凝胶敷料,用于调节糖尿病创面部位的微环境,并在无需额外药物的情况下加速创面愈合过程。ZHANG等[110]通过静电相互作用制备了由壳聚糖、肝素和聚(γ-谷氨酸)组成的不同比例复合水凝胶,通过将超氧化物歧化酶加载到水凝胶上构建了具有抗氧化特性的创面敷料,水凝胶释放的超氧化物歧化酶可以减少慢性创面部位的活性氧生成和氧化应激,从而加速创面愈合。LI等[111]将氯霉素乙酰转移酶加载到中空硫化铜内部,并与甲基丙烯酸化透明质酸水凝胶复合制备了光热响应纳米递送平台,在近红外光照射下该递送平台具有安全的光热性能(< 43 ℃),对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌具有良好的抑制作用,同时通过降低细胞内活性氧水平,调节组织炎症环境,加速创面愈合。
2.3.4 促进组织再生类水凝胶 创面经过止血和炎症期过渡到增殖和重塑期,创面愈合是一个复杂的生物事件,涉及多种细胞类型、细胞相互作用、多种因子的合成和各种介质的分泌[112]。
其中,生长因子在促进组织再生方面发挥着关键作用,如表皮生长因子和转化生长因子能够增强细胞的分裂和增殖速度,并且通过影响细胞运动帮助细胞迁移到受损区域,参与修复过程。血管内皮生长因子也能够通过促进新血管的形成为再生组织提供必要的氧气和营养,提高愈合效果。除此之外,某些生长因子能够将干细胞引导向特定的细胞类型(如成骨细胞或软骨细胞)分化,也可以调节局部炎症反应,促进炎症消退,创造适宜的微环境以支持愈合。然而,生长因子直接给药后难以稳定地保持在创面部位,半衰期短,容易被降解,导致有效浓度迅速下降,从而影响治疗效果。多次给药意味着患者费用的增加,并且弥散的生长因子可能会对周围健康组织造成不良影响[113-114]。因此,利用水凝胶系统缓释生长因子可以延长生长因子的作用时间,确保在合适的时机释放,满足不同修复阶段的需求[115]。
AN等[116]合成了一种含有硫缩醛键的活性氧响应性可注射聚乙二醇水凝胶,并用于递送表皮生长因子,该水凝胶中的硫缩醛键不仅能够清除创面部位过量的活性氧,还实现了响应性和受控的表皮生长因子释放,促进组织再生。ZHAO等[117]使用三聚磷酸钠交联聚乙烯醇,通过负载莫匹罗星和粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子开发了一种活性氧清除水凝胶,该水凝胶通过降低活性氧水平和上调创面周围的M2表型巨噬细胞来促进创面闭合。值得注意的是,载药的活性氧清除水凝胶可用于有效治疗各种类型的创面,包括难以愈合的细菌感染糖尿病创面等。
通过特殊的设计策略来调节智能水凝胶的降解和药物释放行为,使它能够智能感知创面微环境的状态,并实现响应治疗以阻止损伤。由于糖尿病创面微环境的复杂性,引入多重刺激反应激活机制已成为一个重要的研究方向,例如,通过引入可逆共价键交联响应不同生理微环境和外部刺激(电、光、热等),可以实现对药物释放的精确时空控制;除此之外,开发具备实时监测多功能的多糖基水凝胶,对于如何实现监测数据的无线实时传输、降低材料成本以适配临床需求,以及通过体内外实验验证水凝胶的长期安全性与可靠性也是需要关注的重中之重。

| [1] LIANG YP, HE JH, GUO BL. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. Acs Nano. 2021;15(8): 12687-12722. [2] PRIYA S, CHOUDHARI M, TOMAR Y, et al. Exploring polysaccharide-based bio-adhesive topical film as a potential platform for wound dressing application: A review. Carbohyd Polym. 2024;327:121655. [3] DONG RN, GUO BL. Smart wound dressings for wound healing. Nano Today. 2021;41:101290. [4] DU J, ZHANG Y, HUANG Y, et al. Dual-Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Antibacterial Hydrogels with Tough and Adhesive Properties for Wound Dressing. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2023;44(23):e2300325. [5] SRINIVAS US, TAN BWQ, VELLAYAPPAN BA, et al. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol. 2019;25:101084. [6] HUANG C, DONG L, ZHAO B, et al. Anti-inflammatory hydrogel dressings and skin wound healing. Clin Transl Med. 2022; 12(11):e1094. [7] POWERS JG, HIGHAM C, BROUSSARD K, et al. Wound healing and treating wounds: Chronic wound care and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(4):607-625;quiz 625-606. [8] BARDILL JR, LAUGHTER MR, STAGER M, et al. Topical gel-based biomaterials for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Acta Biomater. 2022;138:73-91. [9] TEHRANY PM, RAHMANIAN P, REZAEE A, et al. Multifunctional and theranostic hydrogels for wound healing acceleration: An emphasis on diabetic-related chronic wounds. Environ Res. 2023;238(Pt 1): 117087. [10] ZENG Q, QI X, SHI G, et al. Wound Dressing: From Nanomaterials to Diagnostic Dressings and Healing Evaluations. Acs Nano. 2022; 16(2):1708-1733. [11] GUERRA A, BELINHA J, JORGE RN. Modelling skin wound healing angiogenesis: A review. J Theor Biol. 2018;459:1-17. [12] SIMOES D, MIGUEL SP, RIBEIRO MP, et al. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;127:130-141. [13] MUZZARELLI R. New derivatives of chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Proceedings of the New Dev Ind Polysaccharides Proc Conf, F, 1985. [14] LAURENT TC, LAURENT U, FRASER J. Functions of hyaluronan. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995;54(5):429. [15] COCKBILL. Evaluation in vivo and in vitro of the performance of interactive dressings in the management of animal soft tissue injuries. Vet Dermatol. 1998;9(2):87-98. [16] TRAVAN A, PELILLO C, DONATI I, et al. Non-cytotoxic silver nanoparticle-polysaccharide nanocomposites with antimicrobial activity. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(6):1429-1435. [17] ZHAO SP, ZHOU F, LI LY. pH-and temperature-responsive behaviors of hydrogels resulting from the photopolymerization of allylated chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide, and their drug release profiles. J Polym Res. 2012;19:1-9. [18] SANJANWALA D, LONDHE V, TRIVEDI R, et al. Polysaccharide-based hydrogels for drug delivery and wound management: a review. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022; 19(12):1664-1695. [19] ZHU T, MAO J, CHENG Y, et al. Recent progress of polysaccharide‐based hydrogel interfaces for wound healing and tissue engineering. Adv Mater Interfaces. 2019; 6(17):1900761. [20] PITA-LÓPEZ ML, FLETES-VARGAS G, ESPINOSA-ANDREWS H, et al. Physically cross-linked chitosan-based hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: A state-of-the-art review. Eur Polym J. 2021;145: 110176. [21] YAN X, HUANG H, BAKRY AM, et al. Advances in enhancing the mechanical properties of biopolymer hydrogels via multi-strategic approaches. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;272(Pt 2):132583. [22] LI L, WU P, YU F, et al. Double network hydrogels for energy/environmental applications: challenges and opportunities. J Mater Chem A. 2022;10(17):9215-9247. [23] LEI K, WANG K, SUN Y, et al. Rapid‐fabricated and recoverable dual‐network hydrogel with inherently anti‐bacterial abilities for potential adhesive dressings. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(6):2008010. [24] JI H, SONG X, CHENG H, et al. Biocompatible In Situ Polymerization of Multipurpose Polyacrylamide-Based Hydrogels on Skin via Silver Ion Catalyzation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(28):31079-31089. [25] XIE T, DING J, HAN X, et al. Wound dressing change facilitated by spraying zinc ions. Mater Horiz. 2020;7(2):605-614. [26] ZHU S, DAI Q, YAO L, et al. Engineered multifunctional nanocomposite hydrogel dressing to promote vascularization and anti-inflammation by sustained releasing of Mg2+ for diabetic wounds. Compos B Eng. 2022;231:109569. [27] LI DQ, WANG SY, MENG YJ, et al. Fabrication of self-healing pectin/chitosan hybrid hydrogel via Diels-Alder reactions for drug delivery with high swelling property, pH-responsiveness, and cytocompatibility. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;268:118244. [28] LI M, LIANG Y, HE J, et al. Two-pronged strategy of biomechanically active and biochemically multifunctional hydrogel wound dressing to accelerate wound closure and wound healing. Chem Mater. 2020;32(23):9937-9953. [29] ZHOU Z, XIAO J, GUAN S, et al. A hydrogen-bonded antibacterial curdlan-tannic acid hydrogel with an antioxidant and hemostatic function for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;285:119235. [30] PENG X, LI Y, LI T, et al. Coacervate-Derived Hydrogel with Effective Water Repulsion and Robust Underwater Bioadhesion Promotes Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(31):e2203890. [31] DONG X, YAO F, JIANG L, et al. Facile preparation of a thermosensitive and antibiofouling physically crosslinked hydrogel/powder for wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(13):2215-2229. [32] ZHANG B, HE J, SHI M, et al. Injectable self-healing supramolecular hydrogels with conductivity and photo-thermal antibacterial activity to enhance complete skin regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2020; 400:125994. [33] FAN L, HE Z, PENG X, et al. Injectable, Intrinsically Antibacterial Conductive Hydrogels with Self-Healing and pH Stimulus Responsiveness for Epidermal Sensors and Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(45):53541-53552. [34] GUO H, HUANG S, XU A, et al. Injectable adhesive self-healing multiple-dynamic-bond crosslinked hydrogel with photothermal antibacterial activity for infected wound healing. Chem Mater. 2022;34(6):2655-2671. [35] YUAN Y, SHEN S, FAN D. A physicochemical double cross-linked multifunctional hydrogel for dynamic burn wound healing: shape adaptability, injectable self-healing property and enhanced adhesion. Biomaterials. 2021;276:120838. [36] WANG J, XU W, ZHANG W, et al. UV cross-linked injectable non-swelling dihydrocaffeic acid grafted chitosan hydrogel for promoting wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;314:120926. [37] WANG S, REN K, ZHANG M, et al. Self-Adhesive, Strong Antifouling, and Mechanically Reinforced Methacrylate Hyaluronic Acid Cross-Linked Carboxybetaine Zwitterionic Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2024;25(1):474-485. [38] ZHANG Y, PAN Y, CHANG R, et al. Advancing homogeneous networking principles for the development of fatigue-resistant, low-swelling and sprayable hydrogels for sealing wet, dynamic and concealed wounds in vivo. Bioact Mater. 2024;34:150-163. [39] ZHU H, XU G, HE Y, et al. A Dual-Bioinspired Tissue Adhesive Based on Peptide Dendrimer with Fast and Strong Wet Adhesion. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022; 11(15):e2200874. [40] YE J, FU S, ZHOU S, et al. Advances in hydrogels based on dynamic covalent bonding and prospects for its biomedical application. Eur Polym J. 2020;139:110024. [41] ZHAO X, CHEN X, YUK H, et al. Soft materials by design: unconventional polymer networks give extreme properties. Chem Rev. 2021;121(8):4309-4372. [42] CHENG S, ZHANG C, LI J, et al. Highly efficient removal of antibiotic from biomedical wastewater using Fenton-like catalyst magnetic pullulan hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;262:117951. [43] CHEN H, CHENG J, RAN L, et al. An injectable self-healing hydrogel with adhesive and antibacterial properties effectively promotes wound healing. Carbohyd Polym. 2018;201: 522-531. [44] SHAO Z, YIN T, JIANG J, et al. Wound microenvironment self-adaptive hydrogel with efficient angiogenesis for promoting diabetic wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:561-573. [45] BO Y, ZHANG L, WANG Z, et al. Antibacterial hydrogel with self-healing property for wound-healing applications. ACS Biomater Sci. 2021;7(11):5135-5143. [46] YANG JY, CHEN Y, ZHAO L, et al. Constructions and Properties of Physically Cross-Linked Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers. Polym Rev. 2023;63(3):574-612. [47] WANG Z, LIU J, ZHENG Y, et al. Copper Ion-Inspired Dual Controllable Drug Release Hydrogels for Wound Management: Driven by Hydrogen Bonds. Small. 2024; 20(34):e2401152. [48] XU J, LIN Y, WANG Y, et al. Multifunctional Regeneration Silicon-Loaded Chitosan Hydrogels for MRSA-Infected Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024; 13(10):e2303501. [49] GUO B, LIANG Y, DONG R. Physical dynamic double-network hydrogels as dressings to facilitate tissue repair. Nat Protoc. 2023; 18(11):3322-3354. [50] TAN W, LONG T, WAN Y, et al. Dual-drug loaded polysaccharide-based self-healing hydrogels with multifunctionality for promoting diabetic wound healing. Carbohyd Polym. 2023;312:120824. [51] XIA H, DONG Z, TANG Q, et al. Glycopeptide‐Based Multifunctional Hydrogels Promote Diabetic Wound Healing through pH Regulation of Microenvironment. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33(29):2215116. [52] LI J, ZHAI YN, XU JP, et al. An injectable collagen peptide-based hydrogel with desirable antibacterial, self-healing and wound-healing properties based on multiple-dynamic crosslinking. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;259(Pt 1):129006. [53] BENNETT BL, LITTLEJOHN L. Review of new topical hemostatic dressings for combat casualty care. Mil Med. 2014;179(5): 497-514. [54] KHOSHMOHABAT H, PAYDAR S, KAZEMI HM, et al. Overview of Agents Used for Emergency Hemostasis. Trauma Mon. 2016; 21(1):e26023. [55] ZHU J, LI F, WANG X, et al. Hyaluronic Acid and Polyethylene Glycol Hybrid Hydrogel Encapsulating Nanogel with Hemostasis and Sustainable Antibacterial Property for Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(16):13304-13316. [56] LI M, SHI X, YANG B, et al. Single-component hyaluronic acid hydrogel adhesive based on phenylboronic ester bonds for hemostasis and wound closure. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;296:119953. [57] CHEN W, WANG R, XU T, et al. A mussel-inspired poly (γ-glutamic acid) tissue adhesive with high wet strength for wound closure. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(28): 5668-5678. [58] ZHOU Z, MEI X, HU K, et al. Nanohybrid Double Network Hydrogels Based on a Platinum Nanozyme Composite for Antimicrobial and Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(14):17612-17626. [59] JI Z, WEI T, ZHU J, et al. Actively contractible and antibacterial hydrogel for accelerated wound healing. Nano Res. 2024;17(8): 7394-7403. [60] CUI H, CUI B, CHEN H, et al. A chitosan-based self-healing hydrogel for accelerating infected wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2023; 11(12):4226-4237. [61] WEI X, LIU C, LI Z, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogel dressings for diabetic wound healing via promoting M2 macrophage-polarization. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;331: 121873. [62] GUPTA A, BRIFFA SM, SWINGLER S, et al. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Curcumin-Cyclodextrins Loaded into Bacterial Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(5):1802-1811. [63] ZHOU L, ZHOU L, WEI C, et al. A bioactive dextran-based hydrogel promote the healing of infected wounds via antibacterial and immunomodulatory. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;291:119558. [64] LI N, LIU W, ZHENG X, et al. Antimicrobial hydrogel with multiple pH-responsiveness for infected burn wound healing. Nano Res. 2023;16(8):11139-11148. [65] QIAO B, WANG J, QIAO L, et al. ROS-responsive hydrogels with spatiotemporally sequential delivery of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs for the repair of MRSA-infected wounds. Regen Biomater. 2024;11: rbad110. [66] XU S, YAN S, YOU J, et al. Antibacterial Micelles-Loaded Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan Composite Hydrogels for Enhanced Wound Repairing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(11): 13563-13572. [67] YANG Y, MA Y, WANG H, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogel dressings with antibacterial and antioxidant for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;280(Pt 2):135939. [68] MAO C, XIANG Y, LIU X, et al. Photo-Inspired Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing Acceleration by Hydrogel Embedded with Ag/Ag@AgCl/ZnO Nanostructures. Acs Nano. 2017;11(9):9010-9021. [69] ZHANG M, CHEN S, ZHONG L, et al. Zn(2+)-loaded TOBC nanofiber-reinforced biomimetic calcium alginate hydrogel for antibacterial wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143:235-242. [70] LI J, WANG Y, YANG J, et al. Bacteria activated-macrophage membrane-coated tough nanocomposite hydrogel with targeted photothermal antibacterial ability for infected wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2021;420:127638. [71] WANG Y, WU Y, LONG L, et al. Inflammation-Responsive Drug-Loaded Hydrogels with Sequential Hemostasis, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Behavior for Chronically Infected Diabetic Wound Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(28): 33584-33599. [72] YANG C, DAWULIETI J, ZHANG K, et al. An injectable antibiotic hydrogel that scavenges proinflammatory factors for the treatment of severe abdominal trauma. Adv Funct Materi. 2022;32(27):2111698. [73] XU J, CHANG L, XIONG Y, et al. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels as Antibacterial/Antioxidant/Anti-Inflammation Multifunctional Dressings for Chronic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024; 13(30):e2401490. [74] WANG X, SONG R, JOHNSON M, et al. An Injectable Chitosan-Based Self-Healable Hydrogel System as an Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Materials (Basel). 2021; 14(20):5956. [75] LI S, DONG S, XU W, et al. Antibacterial Hydrogels. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(5): 1700527. [76] MAKVANDI P, WANG CY, ZARE EN, et al. Metal‐based nanomaterials in biomedical applications: antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity aspects. Adv Funct Mater. 2020; 30(22):1910021. [77] XIE M, GAO M, YUN Y, et al. Antibacterial Nanomaterials: Mechanisms, Impacts on Antimicrobial Resistance and Design Principles. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023; 62(17):e202217345. [78] BUTLER J, HANDY RD, UPTON M, et al. Review of Antimicrobial Nanocoatings in Medicine and Dentistry: Mechanisms of Action, Biocompatibility Performance, Safety, and Benefits Compared to Antibiotics. Acs Nano. 2023;17(8): 7064-7092. [79] ZHAO X, TANG H, JIANG X. Deploying Gold Nanomaterials in Combating Multi-Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Acs Nano. 2022; 16(7):10066-10087. [80] ZHANG M, QIAO X, HAN W, et al. Alginate-chitosan oligosaccharide-ZnO composite hydrogel for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;266:118100. [81] LONG L, HU C, LIU W, et al. Injectable multifunctional hyaluronic acid/methylcellulose hydrogels for chronic wounds repairing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022; 289:119456. [82] DONG H, FENG C, ZHU J, et al. Ultrasmall gold Nanoparticles/Carboxymethyl chitosan composite hydrogel: Tough, restorable, biocompatible antimicrobial dressing for wound healing. Appl MaterToday. 2024;38: 102206. [83] ZHANG E, ZHAO X, HU J, et al. Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8): 2569-2612. [84] SUN X, WANG P, TANG L, et al. Multifunctional Hydrogel Containing Oxygen Vacancy‐Rich WOx for Synergistic Photocatalytic O2 Production and Photothermal Therapy Promoting Bacteria‐Infected Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(52):2411117. [85] XIAO J, ZHOU Y, YE M, et al. Freeze-Thawing Chitosan/Ions Hydrogel Coated Gauzes Releasing Multiple Metal Ions on Demand for Improved Infected Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(6):e2001591. [86] GHOSAL D, MAJUMDER N, DAS P, et al. Enhancing Wound Healing With Sprayable Hydrogel Releasing Multi Metallic Ions: Inspired by the Body’s Endogenous Healing Mechanism. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(32):e2402024. [87] FAN YL, LIU HJ, WANG ZL, et al. A One-Nano MOF-Two-Functions Strategy Toward Self-healing, Anti-inflammatory, and Antibacterial Hydrogels for Infected Wound Repair. Chem Eng J. 2024;497:155037. [88] ZHANG Y, CHEN S, QIN X, et al. A Versatile Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Accelerates Infected Wound Healing via Bacterial Elimination, Antioxidation, Immunoregulation, and Angiogenesis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(19):e2400318. [89] FENG Q, XU J, ZHANG K, et al. Dynamic and Cell-Infiltratable Hydrogels as Injectable Carrier of Therapeutic Cells and Drugs for Treating Challenging Bone Defects. ACS Cent Sci. 2019;5(3):440-450. [90] ZHANG X, QIN M, XU M, et al. The fabrication of antibacterial hydrogels for wound healing. Eur Polym J. 2021;146: 110268. [91] LI Z, YOU S, MAO R, et al. Architecting polyelectrolyte hydrogels with Cu-assisted polydopamine nanoparticles for photothermal antibacterial therapy. Mater Today Bio. 2022;15:100264. [92] LIN X, ZHANG M, LV W, et al. Engineering Carbon Nanotube‐Based Photoactive COF to Synergistically Arm a Multifunctional Antibacterial Hydrogel. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(11):2310845. [93] WEI P, WANG L, XIE F, et al. Strong and tough cellulose–graphene oxide composite hydrogels by multi-modulus components strategy as photothermal antibacterial platform. Chem Eng J. 2022;431:133964. [94] DENG QS, GAO Y, RUI BY, et al. Double-network hydrogel enhanced by SS31-loaded mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles: Symphonic collaboration of near-infrared photothermal antibacterial effect and mitochondrial maintenance for full-thickness wound healing in diabetes mellitus. Bioact Mater. 2023;27:409-428. [95] YUAN Z, WANG T, SHAO C, et al. Bioinspired Green Underwater Adhesive Gelatin‐Tannic Acid Hydrogel With Wide Range Adjustable Adhesion Strength and Multiple Environmental Adaptability. Adv Funct Mater. 2024:2412950. doi:10.1002/adfm.202412950 [96] CHEN X, LAN W, XIE J. Natural phenolic compounds: Antimicrobial properties, antimicrobial mechanisms, and potential utilization in the preservation of aquatic products. Food Chem. 2024;440:138198. [97] PARK J, KIM TY, KIM Y, et al. A Mechanically Resilient and Tissue-Conformable Hydrogel with Hemostatic and Antibacterial Capabilities for Wound Care. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(30):e2303651. [98] CHENG X, LI L, YANG L, et al. All‐Small‐Molecule Dynamic Covalent Hydrogels with Heat‐Triggered Release Behavior for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Advanced Funct Mater. 2022;32(44): 2206201. [99] HE G, ZHOU Y, CHEN X, et al. Preparation of poly (vinyl alcohol)/polydopamine/tannin acid composite hydrogels with dual adhesive, antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Eur Polym J. 2024;205:112708. [100] WANG W, ZHENG J, HONG X, et al. Micro-environment triple-responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel dressings to promote antibacterial activity, collagen deposition, and angiogenesis for diabetic wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(19): 4613-4628. [101] WANG Y, ZHOU C, LI Z, et al. Injectable immunoregulatory hydrogels sequentially drive phenotypic polarization of macrophages for infected wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2024;41:193-206. [102] KIM YE, CHOI SW, KIM MK, et al. Therapeutic Hydrogel Patch to Treat Atopic Dermatitis by Regulating Oxidative Stress. Nano Lett. 2022;22(5):2038-2047. [103] SHEN J, JIAO W, YANG J, et al. In situ photocrosslinkable hydrogel treats radiation-induced skin injury by ROS elimination and inflammation regulation. Biomaterials. 2025;314:122891. [104] WU Y, ZHOU Z, ZHANG M, et al. Hollow manganese dioxide-chitosan hydrogel for the treatment of atopic dermatitis through inflammation-suppression and ROS scavenging. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):432. [105] ZHANG M, DONG Q, YANG K, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels with excellent self-healing capacity and photo-enhanced mechanical properties for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;267(Pt 1):131235. [106] WANG X, SUN X, LEI J, et al. Bioinspired zwitterionic lysine glycopolymers: Enhancing wound repair through microenvironment modulation for bacterial elimination and optimal immunoregulation. Nano Today. 2024;57:102354. [107] SHANGGUAN J, YU F, DING B, et al. Hydrogel-forming viscous liquid in response to ROS restores the gut mucosal barrier of colitis mice via regulating oxidative redox homeostasis. Acta Biomater. 2024;184: 127-143. [108] SU K, DENG D, WU X, et al. On-demand detachable adhesive hydrogel based on dual dynamic covalent cross-linked with NIR/pH dual-responsive properties for diabetic wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2024; 479:147646. [109] GUO Q, YIN T, HUANG W, et al. Hybrid Hydrogels for Immunoregulation and Proangiogenesis through Mild Heat Stimulation to Accelerate Whole‐Process Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(18):e2304536. [110] ZHANG L, MA Y, PAN X, et al. A composite hydrogel of chitosan/heparin/poly (gamma-glutamic acid) loaded with superoxide dismutase for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;180:168-174. [111] LI J, ZHAO M, LIANG J, et al. Hollow Copper Sulfide Photothermal Nanodelivery Platform Boosts Angiogenesis of Diabetic Wound by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(4): 4395-4407. [112] PENA OA, MARTIN P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(8):599-616. [113] HUANG R, ZHANG X, LI W, et al. Suction Cups-Inspired Adhesive Patch with Tailorable Patterns for Versatile Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(17):e2100201. [114] SHAN BH, WU FG. Hydrogel-Based Growth Factor Delivery Platforms: Strategies and Recent Advances. Adv Mater. 2024;36(5): e2210707. [115] LEE Y, LIM S, KIM JA, et al. Development of Thiol-Ene Reaction-Based HA Hydrogel with Sustained Release of EGF for Enhanced Skin Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(11):5342-5352. [116] AN Z, ZHANG L, LIU Y, et al. Injectable thioketal-containing hydrogel dressing accelerates skin wound healing with the incorporation of reactive oxygen species scavenging and growth factor release. Biomater Sci. 2021;10(1):100-113. [117] ZHAO H, HUANG J, LI Y, et al. ROS-scavenging hydrogel to promote healing of bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120286. [118] SIMOSKA O, DUAY J, STEVENSON KJ. Electrochemical Detection of Multianalyte Biomarkers in Wound Healing Efficacy. ACS Sens. 2020;5(11):3547-3557. [119] ZHU Y, ZHANG J, SONG J, et al. A multifunctional pro‐healing zwitterionic hydrogel for simultaneous optical monitoring of pH and glucose in diabetic wound treatment. Adv Funct Mater. 2020; 30(6):1905493. [120] MOSTAFALU P, TAMAYOL A, RAHIMI R, et al. Smart Bandage for Monitoring and Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Small. 2018:e1703509. doi: 10.1002/smll.201703509. [121] HE X, YANG S, LIU C, et al. Integrated Wound Recognition in Bandages for Intelligent Treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(22):e2000941. [122] XU T, SONG Y, GAO W, et al. Superwettable Electrochemical Biosensor toward Detection of Cancer Biomarkers. ACS Sens. 2018;3(1):72-78. [123] YANG X, WANG Y, BYRNE R, et al. Concepts of Artificial Intelligence for Computer-Assisted Drug Discovery. Chem Rev. 2019; 119(18):10520-10594. [124] WANG L, ZHOU M, XU T, et al. Multifunctional hydrogel as wound dressing for intelligent wound monitoring. Chem Eng J. 2022;433:134625. [125] SHAN M, CHEN X, ZHANG X, et al. Injectable Conductive Hydrogel with Self-Healing, Motion Monitoring, and Bacteria Theranostics for Bioelectronic Wound Dressing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(11): e2303876. |
| [1] | 郭宇超, 倪前伟, 尹 晨, 吉格尔·赛义力汗, 高 瞻. 季铵化壳聚糖紧急止血材料:合成、机制与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [2] | 刘宏杰, 牟秋菊, 申玉雪, 梁 飞, 祝丽丽. 金属有机框架/羧甲基壳聚糖-氧化海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆水凝胶促糖尿病感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [3] | 管昱杰, 赵 彬 . 人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [4] | 张 也, 安哲庆, 席 歆, 刘晓妍, 洪 伟, 廖 健. 载唑来膦酸可溶性微针贴片抑制脂多糖诱导破骨细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5115-5124. |
| [5] | 许艺璇, 姚 俊, 刘旭璐, 李新莲, 刘志雄, 张志红. 含万古霉素的猪皮脱细胞外基质水凝胶促进皮肤感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5214-5228. |
| [6] | 刁有录, 高 佳, 潘国庆. 生物募集组织修复材料:调控细胞和因子的迁移及改善组织整合的优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5270-5281. |
| [7] | 徐亚伟, 孟世龙, 张 徐, 汪成杰, 袁一峰, 史晓林, 王 娇, 刘 康. 中药有效成分结合水凝胶修复骨缺损:成功与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5295-5303. |
| [8] | 王洁燕, 姚佳沂, 辛颖童 , 张馨文, 李日旺, 刘大海. 壳聚糖水凝胶载药系统治疗口腔溃疡更安全有效的解决方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5331-5340. |
| [9] | 汪 影, 王雅文, 徐颖婕, 王元非, 吴 桐. 乳液静电纺丝法制备聚己内酯/低分子量褐藻多糖纳米纤维及生物相容性评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 433-442. |
| [10] | 谭凤怡, 谢嘉敏, 潘振锋, 张新旭, 郑泽态, 曾祉莹, 周艳芳. 胶原蛋白联合微针治疗皮肤光老化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 451-458. |
| [11] | 刘晓红, 赵 天, 穆云萍, 冯文金, 吕存声, 张智永, 赵子建, 李芳红. 脱细胞真皮基质水凝胶促进大鼠皮肤创面的愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [12] | 李青山, 李润萌, 高宇阳, 韩 纲, 陈继营, 郭全义. 磁性生物活性玻璃支架的磁热抗肿瘤与促成骨性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(14): 3494-3503. |
| [13] | 王 浩, 何 秦, 王枰稀, 张 骏, 吴治林. 负载去铁胺海藻酸锶水凝胶促进大鼠颅骨损伤的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(14): 3609-3617. |
| [14] | 孔小娟, 谈珍瑜, 雷 磊. miR-424-5p修饰外泌体/泊洛沙姆407水凝胶修复大鼠子宫内膜损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(14): 3626-3635. |
| [15] | 杨 标, 吴中桓, 姜福贵, 何成龙, 李廷栋. 负载无细胞脂肪提取物的导电水凝胶修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(14): 3652-3662. |
水凝胶是一类具有三维网络结构的高分子材料,能够吸收并保持大量的水分,而不溶解于水[8]。多糖基水凝胶因独特的优势在创面敷料领域获得了广泛关注。多糖基水凝胶由天然多糖构成,这些多糖通常具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性。图2 为代表性多糖的结构式,不同类型的多糖具有羟基、羧基、乙酰基、氨基、磺酸基等官能团,可以通过物理相互作用(氢键、配位键、静电相互作用、主客体相互作用等)和化学相互作用产生交联,使材料具有理化性能。
多糖基水凝胶作为创面敷料具有许多优势[9-10](图3):能够与人体组织兼容而不引起明显的免疫反应,有利于创面愈合;具有较高的吸水性,能够吸收创面渗出的分泌物,并保持创面周围的湿润环境;具有抗菌性能,可减少创面在愈合过程中的细菌感染;多糖基水凝胶可以提供柔软的支撑,有助于保护创面免受外界刺激;可用于控制药物的释放,在创面表面提供药物治疗;部分多糖基水凝胶是可生物降解的,可以避免二次手术来移除敷料,减轻患者的痛苦并促进愈合。已有部分多糖基水凝胶(Hyalofill®、Tegaderm™ Hydrogel)应用于临床治疗糖尿病足溃疡,通过物理隔离创面、降低疼痛感,然而这些敷料的功能单一,例如吸收渗液能力较弱、不含抗菌成分无法直接抑制细菌繁殖等,因此迫切需要开发新型多功能水凝胶创面敷料。2020-2024年间,多糖基水凝胶的研究和开发正在逐步增加(图4)。
该文总结用于创面敷料的水凝胶制备方法以及其在创面修复领域的研究进展,为设计和开发性能更优异的多糖基水凝胶提供了理论参考。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年12月进行。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2002年1月至2024年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 检索中国知网、万方及PubMed、Web of Science数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“水凝胶,多糖基水凝胶,可逆共价键,创面敷料,创面修复”为中文检索词检索万方数据库和中国知网,以“Hydrogels,polysaccharide-based hydrogels,reversible covalent bonds,Wound dressings,wound repair”为英文检索词检索PubMed和Web of science 数据库。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著及综述。
1.1.6 人工检索 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以Web of Science数据库检索策略为例,如图5。
1.2 入组标准
纳入标准:①与水凝胶合成有关的文献;②与多糖基水凝胶性质有关的文献;③基于可逆共价键多糖基水凝胶的文献;④多糖基水凝胶制备创面敷料的文献。
排除标准:①与研究不符的文献;②文献过于陈旧及重复的文献;③研究不严谨的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估与资料提取 通过关键词检索得到769篇文献,经过初筛和阅读全文后选择与文章内容相关性高的文章进行讨论,最终纳入125篇文献进行综述。文献筛选流程见图6。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该文专注于探讨多糖基水凝胶创面敷料的制备工艺及其功能,不仅介绍了传统的物理与化学交联技术,还引入了光交联、酶交联等制备手段;以创面愈合过程的各个阶段为研究框架,总结了针对各阶段特点的功能化设计策略,也特别关注了多糖基水凝胶功能化设计的最新进展,并对多糖基水凝胶的潜在应用价值进行了深入分析。综上所述,该综述从制备技术和功能化设计2个关键维度出发,旨在为相关领域的研究者和实践者提供一份详尽的参考资料,从而推动多糖基水凝胶创面敷料的科学研究发展。
3.3 该综述的局限性 尽管该文讲述了多糖基水凝胶创面敷料的研究进展及未来发展方向,但仍存在一些局限性:因主要聚焦于材料性能、功能化发展等方面,未能深入探讨不同类型创面的治疗效果差异,也缺乏具体的临床数据支持;文中提到的生产工艺和药物释放控制等技术的实现仍面临许多技术难题,具体的解决方案和实施路径还没有完全展开;由于创面治疗涉及多方面因素,如患者的个体差异、疾病的复杂性等,该文未能完全涵盖所有潜在影响因素,可能导致某些结论在特定情况下的适用性不足。所以,未来的研究需进一步完善这些方面,才能实现多糖基水凝胶创面敷料的广泛应用。
3.4 该综述的重要意义 由于传统创面敷料难以满足复杂创面愈合过程中的多种需求,发展新型创面敷料至关重要。根据前人研究结果,通过总结不同制备方法和功能化设计可以发现,现阶段多糖基水凝胶创面敷料与其他类型水凝胶相比兼具独特优势和局限性,核心优势在于多糖天然来源的生物相容性和可降解性,能够模拟细胞外基质环境,促进创面湿润愈合,并且通常通过物理交联或温和化学交联形成,降解产物无毒且可被机体吸收,避免了可能残留的化学单体引发的炎症风险。然而,多糖基水凝胶的机械强度普遍较弱,在抗菌性方面,多数多糖缺乏固有抗菌能力,需依赖外源添加抗生素或金属离子。此外,多糖基水凝胶的降解速率受环境因素(如pH值、酶活性)影响较大,可能导致与创面愈合阶段不匹配等。总体而言,多糖基水凝胶在生态友好性和生物安全性上表现突出,但需通过材料改性弥补机械性能与功能缺陷。未来多糖基水凝胶创面敷料的发展,应以创面愈合过程为导向,满足愈合过程的功能需要,真正实现对症下药。该综述能够提供关于多糖基创面敷料的信息,有助于激发新的研究思路,推动技术创新,开发出更智能、更高效的创面敷料。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 应该进一步加强对多糖基水凝胶分子结构、物理化学性质及其与生物体的相互作用机制的研究,通过跨学科合作结合多领域知识,优化水凝胶的力学性能、生物相容性和降解特性,以满足不同创面类型和愈合阶段的需求,从而进一步加强临床转化研究。除此之外,本着环境保护的原则,通过选择可再生、可降解的多糖材料作为原料具有较大的应用前景,还可以通过优化生产工艺降低能耗和废弃物排放,实现资源的循环利用。综上所述,多糖基水凝胶创面敷料未来的发展应注重基础研究、技术创新、临床转化、环境保护等多个方面,为创面护理和医疗健康事业做出更大贡献。
围绕多糖基水凝胶伤口敷料的制备工艺及其功能,首先介绍了传统的物理与化学交联技术,然后以伤口愈合的各个阶段(止血、炎症、增殖、重塑)为轴,总结适应各阶段特点的功能化多糖基水凝胶(止血、抗菌、抗氧化与抗炎、促进组织再生等)的设计策略。此外,对多糖基水凝胶智能化实时监测的最新进展以及智能化设计在多糖基水凝胶伤口敷料中的应用进行了分析。综上所述,该文从制备技术和功能化设计两个维度出发,总结了水凝胶的制备方法与功能需要,旨在为相关领域的研究人员提供参考,从而推动多糖基水凝胶伤口敷料的科学研究发展。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||