中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2033-2013.doi: 10.12307/2026.073
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
沸石基咪唑盐框架8纳米材料的活性氧双向调控:从肿瘤治疗、抗菌到细胞保护
王菘芃,刘玉三,于焕英,高晓丽,徐英江,张晓明,刘 敏
- 滨州医学院附属医院,山东省滨州市 256600
-
收稿日期:2024-12-30接受日期:2025-04-16出版日期:2026-03-18发布日期:2025-07-18 -
通讯作者:刘敏,硕士,主治医师,滨州医学院附属医院,山东省滨州市 256600 张晓明,硕士,主任医师,滨州医学院附属医院,山东省滨州市 256600 -
作者简介:王菘芃,男,1999年生,山东省威海市人,汉族,滨州医学院在读硕士,医师,主要从事口腔修复骨组织工程与改建的相关纳米材料的研究。 刘玉三,男,1986年生,山东省滨州市人,汉族,硕士,副教授,副主任医师,主要从事牙周病学与口腔种植学以及相关纳米材料的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(82200981),项目负责人:徐英江;山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2022QH358),项目负责人:徐英江;山东省泰山学者项目专项资金项目(tsqn202312384),项目负责人:徐英江;山东省医药卫生科技发展计划项目(202308011314),项目名称:牙龈卟啉单胞菌外膜囊泡通过调控miRNAs破坏口腔上皮屏障作用机制的研究,项目负责人:刘敏
Bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanomaterials: from tumor therapy and antibacterial activity to cytoprotection
Wang Songpeng, Liu Yusan, Yu Huanying, Gao Xiaoli, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Min
- Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-30Accepted:2025-04-16Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Liu Min, MS, Attending physician, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China Zhang Xiaoming, MS, Chief physician, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Songpeng, Master candidate, Physician, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China Liu Yusan, MS, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82200981 (to XYJ); Shandong Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR2022QH358 (to XYJ); Shandong Taishan Scholars Project (Special Fund Project), No. tsqn202312384 (to XYJ); Shandong Provincial Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan Project, No. 202308011314 (to LM)
摘要:
文题释义:
沸石基咪唑盐框架8:是一种金属有机框架材料,由锌离子与2-甲基咪唑配位形成,具有典型的沸石拓扑结构,孔径约为3.4 nm,具有高比表面积、良好的热化学稳定性及pH值敏感性,广泛应用于催化、气体分离、生物医药等领域。在生物医学中,沸石基咪唑盐框架8因可降解性和金属离子释放特性可实现细菌捕获、靶向杀菌以及抗炎与组织修复功能。
活性氧动态平衡调控:指在生物系统中通过精确调节活性氧的生成和清除维持其适宜水平的过程。适量活性氧参与细胞信号传导、抗菌及组织修复,但过量活性氧可能引发氧化应激,损伤细胞和组织。动态平衡调控通常通过光催化、抗氧化剂或酶的协同作用实现,广泛应用于抗菌材料开发和再生医学,既可提高抗菌效率又能避免活性氧过量导致的不良反应。
背景:沸石基咪唑盐框架8及其衍生物凭借优异的药物控释能力在组织工程领域展现出广泛的应用潜力。
目的:综述沸石基咪唑盐框架8及其改性材料在活性氧生成与清除中的作用机制,探讨它们在抗肿瘤、抗菌及组织保护领域的应用潜力,分析未来发展方向与挑战。
方法:由第一作者通过中国知网、PubMed等数据库检索2000-2024年相关文献,中文检索关键词为“沸石基咪唑盐框架8,活性氧,抗菌,抗肿瘤,活性氧吸收,活性氧平衡,组织修复”,英文检索关键词为“ZIF-8,ROS,antibacterial,antitumor,ROS absorption,Balance of ROS,Tissue regeneration”,最终筛选69篇高质量文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:通过调控沸石基咪唑盐框架8及其改性材料的带隙结构、优化电子转移效率可显著提升光生载流子的分离与迁移效率,从而增强催化反应性能,提高活性氧的产生效率,实现更高效、更具靶向性的抗肿瘤及抗菌作用;同时,采用抗氧化酶系统或表面改性技术构建的活性氧清除装置,能够精准平衡多余活性氧,实现对细胞的有效保护。这种基于带隙调控与电子转移优化的双向调控机制,为动态管理活性氧生成与清除提供了重要策略,在抗肿瘤、抗菌及组织保护等领域展现出广阔的应用前景。
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-5317-6614(王菘芃)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王菘芃, 刘玉三, 于焕英, 高晓丽, 徐英江, 张晓明, 刘 敏. 沸石基咪唑盐框架8纳米材料的活性氧双向调控:从肿瘤治疗、抗菌到细胞保护[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2033-2013.
Wang Songpeng, Liu Yusan, Yu Huanying, Gao Xiaoli, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Min. Bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanomaterials: from tumor therapy and antibacterial activity to cytoprotection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2033-2013.
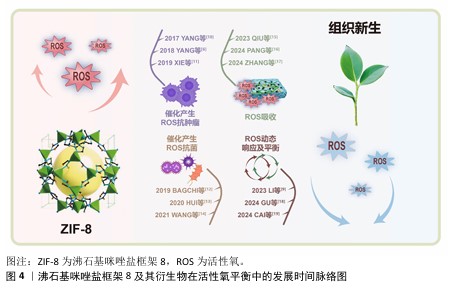
2023年和2024年出现了较多新研究,如QIU等[15]、PANG等[16]、ZHANG等[17]研究活性氧吸收,LI等[9]、GU等[18]、CAI等[19]研究活性氧动态响应及平衡。这些研究借助更为精准的方式来调控活性氧水平,可有效地降低对正常组织所造成的损伤,不过由于其制备过程较为复杂、活性较低以及所处环境复杂等因素,在一定程度上对这些材料的应用形成了限制。ZIF-8及其衍生物在活性氧平衡中的发展时间脉络图,见图4。
2.2 ZIF-8及其衍生物于活性氧生成中的调控机制 ZIF-8作为一种金属有机框架材料,有结构稳定、比表面积较高以及孔隙率较大等特点,在生物医学和环境治理领域有着较为广泛的应用潜力[20]。在活性氧产生这一方面,ZIF-8呈现出独特优势,于特定环境及条件下,ZIF-8及其衍生物可产生活性氧,在抗肿瘤、抗菌等应用里呈现出一定效力。接下来会详细介绍ZIF-8在酸性条件下的降解以及金属离子与光催化的协同提高机制,探讨其在医学领域的应用(表1)。
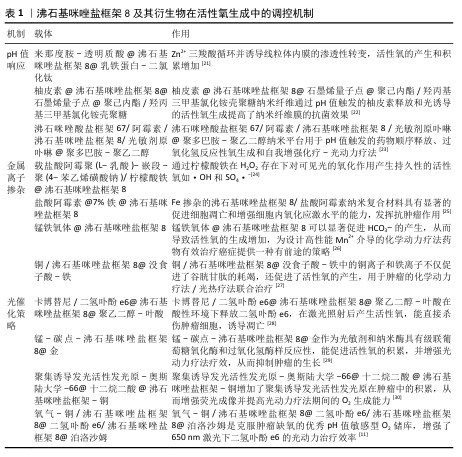
2.2.1 pH值响应机制与酸性环境中的活性氧催化提高 ZIF-8有pH值响应性,在酸性环境里会发生降解,于中性条件下呈现出高稳定性,这意味着ZIF-8可用于递送药物,保证在酸性肿瘤微环境中实现靶向释放,这些特性提高了肿瘤部位的局部药物浓度,提升了抗肿瘤作用[31]。Zn2+的释放在活性氧生成过程中发挥着关键作用,Zn2+抑制三羧酸循环,诱导线粒体内膜的渗透性转变,使得活性氧的产生和积累增多[21],随着ZIF-8在酸性环境中的逐步降解,Zn2+的持续释放使得活性氧的产生具备持效性和持续性,进一步增强了材料在抗肿瘤和抗菌治疗中的效能。
2.2.2 金属离子掺杂对活性氧生成的协同效应 研究人员为了提升ZIF-8生成活性氧的能力,采用金属离子掺杂介导的芬顿反应以及光催化协同产生活性氧等方式来改良其性能,这些办法提升了ZIF-8在肿瘤治疗与抗菌应用中的活性。通过引入金属离子比如铁、铜等,可有效提高ZIF-8生成活性氧的能力。比如Fe掺杂的ZIF-8纳米递送系统,金属有机骨架里丰富的Fe2+/Fe3+介导的芬顿反应可有效产生·OH[32],这种掺杂方法在提高活性氧生成效率同时还提供了环境响应性的靶向治疗手段,有较高的生物应用价值。另外Fe掺杂的ZIF-8纳米递送系统借助共载葡萄糖氧化酶、L-精氨酸和盐酸阿霉素呈现出协同效应以及叶酸受体靶向,该系统依靠级联反应/铁凋亡机制诱导肿瘤细胞死亡[33]。然而近年研究显示,铁凋亡的扩散可能会带来潜在风险,比如,癌细胞依靠铁凋亡产生的脂质过氧化物以及其他介质可能会扩散到正常组织,引发恶病质或者抗癌治疗的不良反应[34]。金属离子掺杂在提高ZIF-8生成活性氧能力方面有显著优势,但其在不同细胞系和微环境中的差异性响应以及潜在的生物安全性问题仍需研究与优化。
2.2.3 光催化策略提升活性氧产生的可操纵性 将ZIF-8与光敏化材料像姜黄素、二氢卟酚e6等复合,在光照下能较大提高活性氧生成,实现更强的抗肿瘤和抗菌效果。因为独特的多孔结构,ZIF-8的粒径可调节、化学表面能改变,可以为光敏化材料提供良好的负载平台[35]。例如负载卡博替尼和二氢卟酚e6的pH值敏感性纳米颗粒卡博替尼/二氢卟酚e6@ZIF-8@聚乙二醇-叶酸,在酸性环境下释放卡博替尼和二氢卟酚e6,二氢卟酚e6在激光照射后产生活性氧,直接杀伤肿瘤细胞,诱导凋亡[28],这种光催化机制让ZIF-8复合材料依靠对光源的控制实现靶向性和特异性,提高了治疗效果并减少不良反应。然而传统光敏剂如卟啉衍生物和二氢卟酚e6等对于临床应用存在几个缺点,比如,二氢卟酚e6在水性环境中是疏水性的,它聚集的趋势限制了活性氧的产生;传统光敏剂的光动力疗法需要长期使用,因为光敏剂具有有限的肿瘤递送能力和低的癌细胞特异性,并且它们凭借全身给药扩散到全身[36]。未来的研究应探讨不同光敏化材料在不同细胞系中的活性氧生成机制,以优化ZIF-8的光催化策略。

2.3 ZIF-8在肿瘤治疗与抗菌领域的应用探索 鉴于ZIF-8在酸性环境里的降解特性,以及金属离子和光催化提高的活性氧生成能力,其在抗肿瘤和抗菌治疗方面有关键的应用价值。ZIF-8的酸敏性以及活性氧生成能力,使它于肿瘤治疗中成为颇具潜力的候选材料。ZIF-8可被紫外光激发产生超氧自由基(·O2-),以此达成光催化驱动的光动力疗法[37]。与光敏化剂相结合的ZIF-8复合材料可用于光动力治疗,借助光照刺激在肿瘤部位生成大量活性氧,对肿瘤细胞实施精准杀伤。这种酸敏性降解与光敏化催化相结合的策略,提高了治疗的选择性,降低了对周围正常细胞的损害,使得ZIF-8成为一种很有前景的肿瘤治疗材料。
ZIF-8的活性氧生成能力在抗菌治疗中也展现出极高的应用价值。在酸性微环境中,ZIF-8易于降解并释放出Zn2+,ZIF-8中存在的Zn2+是对人体有益的元素,并且配体二甲基咪唑表现出优异的抗菌性能。传统的ZIF-8具有强大的光诱导杀菌活性,在光的存在下可产生活性氧,发挥优异的抗菌性能[38-39]。如前文所说,通过掺杂铁、铜等过渡金属离子,ZIF-8可以在感染部位产生更高浓度的活性氧,从而增强抗菌效果。光敏化的ZIF-8复合材料,例如大蒜素@ZIF-8/银纳米颗粒多功能纳米平台,具有pH值响应、活性氧清除、抗炎和抗菌特性,可促进血管生成和感染伤口的愈合[16]。这种酸性条件和光催化增强的抗菌效果使得ZIF-8在医疗器械、创口敷料和植入物涂层中具有潜在的应用价值,有望用于解决医疗领域的感染控制问题。

2.4 ZIF-8在活性氧清除中的动态调节 ZIF-8不仅在活性氧生成中展现出优势,还在活性氧清除方面具有良好的应用潜力。通过ZIF-8制备的纳米酶在清除活性氧方面表现出抗氧化特性,还可以通过对ZIF-8进行改性来发挥抗氧化功能,从而减轻氧化应激对细胞的损伤,在细胞保护和抗氧化治疗方面具有良好的应用前景,详见表2。
2.4.1 纳米酶的活性氧清除机制 ZIF-8在清除活性氧方面存在另一关键机制是利用其制备的锌基纳米酶,这些纳米酶可有效地清除病变局部过量积累的活性氧,对提高细胞抗氧化防御能力起到了关键作用。当ZIF-8在中性或弱酸性条件下逐步降解时会释放出Zn2+,这些Zn2+可支撑纳米酶的催化活性,激活细胞内的抗氧化酶系统,比如超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶,以此提高组织抗氧化能力。纳米酶是一类有酶样活性的纳米材料,可模拟“天然酶”的功能,特别是超氧化物歧化酶类似物和过氧化氢酶类似物,它们拥有清除活性氧的能力[45]。纳米酶与ZIF-8相结合,极大地提高了材料清除活性氧的能力,在细胞保护和抗氧化防护领域呈现出独特的应用价值。与天然酶相比,ZIF-8纳米酶有高稳定性、易于制备、成本低等优势,同时ZIF-8中Zn2+的逐渐释放提升了纳米酶的生物活性和催化性能。
2.4.2 表面功能化材料对活性氧平衡的精准调控 通过对ZIF-8的改性(例如纳米颗粒改性和载体的改性)可实现活性氧的清除,例如在ZIF-8表面涂覆改性材料(如聚多巴胺)实现活性氧的清除。聚多巴胺具有令人满意的稳定性、生物相容性、生物降解性和优异的黏附性能,可以黏附到各种表面以进一步修饰纳米颗粒。聚多巴胺基材料在体外和体内清除多种活性氧方面都表现出更大的前景[46]。利用聚多巴胺的固有性质,聚多巴胺修饰的纳米颗粒可以有效递送化疗药物并产生协同抗肿瘤治疗效果[47]。
2.4.3 载体改性实现活性氧清除的长效性 ZIF-8很难单独用于抗氧化治疗,因为纳米颗粒释放迅速,不能在肿瘤微环境或细菌感染中维持很长时间。水凝胶敷料因良好的生物相容性、可生物降解性、高载药率和优异的控释能力[48],可以作为具有持续释放行为的载体用于肿瘤或抗菌治疗。有研究用聚多巴胺-ZIF-8纳米颗粒制备功能纳米复合水凝胶,具有优异的抗氧化、抗炎和光热协同抗菌能力,通过缓慢释放的Zn2+促进细胞迁移、血管生成和M2巨噬细胞的生成,从而增强了免疫调节能力;此外,复合水凝胶能够消除细菌感染、清除组织活性氧、促进血管再生和创面愈合,在慢性细菌感染创面中具有极好的应用前景[19]。

2.5 ZIF-8在细胞保护与抗氧化治疗中的潜在应用
细胞保护:ZIF-8的活性氧清除机制使它在细胞保护,尤其是神经保护和心血管保护方面展现出巨大潜力。在心血管疾病中,如心肌梗死,活性氧水平升高所产生的内在和复杂的微环境导致心肌细胞凋亡、大量血管细胞死亡、过度炎症浸润和纤维化。负载ZIF-8的聚乙烯醇基水凝胶通过清除活性氧和抑制细菌感染来缓解免疫应答的失衡,调节受损的微环境,该水凝胶表现出较高的活性氧去除效率,对细胞具有良好的保护作用[15]。
抗氧化剂:ZIF-8作为抗氧化剂有重要的应用潜力,在因氧化应激刺激引发的神经系统疾病方面,像结肠黏膜中活性氧和氮类物质过度表达的情况,会加快炎症性肠病的发展进程,对黏膜及其屏障造成破坏。负载锌离子和单宁酸的ZIF-8纳米颗粒里的锌离子-单宁酸纳米颗粒拥有广泛的自由基清除能力,其中涉及清除O2??和NO的能力,作为一种抗氧化剂可有效地去除活性氧和氮,可用于治疗炎症性肠病[17]。

2.6 改性ZIF-8材料在双向活性氧调控中的创新进展 ZIF-8材料凭借其独特的结构以及可调控的活性,在活性氧调控中呈现出双重作用。借助对ZIF-8进行改性,掺杂金属离子、复合光敏化材料以及表面功能化等方式,可更为精准地控制其在不同条件下的活性氧生成和清除能力,拓宽其在抗肿瘤、抗菌、神经保护和抗氧化治疗等领域的应用潜力[49-51]。接下来将从多金属掺杂、光敏化复合材料以及功能化表面改性这三个方面详细探讨改性ZIF-8材料在活性氧调控中的双重作用。
2.6.1 金属/金属氧化物掺杂对活性氧动态调控的优化 金属离子掺杂是提升ZIF-8材料在活性氧调控中双重作用的一种有效方法。通过引入不同种类的金属离子,ZIF-8复合材料可以实现更高的活性氧生成效率或更强的活性氧清除能力,因而适应于多种生物医学需求[52]。
铁和铜掺杂增强活性氧生成:将铁(Fe)或铜(Cu)掺杂到ZIF-8结构中能够增强它在芬顿反应中的催化作用,从而显著提高活性氧的产生效率。ZIF-8在肿瘤的酸性微环境中裂解后释放Zn2+,利用细胞内离子平衡和活性氧激活共同诱导细胞热下垂和免疫治疗。Fe、Cu掺杂的双通道纳米反应器金-硒化铜@ZIF-8@紫红素18纳米颗粒,它靶向肿瘤相关分子模式并在肿瘤微环境内释放Zn2+和活性氧。ZIF-8独特的多孔性和生物响应特性可以保护金-硒化铜的活性位点,促进Cu2+向Cu+的转化产生类芬顿反应,在H2O2自给环境中循环产生大量活性氧,并且Zn2+和活性氧的共同作用能增强肿瘤微环境的免疫原性,有效触发抗原特异性免疫反应[53]。然而,Fe和Cu掺杂的ZIF-8在活性氧生成中的表现也存在一定的局限性,例如,掺杂过量的铁可导致铁死亡途径参与细胞内活性氧代谢并加剧脂质过氧化,癌细胞通过铁凋亡产生的脂质过氧化物和其他介质可能会导致恶病质或抗癌治疗的不良反应;Cu2+的细胞毒性(肝细胞和肾细胞)也在一定程度上限制了Cu掺杂ZIF-8复合材料的应用[54]。
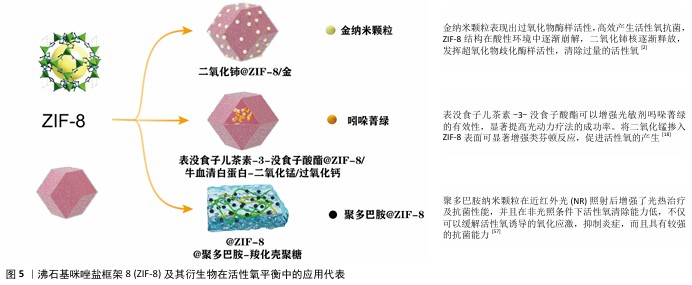
铈(Ce)掺杂增强活性氧清除能力:为了增强ZIF-8的抗氧化能力,可引入具有抗氧化特性的二氧化铈掺杂提供额外的抗氧化功能,清除体内多余的活性氧。Ce、Au掺杂一种核壳结构的纳米酶二氧化铈@ZIF-8/金,能够自发激活活性氧产生和清除功能,实现杀菌、消炎、促进伤口愈合等多方面功能。壳层上的金纳米颗粒表现出高效的过氧化物酶样活性,产生活性氧以杀死细菌;同时,ZIF-8内的二氧化铈核心封装提供了暂时限制二氧化铈纳米颗粒超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化氢酶样活性的密封,这两种功能自动持续地调节活性氧水平平衡,最终达到杀灭细菌、减轻炎症、促进伤口愈合的功能,这种创新的活性氧自发调节剂在抗菌剂和治疗领域具有革命性的潜力[2]。然而,铈掺杂的ZIF-8在活性氧生成方面的能力较弱,多用于清除过多活性氧的炎症治疗和促进伤口愈合,可能无法高效满足需要高活性氧生成的抗肿瘤治疗。
2.6.2 光敏化复合策略在活性氧生成与清除中的应用
表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯与ZIF-8复合:表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯是一种天然化合物,具有有效促进伤口愈合和强效抗炎作用,可增强光敏剂的效力,显著提高光动力疗法成功率,然而它的应用受到生物利用度低和不稳定性的影响。近年来,通过将表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯加入ZIF-8中是一种有前景的解决方案。开发一种新型非抗生素治疗剂表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯@ZIF-8/牛血清白蛋白-二氧化锰/过氧化钙,在该系统中CaO2缓解缺氧,而ZIF-8能够靶向释放表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯并促进光动力疗法和化疗动力学疗法抗菌治疗,显著提高细胞内活性氧和H2O2水平,抑制细菌,以减少炎症并促进伤口愈合。这一光敏化ZIF-8复合材料通过利用光动力疗法和化学动力疗法的协同作用来发挥抗炎作用,为感染伤口愈合提供有效的补救措施[18]。
阿霉素同二氧化铈复合:阿霉素作为一种广谱蒽环类抗生素,是乳腺癌治疗的常用药物之一。有一种负载阿霉素的ZIF-8@二氧化铈@甲基丙烯酰明胶可注射水凝胶,一方面借助阿霉素在肿瘤部位的pH值敏感性释放,另一方面依靠二氧化铈发挥超氧化物歧化酶以及过氧化氢酶样活性,确保有效根除残留肿瘤细胞并且减轻氧化应激,这种复合材料呈现出有效的局部肿瘤抑制以及促伤口愈合的作用[42]。不过阿霉素对正常细胞同样存在毒性作用,会引发不可逆的心脏毒性,这在一定程度上对负载阿霉素复合材料的应用形成了限制。
2.6.3 表面功能化改性实现环境响应性调控 在ZIF-8表面进行功能化修饰可以赋予它更为精准的活性氧调控能力。通过表面修饰抗氧化分子或控释材料[55],可以在不同条件下调节ZIF-8的抗氧化或促氧化作用;在ZIF-8表面修饰抗氧化酶或抗氧化分子,如聚多巴胺、超氧化物歧化酶等,可以增强它的抗氧化效果,这种修饰方式能够在炎症或氧化应激环境中快速清除多余的活性氧,减少对正常细胞的损伤。将超氧化物歧化酶和四氧化三铁纳米颗粒包封在ZIF-8纳米颗粒中,在脊髓炎症反应期间可以在弱酸性炎症环境中降解以释放负载的超氧化物歧化酶和四氧化三铁纳米颗粒,然后被炎症细胞内吞,之后炎症细胞产生的活性氧通过超氧化物歧化酶和四氧化三铁介导的级联催化反应转化为H2O2和O2,从而减少胶质细胞的氧化损伤,减轻中枢致敏[56]。
为了更有效地控制Zn2+的释放,可借助于在ZIF-8表面引入控释材料的方式来达成Zn2+的缓慢释放目的。控释修饰可强化ZIF-8在肿瘤以及感染部位的靶向效果,还可达成活性氧的精准调控。聚多巴胺修饰的ZIF-8表面提升了ZIF-8的水稳定性,还提升了ZIF-8的光催化以及光热性能[57],这种控释修饰为ZIF-8的精确调控开辟了新的途径,在癌症与感染的治疗方面有关键的应用价值。ZIF-8及其衍生物在活性氧平衡中的应用代表,见图5。
2.7 未来发展方向和挑战 ZIF-8及其改性材料在活性氧调控方面有双重作用,这使得它们在抗肿瘤、抗菌、抗氧化等生物医学应用领域呈现出相当大的潜力。不过在推进ZIF-8的临床应用进程中,仍要克服一系列挑战,通过发展相关技术来达成它在复杂生物环境里的精确调控。下面会从精准调控机制、生物相容性与安全性、多功能复合材料开发这三个方面探讨ZIF-8的未来发展方向以及面临的挑战。
2.7.1 精准调控机制 达成ZIF-8及其改性材料对活性氧产生以及清除的精准调控是未来研究的关键方向之一。ZIF-8材料有多功能性,这让它在不同环境中能表现出抗氧化或者促氧化特性,这种双重功能赋予了材料多样的应用前景,但也带来了控制难度,尤其是在复杂的生物环境中,ZIF-8需要在不同组织以及病理条件下达成特定的活性氧调节,这对材料的响应机制提出了更高要求。针对这方面的研究可聚焦于对ZIF-8在不同环境条件(如pH值、氧气浓度、光催化、金属离子浓度等)下的响应特性展开深入分析,探索材料在不同微环境中的稳定性以及其对活性氧的调控效率。比如在光动力学治疗中,焦脱镁叶绿素结合的Mn3O4纳米酶可清除正常组织中的活性氧,还可在肿瘤微环境中产生活性氧[9]。在光动力疗法或者光热疗法的帮助下,纳米二氧化铈和二硫化钼-二氧化铈纳米材料也可用于提高抗菌和抗氧化活性[58-59],这些进展为ZIF-8在不同环境条件下的响应提供了新方向。凭借计算模拟与实验研究相结合的办法,建立不同因素对ZIF-8活性氧调控作用的影响模型,设计出可在多种生物条件下保持稳定且有选择性的ZIF-8复合材料。
2.7.2 生物相容性与安全性 将ZIF-8运用到体内治疗时其生物相容性与安全性是急需关注的问题[60]。由2-甲基咪唑和锌离子构建的ZIF-8在水性以及碱性介质里有化学稳定性,然而其分解产物(如Zn2+)在不同浓度情况下或许会对细胞与组织产生一定毒性[61]。尽管有一些论文说明了其他金属-有机骨架材料在体内的生物安全性,不过评估ZIF-8在哺乳动物体内生物相容性的严格研究尚未完成[62],保证ZIF-8在不同应用条件下长期使用时的生物安全性,是临床应用里的一项关键挑战[61]。未来的研究可通过比较具有类似生物医学功能的纳米材料在组成、尺寸相似性和生物学应用等的生物安全性,开发出更安全且更有效的纳米材料用于各类生物医学领域[63]。
2.7.3 多功能复合材料开发 将ZIF-8与其他纳米材料结合开发具备多重响应性的智能复合材料,是实现特定条件下活性氧精准调控的重要途径。通过引入光敏化材料、温度响应材料、pH值敏感材料等,可以显著增强ZIF-8在不同条件下的反应效率和选择性,进而在多种生物医学应用中实现更为精确的活性氧调控。例如,将ZIF-8与光敏材料姜黄素复合,可以在紫外光或近红外光照射下激活材料的活性氧生成,应用于光动力治疗中[64]。将ZIF-8与聚多巴胺、二氧化铈结合,在近红外光照射下,聚多巴胺由于良好的光-热转换效率而有效清除活性氧并导致发炎区域的温度升高;ZIF-8的酸响应性骨架塌陷以释放包封的二氧化铈,释放出来的氧化铈发挥过氧化氢酶样活性,借助分解在炎症部位高度表达的H2O2来产生氧气,以此缓解缺氧状况,达成肿瘤的协同治疗,可在肿瘤区域的微环境温度产生变化时,调节活性氧的释放效率,实现靶向肿瘤治疗[65]。借助复合pH值敏感材料,可让ZIF-8在酸性肿瘤微环境里降解并产生活性氧,而在中性条件下呈现出抗氧化效果,减少对正常细胞的影响。多功能复合材料的设计还可覆盖调节药物释放速率的功能,让ZIF-8复合材料可在体内长时间保持稳定的药效[66]。这一策略在开发个性化治疗方案方面有着关键作用,通过控制光、pH值、温度等条件,实现多重响应的精准活性氧调控,会提升ZIF-8的治疗效果和适用性。

| [1] SIES H, BELOUSOV VV, CHANDEL NS, et al. Defining roles of specific reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cell biology and physiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(7):499-515. [2] ZHOU X, ZHOU Q, HE Z, et al. ROS Balance Autoregulating Core–Shell CeO2@ZIF-8/Au Nanoplatform for Wound Repair. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024;16(1):156. [3] LIU J, HAN X, ZHANG T, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: from mechanism to therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2023;16(1):116. [4] ZHANG W, LIANG L, YUAN X, et al. Intelligent dual responsive modified ZIF-8 nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Mater Design. 2021;209:109964. [5] HE L, HUANG G, LIU H, et al. Highly bioactive zeolitic imidazolate framework-8–capped nanotherapeutics for efficient reversal of reperfusion-induced injury in ischemic stroke. Sci Adv. 2020;6(12):eaay9751. [6] YANG C, XU J, YANG D, et al. ICG@ZIF-8: one-step encapsulation of indocyanine green in ZIF-8 and use as a therapeutic nanoplatform. Chin Chem Lett. 2018;29(9): 1421-1424. [7] ZHONG Y, YANG Y, XU Y, et al. Design of a Zn-based nanozyme injectable multifunctional hydrogel with ROS scavenging activity for myocardial infarction therapy. Acta Biomater. 2024;177:62-76. [8] RAN B, RAN L, WANG Z, et al. Photocatalytic antimicrobials: principles, design strategies, and applications. Chem Rev. 2023;123(22): 12371-12430. [9] LI M, HUO L, ZENG J, et al. Switchable ROS Scavenger/Generator for MRI‐Guided Anti‐Inflammation and Anti‐Tumor Therapy with Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy and Reduced Side Effects. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(5):2202043. [10] YANG D, YANG G, GAI S, et al. Multifunctional theranostics for dual-modal photodynamic synergistic therapy via stepwise water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(8):6829-6838. [11] XIE Z, LIANG S, CAI X, et al. O2 -Cu/ZIF-8@Ce6/ZIF-8@F127 composite as a tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoplatform with enhanced photo-/chemodynamic antitumor efficacy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(35):31671-31680. [12] BAGCHI D, BHATTACHARYA A, DUTTA T, et al. Nano MOF entrapping hydrophobic photosensitizer for dual-stimuli-responsive unprecedented therapeutic action against drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2019;2(4):1772-1780. [13] HUI S, LIU Q, HUANG Z, et al. Gold nanoclusters-decorated zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with reactive oxygen species generation for photoenhanced antibacterial study. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020;31(10): 2439-2445. [14] WANG M, NIAN L, CHENG Y, et al. Encapsulation of colloidal semiconductor quantum dots into metal-organic frameworks for enhanced antibacterial activity through interfacial electron transfer. Chem Eng J. 2021;426:130832. [15] QIU L, OUYANG C, ZHANG W, et al. Zn-MOF hydrogel: regulation of ROS-mediated inflammatory microenvironment for treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21(1):163. [16] PANG Y, ZHAO M, XIE Y, et al. Multifunctional Ac@ZIF-8/AgNPs nanoplatform with pH-responsive and ROS scavenging antibacterial properties promotes infected wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2024;489:151485. [17] ZHANG C, LI Q, XING J, et al. Tannic acid and zinc ion coordination of nanase for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease by promoting mucosal repair and removing reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Acta Biomater. 2024;177:347-360. [18] GU Y, YOU Y, YANG Y, et al. Multifunctional EGCG@ZIF-8 Nanoplatform with Photodynamic Therapy/Chemodynamic Therapy Antibacterial Properties Promotes Infected Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(38):50238-50250. [19] CAI J, LIU S, ZHONG Q, et al. Multifunctional PDA/ZIF8 based hydrogel dressing modulates the microenvironment to accelerate chronic wound healing by ROS scavenging and macrophage polarization. Chem Eng J. 2024;487:150632. [20] WANG Y, YAN J, WEN N, et al. Metal-organic frameworks for stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2020;230:119619. [21] PANDEY A, KULKARNI S, VINCENT AP, et al. Hyaluronic acid-drug conjugate modified core-shell MOFs as pH responsive nanoplatform for multimodal therapy of glioblastoma. Int J Pharm. 2020;588:119735. [22] ZOU Y, WENG J, QIN Z, et al. Metal–organic framework- and graphene quantum dot-incorporated nanofibers as dual stimuli-responsive platforms for day/night antibacterial bio-protection. Chem Eng J. 2023;473:145365. [23] REN SZ, WANG B, ZHU XH, et al. Oxygen self-sufficient core–shell metal–organic framework-based smart nanoplatform for enhanced synergistic chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(22):24662-24674. [24] LEI Z, JU Y, LIN Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species synergistic pH/H2O2 -responsive poly( l -lactic acid)- block -poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate)/citrate-Fe(III)@ZIF-8 hybrid nanocomposites for controlled drug release. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2019; 2(8):3648-3658. [25] ZHONG Y, PENG Z, PENG Y, et al. Construction of Fe-doped ZIF-8/DOX nanocomposites for ferroptosis strategy in the treatment of breast cancer. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(27):6335-6345. [26] DONG MJ, LI W, XIANG Q, et al. Engineering Metal–Organic Framework Hybrid AIEgens with Tumor-Activated Accumulation and Emission for the Image-Guided GSH Depletion ROS Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(26):29599-29612. [27] YANG P, LIU S, CHEN Z, et al. Proton nanomodulators for enhanced Mn2+-mediated chemodynamic therapy of tumors via HCO3− regulation. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024;22(1):670. [28] KONG J, LAI J, WANG M, et al. A glutathione-consuming bimetallic nano-bomb with the combination of photothermal and chemodynamic therapy for tumors: an in vivo and in vitro study. Int J Nanomed. 2024;19:8541-8553. [29] JIA W, JIN B, XU W, et al. pH-Responsive and Actively Targeted Metal–Organic Framework Structures for Multimodal Antitumor Therapy and Inhibition of Tumor Invasion and Metastasis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(43):50069-50082. [30] LUO T, YANG H, WANG R, et al. Bifunctional cascading nanozymes based on carbon dots promotes photodynamic therapy by regulating hypoxia and glycolysis. ACS Nano. 2023;17(17):16715-16730. [31] ZHAO S, CHEN M, YU Z, et al. Biomimetic cytomembrane-coated ZIF-8-loaded DMDD nanoparticle and sonodynamic co-therapy for cancer. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(18):971-971. [32] DIXON SJ, STOCKWELL BR. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(1):9-17. [33] LI G, LU X, ZHANG S, et al. Multi-Enzyme Cascade-Triggered Nitric Oxide Release Nanoplatform Combined with Chemo Starvation-like Therapy for Multidrug-Resistant Cancers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(26):31285-31299. [34] NISHIZAWA H, MATSUMOTO M, CHEN G, et al. Lipid peroxidation and the subsequent cell death transmitting from ferroptotic cells to neighboring cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):332. [35] YANG RG, FU YM, WANG HN, et al. ZIF-8/covalent organic framework for enhanced CO2 photocatalytic reduction in gas-solid system. Chem Eng J. 2022;450:138040. [36] BAE I, KIM T G, KIM T, et al. Phenethyl isothiocyanate-conjugated chitosan oligosaccharide nanophotosensitizers for photodynamic treatment of human cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22):13802. [37] LI C, YE J, YANG X, et al. Fe/Mn Bimetal-Doped ZIF-8-Coated Luminescent Nanoparticles with Up/Downconversion Dual-Mode Emission for Tumor Self-Enhanced NIR-II Imaging and Catalytic Therapy. ACS Nano. 2022;16(11):18143-18156. [38] WU B, FU J, ZHOU Y, et al. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Chemo-Photothermal Combinational System for Precise, Rapid, and Efficient Antibacterial Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(9):463. [39] SHEN B, WANG Y, WANG X, et al. A Cruciform Petal-like (ZIF-8) with Bactericidal Activity against Foodborne Gram-Positive Bacteria for Antibacterial Food Packaging. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14): 7510. [40] GUO C, WANG Y, LIU H, et al. A refractory wound healing hydrogel with integrated functions of photothermal anti-infection, superoxide dismutase mimicking activity, and intelligent infection management. Mater Des. 2022;224:111280. [41] LI Q, FENG R, CHANG Z, et al. Hybrid biomimetic assembly enzymes based on ZIF-8 as “intracellular scavenger” mitigating neuronal damage caused by oxidative stress. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:991949. [42] ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, CHEN H, et al. Injectable hydrogel with doxorubicin-loaded ZIF-8 nanoparticles for tumor postoperative treatments and wound repair. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):9983. [43] HUANG E, LI H, HAN H, et al. Polydopamine-coated kaempferol-loaded MOF nanoparticles: a novel therapeutic strategy for postoperative neurocognitive disorder. Int J Nanomed. 2024;19:4569-4588. [44] GONG J, WANG H, XIE C, et al. A multifunctional injectable hydrogel for boosted diabetic wound healing assisted by Quercetin-ZIF system. Chem Eng J. 2024; 495:153425. [45] ZHANG Y, JIN Y, CUI H, et al. Nanozyme-based catalytic theranostics. RSC Adv. 2020;10(1):10-20. [46] BAO X, ZHAO J, SUN J, et al. Polydopamine Nanoparticles as Efficient Scavengers for Reactive Oxygen Species in Periodontal Disease. ACS Nano. 2018;12(9):8882-8892. [47] YIN X, RAN S, CHENG H, et al. Polydopamine-modified ZIF-8 nanoparticles as a drug carrier for combined chemo-photothermal osteosarcoma therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;216:112507. [48] HUANG S, HONG X, ZHAO M, et al. Nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;7(3): e10315. [49] MENG X, JIA K, SUN K, et al. Smart responsive nanoplatform via in situ forming disulfiram-copper ion chelation complex for cancer combination chemotherapy. Chem Eng J. 2021;415:128947. [50] WANG J, MA X, CHEN M, et al. Prussian blue@zeolitic imidazolate framework composite toward solar-triggered biodecontamination. Chem Eng J. 2023;452:138562. [51] ZHOU H, LI Z, JING S, et al. Repair spinal cord injury with a versatile anti-oxidant and neural regenerative nanoplatform. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024;22(1):351. [52] LI R, CHEN T, LU J, et al. Metal–organic frameworks doped with metal ions for efficient sterilization: Enhanced photocatalytic activity and photothermal effect. Water Res. 2023;229:119366. [53] YAN X, CHEN C, REN Y, et al. A dual-pathway pyroptosis inducer based on Au–Cu2-xSe@ZIF-8 enhances tumor immunotherapy by disrupting the zinc ion homeostasis. Acta Biomater. 2024; 188:329-343. [54] MAVIL-GUERRERO E, VAZQUEZ-DUHALT R, JUAREZ-MORENO K. Exploring the cytotoxicity mechanisms of copper ions and copper oxide nanoparticles in cells from the excretory system. Chemosphere. 2024;347:140713. [55] FORMAN HJ, ZHANG H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(9):68-709. [56] LING Y, NIE D, HUANG Y, et al. Antioxidant Cascade Nanoenzyme Antagonize Inflammatory Pain by Modulating MAPK/p‐65 Signaling Pathway. Adv Sci. 2023;10(12):2206934. [57] WANG X, REN M, WANG N, et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8@polydopamine decorated carboxylated chitosan hydrogel with photocatalytic and photothermal antibacterial activity for infected wound healing. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024;675:1040-1051. [58] SUN Y, SUN X, LI X, et al. A versatile nanocomposite based on nanoceria for antibacterial enhancement and protection from aPDT-aggravated inflammation via modulation of macrophage polarization. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120614. [59] MA T, ZHAI X, HUANG Y, et al. A Smart Nanoplatform with Photothermal Antibacterial Capability and Antioxidant Activity for Chronic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(13):2100033. [60] WANG Q, SUN Y, LI S, et al. Synthesis and modification of ZIF-8 and its application in drug delivery and tumor therapy. RSC Adv. 2020;10(62):37600-37620. [61] HOOP M, WALDE CF, RICCÒ R, et al. Biocompatibility characteristics of the metal organic framework ZIF-8 for therapeutical applications. Appl Mater Today. 2018;11:13-21. [62] KUMARI S, HOWLETT TS, EHRMAN RN, et al. In vivo biocompatibility of ZIF-8 for slow release via intranasal administration. Chem Sci. 2023;14(21):5774-5782. [63] MAO Y, WANG L, XU Z, et al. Developing a Selection Framework for Zinc Ion-Based Biomaterial Design: Guided by the Biosafety Assessment of ZIF-8 and ZnO. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024;10(5):2967-2982. [64] ZHANG S, YE J, LIU X, et al. Dual stimuli-responsive smart fibrous membranes for efficient photothermal/photodynamic/chemo-therapy of drug-resistant bacterial infection. Chem Eng J. 2022;432:134351. [65] CHEN MW, LU QJ, CHEN YJ, et al. NIR-PTT/ROS-Scavenging/Oxygen-Enriched Synergetic Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis by a pH-Responsive Hybrid CeO2 -ZIF-8 Coated with Polydopamine. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8(8):3361-3376. [66] MI X, HU M, DONG M, et al. Folic Acid Decorated Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) Loaded with Baicalin as a Nano-Drug Delivery System for Breast Cancer Therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16: 8337-8352. [67] CHEN P, HE M, CHEN B, et al. Size- and dose-dependent cytotoxicity of ZIF-8 based on single cell analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;205:111110. [68] CHEUNG EC, DENICOLA GM, NIXON C, et al. Dynamic ROS control by TIGAR regulates the initiation and progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. 2020; 37(2):168-182.e4. [69] GENG C, HE S, YU S, et al. Achieving clearance of drug‐resistant bacterial infection and rapid cutaneous wound regeneration using an ROS‐balancing‐engineered heterojunction. Adv Mater. 2024;36(16):2310599. |
| [1] | 王奇飒, 卢雨征, 韩秀峰, 赵文玲, 石海涛, 徐 哲. 3D打印甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸/脱细胞皮肤水凝胶支架的细胞相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [2] | 高艳果, 郭 旭, 李晓晗, 陈仕琦, 朱海涛, 黄良永, 叶 方, 卢 伟, 王启斌, 郑 涛, 陈 黎. 糖尿病皮肤创面模型小鼠正交实验优选“红黄白”凝胶的处方配比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [3] | 刘宏杰, 牟秋菊, 申玉雪, 梁 飞, 祝丽丽. 金属有机框架/羧甲基壳聚糖-氧化海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆水凝胶促糖尿病感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [4] | 闵昌琴, 黄 英. pH值/近红外激光刺激响应型载药系统的构建及在抗口腔鳞癌中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [5] | 邵子瑜, 李 倩, 曲曼姑丽·阿布都克力木, 韩友军, 胡 杨. 三种比例双相磷酸钙的制备及性能表征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1952-1961. |
| [6] | 郑旭颖, 胡洪成, 许礼兵, 韩建民, 邸 萍. 不同载荷形式和内连接形状下两段式粘接固位氧化锆种植体的应力大小和分布[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [7] | 周红丽, 王晓龙, 郭 蕊, 姚轩轩, 郭 茹, 周熊涛, 何祥一. 纳米羟基磷灰石/海藻酸钠/聚己内酯/阿仑膦酸钠支架的制备及表征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [8] | 杨利霞, 刁立琴, 李 华, 冯亚婵, 刘 鑫, 于月欣, 窦茜茜, 谷辉峰, 徐兰举. 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白改善大鼠光老化皮肤的调控机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000. |
| [9] | 董春阳, 周天恩, 莫孟学, 吕文权, 高 明, 朱瑞凯, 高志伟. 二甲双胍联合血水草敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013. |
| [10] | 潘之怡, 黄嘉雯, 薛文君, 徐建达. MXene柔性电子传感器的优势及在糖尿病足创面监测中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| [11] | 孙 蕾, 张 琦, 张 宇. 绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜的促成骨效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [12] | 吴妍廷, 李 宇, 廖金凤. 氧化镁纳米粒调控成骨与血管生成相关基因表达促进骨缺损愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [13] | 黎清斌, 林建辉, 黄文杰, 王明爽, 杜间开, 劳永锵. 膝关节周围骨巨细胞瘤病灶扩大刮除后填充骨水泥:软骨下植骨与不植骨的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [14] | 蒋星海, 宋玉林, 李德津, 邵建敏, 徐军志, 刘华凯, 吴应国, 沈岳辉, 冯思诚. 血管内皮生长因子165基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞构建血管化两亲性肽凝胶模块[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [15] | 杨学涛, 朱梦菡, 张宸熙, 孙一民, 叶 玲. 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
ZIF-8的活性氧双向调控特性主要是基于其表面功能化以及药物负载策略。在生理状况下,ZIF-8呈现出优良的稳定性,借助精准的表面功能化或者负载特定功能分子,可有效提升其在不同环境里对活性氧生成与清除的调控能力。在酸性微环境中,像肿瘤组织和酸性细胞器[5],功能化的ZIF-8通过质子化效应发生分解并释放出Zn²+来催化活性氧的生成,在肿瘤微环境或者感染部位达成高效的抗肿瘤以及抗菌效果;负载Fe³+的ZIF-8凭借芬顿或类芬顿反应强化活性氧生成,有效提高其在化学动力学抗肿瘤治疗中的催化效能;把吲哚菁绿嵌入ZIF-8纳米孔隙中,在激光照射诱导下可高效生成细胞毒性活性氧,呈现出卓越的光动力抗菌潜力[6]。另外ZIF-8凭借功能分子负载实现对活性氧的动态吸收与消耗调控,在中性或弱碱性环境中,负载的功能性抗氧化分子可激活细胞内抗氧化酶系统,比如超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶[7],将多余的活性氧高效清除或者转化为无害的分子,如H2O2和O2,有效缓解氧化应激损伤,保护细胞功能。作为ZIF-8的协同载体,多巴胺水凝胶凭借其酚羟基的强亲氧特性可高效捕获活性氧,将活性氧转化为更稳定的产物,如水和氧气,减轻活性氧对细胞的毒性,还提高了ZIF-8在光催化和光动力治疗中的应用效能。基于环境响应及多功能设计的表面功能化与药物负载策略,使得ZIF-8及其改性材料在肿瘤治疗、抗菌以及组织保护等生物医学领域呈现出较大的应用潜力。
一些研究表明,ZIF-8及其改性材料在活性氧双向调控中具有巨大的潜力[8-9],但关于ZIF-8在活性氧双向调控中的系统研究仍然有限。该综述旨在全面探讨ZIF-8及其改性材料的活性氧产生、清除、双向调控机制,突出其双向动态调节能力及在光敏化、金属掺杂等最新研究中的应用亮点(图1),总结ZIF-8纳米材料在肿瘤治疗、抗菌及组织修复中的最新进展,详细分析了其在各领域的应用现状和局限性,并提出未来发展及应用的研究方向。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者于2024年6月完成检索工作。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2000-2024年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网(CNKI)和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索关键词 中文检索关键词为“沸石基咪唑盐框架8,活性氧,抗菌,抗肿瘤,活性氧吸收,活性氧平衡,组织修复”,英文检索关键词为“ZIF-8,ROS,antibacterial,antitumor,ROS absorption,Balance of ROS,Tissue regenration”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 纳入的文献类型包括综述性论文和研究性论文。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 中国知网、PubMed数据库检索策略,见图2。
1.2 检索方法
纳入标准:涉及ZIF-8或其改性材料在活性氧调控方面的应用研究;包含抗肿瘤、抗菌或组织修复领域的实验或临床数据;研究结果明确,具有较高学术价值;近5年发表在高影响因子期刊上的相关文献优先纳入。
排除标准:与主题关联性较弱的研究;实验设计不严谨或数据质量不完整的文献;重复发表的文献或综述内容高度重复的文献;无法获取完整文本或分析数据的文献。
1.3 数据提取 共获取文献599篇,经过筛选,剔除内容相似、研究结果不完善或重复发表的文献,最终纳入69篇符合标准的文献进行综述分析。文献筛选流程见图3。
3.1.1 精准调控机制的不足 当下针对ZIF-8在复杂生物环境里的精准调控机制所展开的研究仍有所欠缺,在多种病理条件下的响应特性还需要进一步阐明。ZIF-8属于酸敏感材料,将ZIF-8用作药物递送载体或许会使药物从其结构中释放不均匀,致使治疗水平的有效药物浓度维持不足,损害药物功效。而且pH值水平以及酶活性的波动可诱导ZIF-8的结构出现不稳定性或者降解,影响药物释放动力学以及整体稳定性。
3.1.2 生物相容性与长期安全性问题 ZIF-8的固有细胞毒性对其生物医学应用造成了限制[67]。ZIF-8在细胞上的功能被认为主要和锌在细胞内的积累存在关联。ZIF-8纳米颗粒的粒径越小,锌的积累以及毒性就越高,其可能的作用途径是锌在ZIF-8孵育细胞中的高积累引发高活性氧水平以及细胞炎症,最终诱导细胞坏死。
3.1.3 改性策略的局限性 目前的改性策略大多集中在单一功能的优化方面,缺少可同时实现活性氧生成与清除并且提高生物安全性和靶向性的智能复合材料。ZIF-8材料在制备过程中往往存在分布不均匀的状况,这会致使材料表面粗糙,对它的性能产生影响。
3.1.4 规模化生产和应用一致性问题 规模化生产和应用一致性问题也急需解决,以此来保证ZIF-8在临床应用中的可行性和可靠性。ZIF-8的合成和功能化涉及复杂的程序,这可能给大规模生产以及有效的质量控制带来挑战。ZIF-8的合成一般涉及精确控制的合成条件,覆盖溶剂选择、温度、pH值等因素。
3.1.5 未来研究方向 未来借助优化合成工艺来实现ZIF-8材料的再现性和可扩展性,开发稳定的制剂来保证临床使用期间的功效和稳定性,以及开发同时有活性氧生成、清除、靶向性和生物安全性的智能复合材料等途径,ZIF-8材料在抗肿瘤、抗菌及细胞保护等领域有望达成从实验室研究到临床转化的飞跃。虽然ZIF-8在药物递送方面拥有巨大潜力,但需要加大研究力度去解决安全性和技术挑战,以实现成功的临床应用。
3.2 该综述的学术价值与创新特色
3.2.1 系统性总结ZIF-8在活性氧双向调控中的机制 已有一些文章对ZIF-8光催化产生活性氧用于抗菌的应用进行了综述[8],关于ZIF-8在活性氧双向调控中的系统研究仍然有限。该综述系统总结了ZIF-8及其改性材料在在活性氧双向调控中的机制,从材料学、生物医学等多学科角度深入探讨金属/金属氧化物掺杂对活性氧动态调控的优化、光敏化复合策略在活性氧生成与清除中的应用、表面功能化改性实现环境响应性调控等,填补了关于ZIF-8在活性氧双向调控中的系统研究的空白。
3.2.2 未来研究方向的开创性见解
智能响应型复合材料:笔者认为具有多重响应性的智能响应型复合材料对于活性氧双重调控有着巨大的应用潜力,未来可以探究更多的多重响应性纳米材料(如pH值、温度、光、磁场响应性材料),通过ZIF-8与多重响应性纳米材料结合发挥更好的活性氧双向调控作用。
深入探究不同生物微环境下的活性氧调控机制:未来可深入探究不同生物微环境(如肿瘤微环境、炎症微环境、神经微环境等)下的活性氧调控机制,例如,通过深入研究肿瘤微环境中pH值对ZIF-8调控活性氧的影响、抗氧化蛋白TIGAR对活性氧的调控和氧化剂的作用机制等[55,68],提高ZIF-8基复合材料的靶向性,实现精准调控。
引入可调控活性氧生成与清除平衡的“杠杆”: 通过引入调控活性氧生成和清除平衡的“杠杆”[69],像金属氧化物(二氧化铈)、纳米酶(Mn3O4纳米酶)、多功能复合材料(二氧化铈@ZIF-8/金)等,以此提高ZIF-8的治疗效果,并且减少其对正常细胞造成的损伤。
3.2.3 未来发展和应用的创新见解
针对当前领域瓶颈的创新解决方案:该综述针对当前领域的瓶颈,包括精准调控机制的不足、生物相容性与长期安全性问题、改性策略的局限性、规模化生产和应用一致性问题等,提出了以下创新解决方案:未来可以通过优化合成工艺,以实现ZIF-8材料的再现性和可扩展性;开发稳定的制剂,以确保临床使用期间的功效和稳定性;开发同时具备活性氧生成、清除、靶向性和生物安全性的智能复合材料等方式,推动ZIF-8材料在抗肿瘤、抗菌及细胞保护等领域的应用,有望实现从实验室研究到临床转化的飞跃。
未来研究方向与创新性设计思路:笔者认为未来通过深入探究不同生物微环境(如肿瘤微环境、炎症微环境、神经微环境等)下的活性氧调控机制,开发具有多重响应性的智能响应型复合材料,并引入调控活性氧生成和清除平衡的“杠杆”等方式,有望实现ZIF-8基材料对活性氧平衡的精准调控和智能控制。这些创新性的设计思路为ZIF-8在抗肿瘤、抗菌及细胞保护等领域的应用提供了新的方向。
3.3 该综述的局限性 该综述重点探讨了ZIF-8在活性氧调控中的双重作用,但对其他金属有机骨架或相关纳米材料的对比分析不足,可能限制视角全面性;此外,临床应用中的剂量控制、生物代谢和长期安全性等问题未深入讨论;部分结论基于间接推断,缺乏直接实验数据支持,未来需结合更多实验和临床研究,完善对ZIF-8的全面理解与实际应用探索。
3.4 该综述对未来研究的指导意义 该综述在理论和实践层面均具有重要意义。在理论层面,系统总结了ZIF-8及其改性材料在活性氧调控中的双向作用机制,为深入理解其多功能性和动态调节能力奠定了坚实基础。在实践层面,通过总结ZIF-8在抗肿瘤、抗菌及细胞保护中的应用进展,为材料开发和实验设计提供了具体参考。而且综述清晰提出了ZIF-8在生物医学应用中的研究挑战和未来发展方向,为相关领域的深入剖析提供了清晰目标。另外该综述融合跨学科视角,为材料科学、生物医学工程以及环境治理领域的研究者给予了新的研究思路,促进了多学科交叉合作的发展。
沸石基咪唑盐框架8(ZIF-8)因其高比表面积、优异的热化学稳定性及 pH值响应特性,在药物控释、抗菌、抗肿瘤及组织修复等领域展现出广泛的应用潜力。以往研究主要聚焦于 ZIF-8在活性氧产生方面的应用,因为其能够降低药物滥用引发的耐药性。然而过量活性氧可能引发氧化损伤、影响正常组织功能,因此逐渐被人们关注。相比于传统的治疗模式,基于ZIF-8的智能活性氧杠杆系统可在病理环境下精准释放活性氧,高效杀伤肿瘤或病原体,并在治疗后期自适应降低活性氧水平,缓解氧化应激,保护正常组织,有效减少耐药性及不良反应。该文进一步总结了ZIF-8及其衍生物在活性氧产生与调控中的研究进展,探讨其在抗菌、抗肿瘤及组织修复等领域的应用潜力,并提出优化策略,以期为高效、安全、可控的活性氧相关治疗体系的构建提供新的思路和未来发展方向。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||