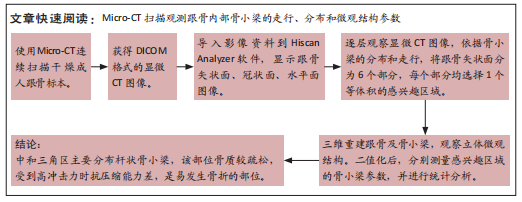
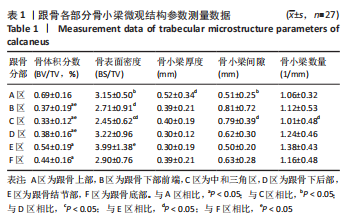
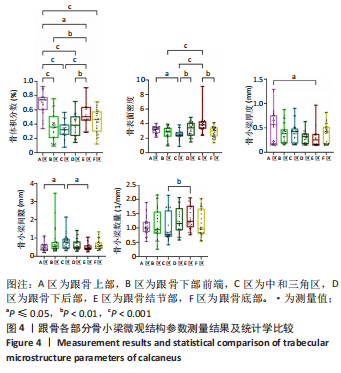
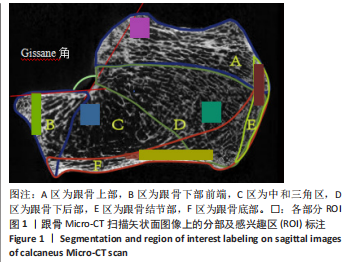
[1] HALLINAN JTPD, WANG W, PATHRIA MN, et al. The peroneus longus muscle and tendon: a review of its anatomy and pathology. Skeletal Radiol. 2019;48(9):1329-1344.
[2] ALSAYEDNOOR J, METCALF L, ROCHESTER J, et al. Comparison of HR-pQCT- and microCT-based finite element models for the estimation of the mechanical properties of the calcaneus trabecular bone. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;17(6):1715-1730.
[3] CALLENS SJP, TOUROLLE NÉ BETTS DC, MÜLLER R, et al. The local and global geometry of trabecular bone. Acta Biomater. 2021;130:343-361.
[4] 徐光华,刘鸿宇,张立夫,等.跆拳道运动对跟骨骨皮质厚度与骨小梁应力分布的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5582-5587.
[5] SAMELSON EJ, BROE KE, XU H, et al. Cortical and trabecular bone microarchitecture as an independent predictor of incident fracture risk in older women and men in the Bone Microarchitecture International Consortium (BoMIC): a prospective study [published correction appears in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(1):e1] [published correction appears in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Jun;7(6):e18]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(1):34-43.
[6] BERNHARDT R, KUHLISCH E, SCHULZ MC, et al. Comparison of bone-implant contact and bone-implant volume between 2D-histological sections and 3D-SRµCT slices. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;23:237-248.
[7] 马剑雄,赵杰,何伟伟,等.高分辨率外周定量计算机断层扫描评估骨小梁微结构和骨强度的研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2018,35(3): 468-474.
[8] SOLDATI E, ROSEREN F, GUENOUN D, et al. Multiscale Femoral Neck Imaging and Multimodal Trabeculae Quality Characterization in an Osteoporotic Bone Sample. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(22):8048.
[9] IBRAHIM N, PARSA A, HASSAN B, et al. Comparison of anterior and posterior trabecular bone microstructure of human mandible using cone-beam CT and micro CT. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):249.
[10] CLARK DP, BADEA CT. Advances in micro-CT imaging of small animals. Phys Med. 2021;88:175-192.
[11] 朱芳芳. CBCT测量骨小梁孔隙率评价骨小梁结构的应用研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2021.
[12] SHEVROJA E, CAFARELLI FP, GUGLIELMI G, et al. DXA parameters, Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) and Bone Mineral Density (BMD), in fracture risk prediction in endocrine-mediated secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine. 2021;74(1):20-28.
[13] CHU L, HE Z, QU X, et al. Different subchondral trabecular bone microstructure and biomechanical properties between developmental dysplasia of the hip and primary osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2019; 22:50-57.
[14] ALMHDIE-IMJABBAR A, PODSIADLO P, LJUHAR R, et al. Trabecular bone texture analysis of conventional radiographs in the assessment of knee osteoarthritis: review and viewpoint. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):208.
[15] YU YE, HU YJ, ZHOU B, et al. Microstructure Determines Apparent-Level Mechanics Despite Tissue-Level Anisotropy and Heterogeneity of Individual Plates and Rods in Normal Human Trabecular Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2021; 36(9):1796-1807.
[16] 张喻磊,胡家军,王臻.小切口解剖钢板联合加压螺栓微创术对跟骨关节内骨折患者足功能恢复的促进作用[J].临床研究,2020,28(12):46-47.
[17] 田国富,李君基,李文杰.人体跟骨模型的建立及其骨折力学研究[J].机械设计与制造,2021(11):52-55.
[18] 林娟颖,刘晓颖,邢立杰,等.基于有限元法的跟骨生物力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(1):37-41.
[19] GALLUZZO M, GRECO F, PIETRAGALLA M, et al. Calcaneal fractures: radiological and CT evaluation and classification systems. Acta Biomed. 2018;89(1-S):138-150.
[20] 魏霞,刘海玉.2200例健康体检者超声桡骨骨密度检测结果分析[J].影像研究与医学应用,2020,4(2):144-145.
[21] NICOLIELO LFP, VAN DESSEL J, JACOBS R, et al.Relationship between trabecular bone architecture and early dental implant failure in the posterior region of the mandible. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020;31(2):153-161.
[22] SAERS JPP, RYAN TM, STOCK JT. Baby steps towards linking calcaneal trabecular bone ontogeny and the development of bipedal human gait. J Anat. 2020;236(3):474-492.
[23] 徐光华,刘鸿宇,张立夫,等.跆拳道运动对跟骨骨皮质厚度与骨小梁应力分布的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5582-5587.
[24] BURT LA, SCHIPILOW JD, BOYD SK. Competitive trampolining influences trabecular bone structure, bone size, and bone strength. J Sport Health Sci. 2016;5(4):469-475.
[25] VAN AS C, KOEDAM M, MCLUSKEY A, et al. Loss of Anti-Müllerian Hormone Signaling in Mice Affects Trabecular Bone Mass in a Sex- and Age-Dependent Manner. Endocrinology. 2022;163(11):bqac157.
[26] OKADA R, YAMATO K, KAWAKAMI M, et al. Low magnetic field promotes recombinant human BMP-2-induced bone formation and influences orientation of trabeculae and bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Bone Rep. 2021;14:100757.
[27] ATHAVALE SA, JOSHI SD, JOSHI SS. Internal architecture of calcaneus: correlations with mechanics and pathoanatomy of calcaneal fractures. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010;32(2):115-122.
[28] GONG H, WANG L, FAN Y, et al. Apparent- and Tissue-Level Yield Behaviors of L4 Vertebral Trabecular Bone and Their Associations with Microarchitectures. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(4):1204-1223.
[29] 吴宇航,郑利钦,张彪,等.去势大鼠骨质疏松性骨小梁的压缩断裂仿真[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(15):2387-2392.
[30] SANDINO C, MCERLAIN DD, SCHIPILOW J, et al. Mechanical stimuli of trabecular bone in osteoporosis: A numerical simulation by finite element analysis of microarchitecture. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;66:19-27.
[31] RIEGER R, AUREGAN JC, HOC T. Micro-finite-element method to assess elastic properties of trabecular bone at micro- and macroscopic level. Morphologie. 2018;102(336):12-20.
[32] MAQUER G, MUSY SN, WANDEL J, et al. Bone volume fraction and fabric anisotropy are better determinants of trabecular bone stiffness than other morphological variables. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6):1000-1008.
[33] 杨锐敏,吴文正,郑永泽,等.不同松质骨体积分数影响股骨近端表观力学响应的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36):5765-5770.
[34] 沛泽,罗守华,陈功,等.基于MicroCT的骨小梁参数测量系统的应用效果分析[J].中国医疗设备,2016,31(4):45-48+39.
[35] YU Q, LI Z, LI J, et al. Calcaneal fracture maps and their determinants. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):39.
|