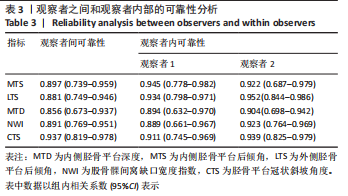
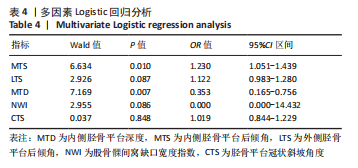
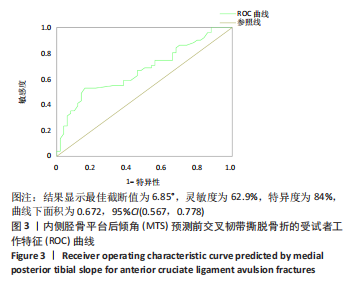
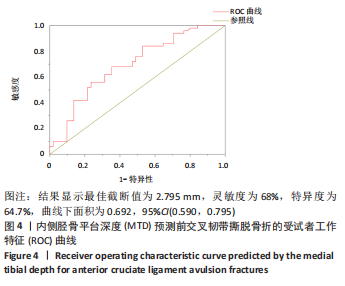
[1] WHITTAKER JL, LOSCIALE JM, JUHL CB, et al. Risk factors for knee osteoarthritis after traumatic knee injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies for the OPTIKNEE Consensus. Br J Sports Med. 2022;24:1406-1421.
[2] DUTHON VB, BAREA C, ABRASSART S, et al. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;3:204-213.
[3] EDMONDS EW, FORNARI ED, DASHE J, et al. Results of displaced pediatric tibial spine fractures: A comparison between open, arthroscopic, and closed management. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015;35(7): 651-656.
[4] JÄÄSKELÄ M, TURATI M, LEMPAINEN L, et al. Long-term Outcomes of Tibial Spine Avulsion Fractures After Open Reduction With Osteosuturing Versus Arthroscopic Screw Fixation: A Multicenter Comparative Study. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;6: 23259671231176991.
[5] GANS I, BALDWIN KD, GANLEY TJ. Treatment and management outcomes of tibial eminence fractures in pediatric patients: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:1743-1750.
[6] ISHIBASHI Y, TSUDA E, SASAKI T, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging AIDS in detecting concomitant injuries in patients with tibial spine fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;434:207-212.
[7] HAYES JM, MASEAR VR. Avulsion fracture of the tibial eminence associated with severe medial ligamentous injury in an adolescent. A case report and literature review. Am J Sports Med. 1984;12:330-333.
[8] STRAUSS EJ,KAPLAN DJ,WEINBERG ME, et al.Arthroscopic Management of Tibial Spine Avulsion Fractures: Principles and Techniques. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;10:360-367.
[9] GREEN D, TUCA M, LUDEROWSKI E, et al. A new, MRI-based classification system for tibial spine fractures changes clinical treatment recommendations when compared to Myers and Mckeever. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;1:86-92.
[10] WANG LJ, ZENG N, YAN ZP, et al. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis following ACL injury. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;1:57.
[11] ZENG C, YANG T, WU S, et al. Is posterior tibial slope associated with noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;3:830-837.
[12] BOJICIC KM, BEAULIEU ML, IMAIZUMI KRIEGER DY, et al. Association Between Lateral Posterior Tibial Slope, Body Mass Index, and ACL Injury Risk. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;2:2325967116688664.
[13] LI Z, LI C, LI L, et al. Correlation between notch width index assessed via magnetic resonance imaging and risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury: an updated meta-analysis. Surg Radiol Anat. 2020;10:1209-1217.
[14] HASHEMI J, CHANDRASHEKAR N, MANSOURI H, et al. Shallow medial tibial plateau and steep medial and lateral tibial slopes: new risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injuries.Am J Sports Med. 2010; 1:54-62.
[15] HOHMANN E, BRYANT A, REABURN P, et al. Is there a correlation between posterior tibial slope and non-contact anterior cruciate ligament injuries? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(Suppl 1):S109-114.
[16] HOHMANN E, TETSWORTH K, GLATT V, et al. Medial and lateral posterior tibial slope are independent risk factors for non-contact ACL injury in both men and women. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9: 23259671211015940.
[17] HASHEMI J, CHANDRASHEKAR N, MANSOURI H, et al. Shallow medial tibial plateau and steep medial and lateral tibial slopes: new risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injuries.Am J Sports Med. 2010;1:54-62.
[18] LANSDOWN D, MA CB. The Influence of Tibial and Femoral Bone Morphology on Knee Kinematics in the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injured Knee. Clin Sports Med. 2018;1:127-136.
[19] HUDEK R, FUCHS B, REGENFELDER F, et al. Is noncontact ACL injury associated with the posterior tibial and meniscal slope? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;8:2377-2384.
[20] HASHEMI J, CHANDRASHEKAR N, GILL B, et al. The geometry of the tibial plateau and its influence on the biomechanics of the tibiofemoral joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(12):2724e2734.
[21] STEIN V, LI L, GUERMAZI A, et al. The relation of femoral notch stenosis to ACL tears in persons with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18:192-199.
[22] ALENTORN-GELI E, PELFORT X, MINGO F, et al. An evaluation of the association between radiographic intercondylar notch narrowing and anterior cruciate ligament injury in men: the notch angle is a better parameter than notch width. Arthroscopy. 2015;31:2004-2013.
[23] TUCA M, BERNAL N, LUDEROWSKI E, et al. Tibial spine avulsion fractures: treatment update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2019;1:103-111.
[24] EDMONDS EW, FORNARI ED, DASHE J, et al. Results of displaced pediatric tibial spine fractures: a comparison between open, arthroscopic, and closed management. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015;35: 651-656.
[25] SIMON RA, EVERHART JS, NAGARAJA HN, et al. A case-control study of anterior cruciate ligament volume, tibial plateau slopes and intercondylar notch dimensions in ACL-injured knees. J Biomech. 2010;43:1702-1707.
[26] DEAN RS, DEPHILLIPO NN, LAPRADE RF. Posterior tibial slope in patients with torn ACL reconstruction grafts compared with primary tear or native ACL: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022;10:23259671221079380.
[27] WEBB JM, SALMON LJ, LECLERC E, et al. Posterior tibial slope and further anterior cruciate ligament injuries in the anterior cruciate ligament-reconstructed patient. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:2800-2804.
[28] SHEN L, JIN ZG, DONG QR, et al. Anatomical risk factors of anterior cruciate ligament injury. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131:2960-2967.
[29] SAMORA W, BERAN MC, PARIKH SN. Intercondylar roof inclination angle: is it a risk factor for ACL tears or tibial spine fractures? J Pediatr Orthop. 2016;36:e71-e74.
[30] MESSNER MK, MCGEE AS, ELPHINGSTONE JW, et al. The Relationship Between Posterior Tibial Slope and Pediatric Tibial Eminence Fractures. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(1):32-37.
[31] AMERINATANZI A, SUMMERS RK, AHMADI K, et al. Automated measurement of patient-specific tibial slopes from MRI. Bioengineering (Basel). 2017;4:69.
[32] PALMER I. On the injuries to the ligaments of the knee joint. A clinical study. Acta Chir Scand. 1938;53:1-28.
[33] JEON N, CHOI NH, HWANGBO BH, et al. An Increased Lateral Femoral Condyle Ratio in Addition to Increased Posterior Tibial Slope and Narrower Notch Index Is a Risk Factor for Female Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Arthroscopy. 2022;5:1597-1604.
[34] SCHICKENDANTZ MS, WEIKER GG. The predictive value of radiographs in the evaluation of unilateral and bilateral anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1993;21:110-113.
[35] HERZOG RJ, SILLIMAN JF, HUTTON K, et al. Measurements of the intercondylar notch by plain film radiography and magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22:204-210.
[36] ROLLET ME, KNAFO Y, GRANGER B, et al. Femoral intercondylar notch: Accuracy of a novel MRI measurement protocol. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022;3:103238.
[37] LI H, ZENG C, WANG Y, et al. Association Between Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Measured Intercondylar Notch Dimensions and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy. 2018;3:889-900.
[38] IRIUCHISHIMA T, GOTO B, FU FH. The occurrence of ACL injury influenced by the variance in width between the tibial spine and the femoral intercondylar notch. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;11:3625-3630.
[39] KOCHER MS, MANDIGA R, KLINGELE K, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injury versus tibial spine fracture in the skeletally immature knee: a comparison of skeletal maturation and notch width index. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;2:185-188.
[40] 徐兴全,刘玉宝,孙梓荧,等.股骨髁间窝宽度指数在胫骨髁间嵴撕脱骨折与前交叉韧带损伤中的差异比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2019,21(2):122-126.
[41] STURNICK DR, VACEK PM, DESARNO MJ, et al. Combined anatomic factors predicting risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury for males and females. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43:839-847.
[42] HUANG YL, JUNG J, MULLIGAN C, et al. A majority of anterior cruciate ligament injuries can be prevented by injury prevention programs: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials and cluster-randomized controlled trials with meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48:1505-1515. |