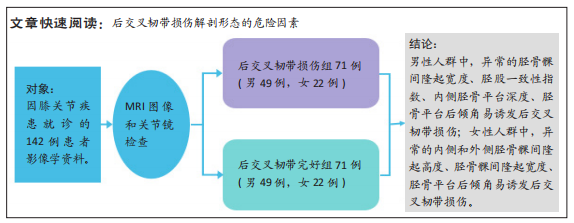
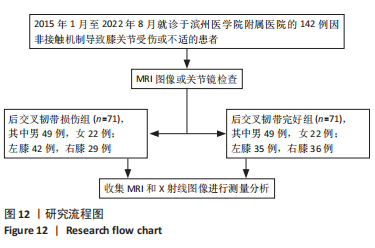
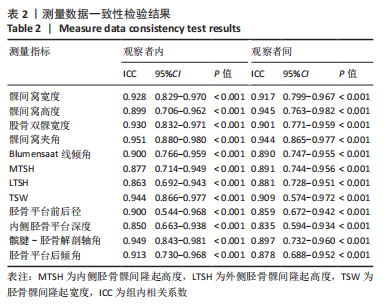
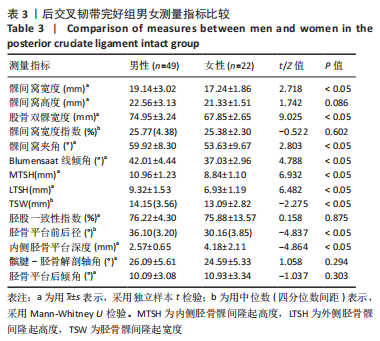
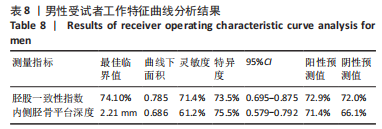
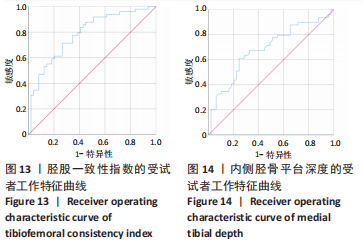
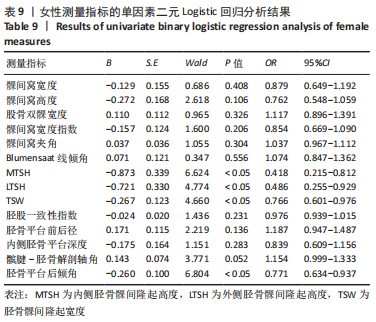
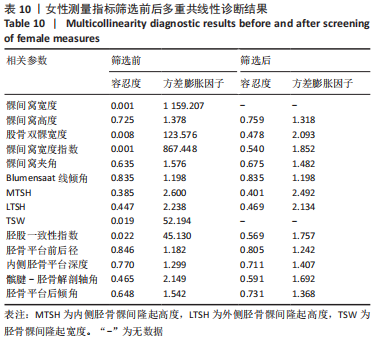
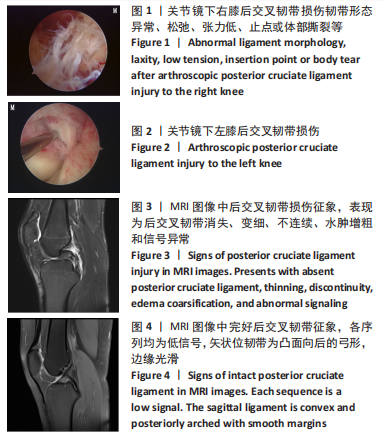
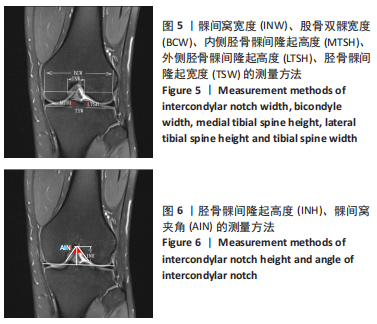
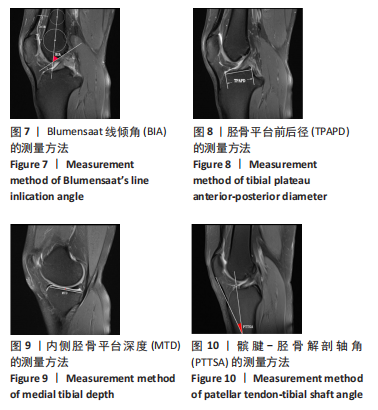
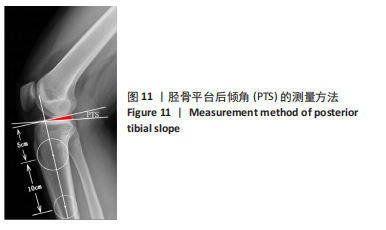
[1] 徐宝鋆,付维力.膝后交叉韧带损伤的诊治及康复策略[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(11):1766-1772.
[2] KATO T, SMIGIELSKI R, GE Y, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament is twisted and flat structure: new prospective on anatomical morphology. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(1):31-39.
[3] WINKLER PW, ZSIDAI B, WAGALA NN, et al. Evolving evidence in the treatment of primary and recurrent posterior cruciate ligament injuries, part 1: anatomy, biomechanics and diagnostics. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3): 672-681.
[4] LAPRADE RF, FLOYD ER, FALAAS KL, et al. The posterior cruciate ligament: Anatomy, biomechanics, and double-bundle reconstruction. J Arthrosc Surg Sports Med 2021;2(2):94-107.
[5] SCHLUMBERGER M, SCHUSTER P, EICHINGER M, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament lesions are mainly present as combined lesions even in sports injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(7):2091-2098.
[6] 焦晨, 敖英芳. 后交叉韧带损伤的临床流行病学研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2008,27(4):420-423.
[7] 陈刚, 付维力, 唐新,等.膝关节后交叉韧带损伤的临床流行病学分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2015,28(7):638-642.
[8] BADRI A, GONZALEZ-LOMAS G, JAZRAWI L. Clinical and radiologic evaluation of the posterior cruciate ligament-injured knee. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018; 11(3):515-520.
[9] VAN KUIJK KSR, REIJMAN M, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SMA, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament injury is influenced by intercondylar shape and size of tibial eminence. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(9):1058-1062.
[10] LIU F, ZHANG S, XIAO Y, et al. Stenotic intercondylar notch is not a risk factor for posterior cruciate ligament rupture: a morphological analyses using magnetic resonance imaging. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(5):1711-1717.
[11] VAN KUIJK KSR, REIJMAN M, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SMA, et al. Smaller intercondylar notch size and smaller ACL volume increase posterior cruciate ligament rupture risk. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(2):449-454.
[12] HUANG WT, KANG K, WANG J, et al. Morphological Risk Factors for Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear and Tibial Avulsion Injuries of the Tibial Plateau and Femoral Condyle. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(1):129-140.
[13] SINGERMAN R, DEAN JC, PAGAN HD, et al. Decreased posterior tibial slope increases strain in the posterior cruciate ligament following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11(1):99-103.
[14] LIPPS DB, WILSON AM, ASHTON-MILLER JA, et al. Evaluation of different methods for measuring lateral tibial slope using magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(12):2731-2736.
[15] GIFFIN JR, STABILE KJ, ZANTOP T, et al. Importance of tibial slope for stability of the posterior cruciate ligament deficient knee. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(9):1443-1449.
[16] YIN B, ZHAO P, CHEN J, et al. Decreased lateral posterior tibial slope and medial tibial depth are underlying anatomic risk factors for posterior cruciate ligament injury: a case-control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):689.
[17] KIZILGÖZ V, SIVRIOĞLU AK, ULUSOY GR, et al. Analysis of the risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injury: an investigation of structural tendencies. Clin Imaging. 2018;50:20-30.
[18] 张伟,刘云鹏,王星亮,等.膝关节前交叉韧带损伤危险因素的影像学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2361-2366.
[19] FAN N, ZHENG YC, ZANG L, et al. What is the impact of knee morphology on posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture in men and women: a case control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):100.
[20] BAYER S, MEREDITH SJ, WILSON KW, et al. Knee Morphological Risk Factors for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Systematic Review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(8):703-718.
[21] TENG Y, GUO L, WU M, et al. MRI analysis of tibial PCL attachment in a large population of adult patients: reference data for anatomic PCL reconstruction. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):384.
[22] NUNLEY RM, WRIGHT D, RENNER JB, et al. Gender Comparison of Patellar Tendon Tibial Shaft Angle with Weight Bearing. Res Sports Med. 2006;11(3):173-185.
[23] BERNHARDSON AS, DEPHILLIPO NN, DANEY BT, et al. Posterior Tibial Slope and Risk of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(2):312-317.
[24] 倪乾坤,宋关阳,张志军,等.基于不同长度胫骨轴线胫骨平台后倾角测量值的差异比较分析[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(9):681-684.
[25] KANG KT, KOH YG, JUNG M, et al. The effects of posterior cruciate ligament deficiency on posterolateral corner structures under gait- and squat-loading conditions: A computational knee model. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(1):31-42.
[26] WANG D, GRAZIANO J, WILLIAMS RJ 3RD, et al. Nonoperative Treatment of PCL Injuries: Goals of Rehabilitation and the Natural History of Conservative Care. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(2):290-297.
[27] CHAHLA J, WILLIAMS BT, LAPRADE RF. Posterior Cruciate Ligament. Arthroscopy. 2020;36(2):333-335.
[28] SONG EK, PARK HW, AHN YS, et al. Transtibial versus tibial inlay techniques for posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: long-term follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(12):2964-2971.
[29] LI Y, CHOU K, ZHU W, et al. Enlarged tibial eminence may be a protective factor of anterior cruciate ligament. Med Hypotheses. 2020;144:110230.
[30] IRIUCHISHIMA T, GOTO B, FU FH. The occurrence of ACL injury influenced by the variance in width between the tibial spine and the femoral intercondylar notch. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(11):3625-3630.
[31] SHELBURNE KB, KIM HJ, STERETT WI, et al. Effect of posterior tibial slope on knee biomechanics during functional activity. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(2):223-231.
[32] HOHMANN E, BRYANT A, REABURN P, et al. Is there a correlation between posterior tibial slope and non-contact anterior cruciate ligament injuries? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19 Suppl 1:S109-S114.
[33] KIAPOUR AM, YANG DS, BADGER GJ, et al. Anatomic Features of the Tibial Plateau Predict Outcomes of ACL Reconstruction Within 7 Years After Surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(2):303-311.
[34] KAPLAN JT, RAMSAY JW, CAMERON SE, et al. Association Between Knee Anatomic Metrics and Biomechanics for Male Soldiers Landing With Load. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(6):1389-1397.
[35] RAO Z, ZHOU C, KERNKAMP WA, et al. In vivo kinematics and ligamentous function of the knee during weight-bearing flexion: an investigation on mid-range flexion of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(3):797-805.
[36] K S, CHAMALA T, KUMAR A. Comparison of anatomical risk factors for noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury using magnetic resonance imaging. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(1):143-148.
[37] MITCHELL JJ, CINQUE ME, DORNAN GJ, et al. Primary Versus Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Patient Demographics, Radiographic Findings, and Associated Lesions. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(3):695-703.
[38] GWINNER C, WEILER A, ROIDER M, et al. Tibial Slope Strongly Influences Knee Stability After Posterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Prospective 5- to 15-Year Follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45:355-361.
[39] RAHNEMAI-AZAR AA, ABEBE ES, JOHNSON P, et al. Increased lateral tibial slope predicts high-grade rotatory knee laxity pre-operatively in ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(4):1170-1176.
[40] SIMON RA, EVERHART JS, NAGARAJA HN, et al. A case-control study of anterior cruciate ligament volume, tibial plateau slopes and intercondylar notch dimensions in ACL-injured knees. J Biomech. 2010;43(9):1702-1707.
[41] HUANG YL, JUNG J, MULLIGAN CMS, et al. A Majority of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries Can Be Prevented by Injury Prevention Programs: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials and Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trials With Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(6):1505-1515.
|