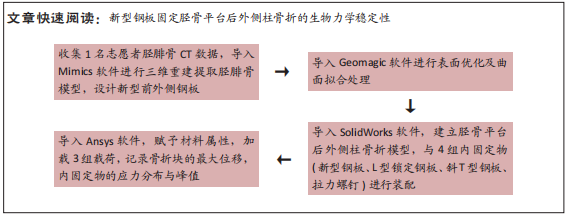
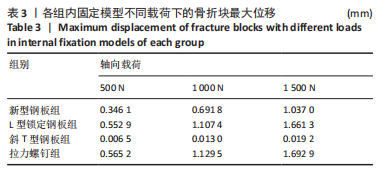
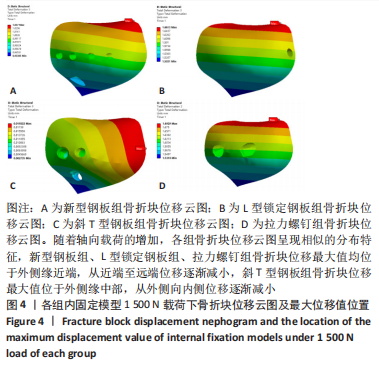
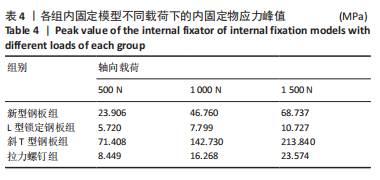
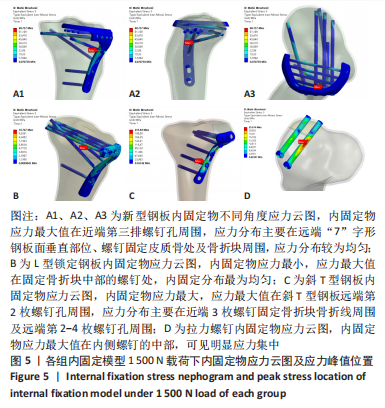
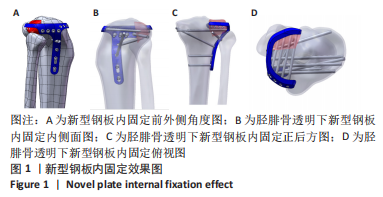
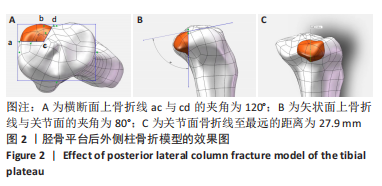
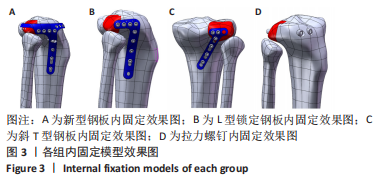
[1] YANG G, ZHAI Q, ZHU Y, et al. The incidence of posterior tibial plateau fracture: an investigation of 525 fractures by using a CT-based classification system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(7):929-934.
[2] HUA K, JIANG X, ZHA Y, et al. Retrospective analysis of 514 cases of tibial plateau fractures based on morphology and injury mechanism. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):267.
[3] 罗从风,胡承方,高洪,等.基于CT的胫骨平台骨折的三柱分型[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(3):201-205.
[4] RAUSCH V, HACKL M, OPPERMANN J, et al. Peroneal nerve location at the fibular head: an anatomic study using 3D imaging. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(7):921-926.
[5] 储旭东,刘晓晖,陈伟南,等.经腓骨小头上入路治疗胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折的临床研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(2):155-159.
[6] REN W, ZHANG W, JIANG S, et al. The Study of Biomechanics and Clinical Anatomy on a Novel Plate Designed for Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fractures via Anterolateral Approach. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:818610.
[7] CHEN YF, REN D, GENG LD, et al. Treatment of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures with a rotational support plate and special pressurizer: technical note and retrospective case series. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):407.
[8] 储旭东,许斌,钱华钧,等.胫骨平台后外侧髁解剖钢板的设计与生物力学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(11):978-982.
[9] YI Z, HUI S, BINBIN Z, et al. A new strategy to fix posterolateral depression in tibial plateau fractures: Introduction of a new modified Frosch approach and a “Barrel hoop plate” technique. Injury. 2020; 51(3):723-734.
[10] 李玉,马建文,黄永.万向锁定钢板内固定治疗Myerson B型Lisfranc损伤疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(12): 1319-1320.
[11] NISHIWAKI M, TERASAKA Y, KIYOTA Y, et al. A Prospective Randomized Comparison of Variable-Angle and Fixed-Angle Volar Locking Plating for Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2021;46(7): 584-593.
[12] ZHANG W, LUO CF, PUTNIS S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of four different fixations for the posterolateral shearing tibial plateau fracture. Knee. 2012;19(2):94-98.
[13] CHANG SM, ZHENG HP, LI HF, et al. Treatment of isolated posterior coronal fracture of the lateral tibial plateau through posterolateral approach for direct exposure and buttress plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(7):955-962.
[14] REN D, LIU Y, LU J, et al. A Novel Design of a Plate for Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fractures Through Traditional Anterolateral Approach. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16418.
[15] 王倞,李元超,汪方,等.人体松质骨矿质密度与弹性模量关系[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(5):465-470.
[16] 杨宗酉,程晓东,朱炼,等.内侧和外侧锁定钢板固定Schatzker Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(2): 157-161.
[17] 张强,巫宗德,刘亮,等.胫骨内侧、外侧解剖锁定钢板固定胫骨中下段外旋型螺旋骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(36):5750-5754.
[18] CHEN P, LU H, SHEN H, et al. Newly designed anterolateral and posterolateral locking anatomic plates for lateral tibial plateau fractures: a finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1): 35.
[19] BEIRAMI S, NIKKHOO M, HASSANI K, et al. A comparative finite element simulation of locking compression plate materials for tibial fracture treatment. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(10):1064-1072.
[20] SAMSAMI S, HERRMANN S, PÄTZOLD R, et al. Finite element analysis of Bi-condylar Tibial Plateau fractures to assess the effect of coronal splits. Med Eng Phys. 2020;84:84-95.
[21] HUO Y, XU G, YIN Z, et al. Effects of surgical approaches and morphological characteristics on the follow up outcomes of patients with posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99(17):e19854.
[22] MAY H, KASTAN O, EMRE TY, et al. Anterior Tibial Artery and Its Clinical Importance in the Posterolateral Approach to the Tibial Plateau: An Angiographic Study on 219 Lower Limbs. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(7):725-730.
[23] 张逸飞,周业金.经后外侧入路治疗单独性后外侧胫骨平台劈裂塌陷骨折11例[J].安徽医药,2019,23(3):554-556.
[24] ZHU F, WU C, WU Q, et al. Retrospective Study of 23 Patients with Traumatic Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fracture Treated in a Single Center Between 2017 and 2019 with Lateral Arthrotomy, Reduction, and Plate Fixation Using the Frosch Approach. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28: e935377.
[25] LIU Y, ZHANG Y, LIANG X, et al. Relative Incidence of Proximal Fibula Fractures with Tibial Plateau Fractures: An Investigation of 354 Cases. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(6):531-535.
[26] CHEN L, XIONG Y, YAN C, et al. Fibular Neck Osteotomy Approach in Treatment of Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fractures: A Retrospective Case Series. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e927370.
[27] KRAUSE M, FRINGS J, ISIK H, et al. Comparison of extended lateral approaches to the tibial plateau: The articular exposure of lateral epicondyle osteotomy with and without popliteus tendon vs. fibula osteotomy. Injury. 2020;51(8):1874-1878.
[28] 白求恩•骨科加速康复联盟,白求恩公益基金会创伤骨科专业委员会,白求恩公益基金会关节外科专业委员会,等.加速康复外科理念下胫骨平台骨折诊疗方案优化的专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(10): 829-840.
[29] 杨通池,胡居正,王仁崇,等.股骨颈系统治疗成人PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(36): 5775-5780.
|