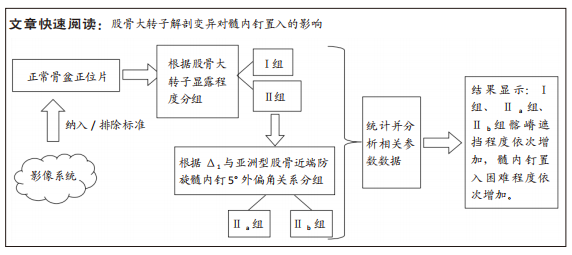
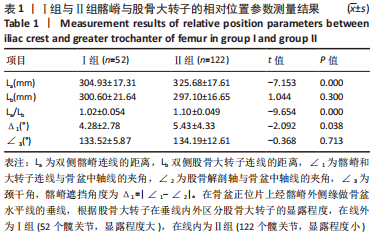
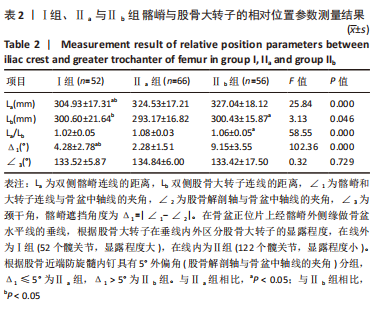
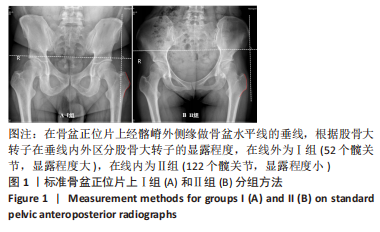
[1] 韩金,李文龙.防旋型股骨近端髓内钉与动力髋螺钉治疗老年人股骨粗隆间骨折的效果比较[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2021,31(10): 153-155.
[2] KARAKUS O, OZDEMIR G, KARACA S, et al. The relationship between the type of unstable intertrochanteric femur fracture and mobility in the elderly. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):207.
[3] REN H, AO R, WU L, et al. Effect of lesser trochanter posteromedial wall defect on the stability of femoral intertrochanteric fracture using 3D simulation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):242.
[4] 梁志强,李强,董钦铭,等.经皮骨钩技术在老年股骨粗隆间骨折闭合复位股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):161-162.
[5] 番子加,段恒都,赵四强,等.组合式外固定架辅助闭合复位髓内钉内固定治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的临床体会[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):165-166.
[6] 刘振刚,杨超,施建东,等.人工股骨头置换术与髓内钉内固定治疗老年骨质疏松性不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):158-160.
[7] 陈灿,马家富,陈秋萍.小切口股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定术治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的临床效果[J].广西医学,2019,41(3):388-390.
[8] 李云飞,高生,张秋琴,等.非透视下确定顺行股骨髓内钉大转子进钉点的解剖观察及临床应用[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2016, 21(3):210-214.
[9] ADEEL M, ZARDAD S, JADOON SM, et al. Outcome Of Open Interlocking Nailing In Closed Fracture Shaft Of Femur. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2020;32(4):546-550.
[10] 闫军,孙成良,周劲松,等.股骨粗隆间骨折PFNA内固定术中闭合复位技巧[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(5):552-553.
[11] 唐胜斌.股骨近端防旋髓内钉小切口治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的效果和安全性分析[J].实用老年医学,2019,33(1):49-52.
[12] 刘康,孙龙泰,邓先辉,等.改良股骨近端锁定钢板治疗骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折的临床观察[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(8):689-692.
[13] XIE Y, DONG Q, XIE Z. Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) and hemi-arthroplasty in the treatment of elderly intertrochanteric fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2019;85(2):199-204.
[14] MU W, ZHOU J. PFNA-II Internal Fixation Helps Hip Joint Recovery and Improves Quality of Life of Patients with Lateral-Wall Dangerous Type of Intertrochanteric Fracture. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5911868.
[15] HU SJ, CHANG SM, MA Z, et al. PFNA-II protrusion over the greater trochanter in the Asian population used in proximal femoral fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2016;50(6):641-646.
[16] JANG Y, KEMPTON LB, MCKINLEY TO, et al. Insertion-related pain with intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 1:S18-S21.
[17] PU JS, LIU L, WANG GL, et al. Results of the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in elderly Chinese patients. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5): 1441-1444.
[18] ZHANG S, ZHANG K, JIA Y, et al. InterTan nail versus Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-Asia in the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(3):e288-294.
[19] FARHANG K, DESAI R, WILBER JH, et al. An anatomical study of the entry point in the greater trochanter for intramedullary nailing. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(9):1274-1281.
[20] PARK PJ, WEINBERG DS, PETRO KF, et al. An Anatomic Study of the Greater Trochanter Starting Point for Intramedullary Nailing in the Skeletally Immature. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(1):67-73.
[21] HUSEYNOV A, ZOLLIKOFER CP, COUDYZER W, et al. Developmental evidence for obstetric adaptation of the human female pelvis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(19):5227-5232.
[22] KURKI HK. Pelvic dimorphism in relation to body size and body size dimorphism in humans. J Hum Evol. 2011;61(6):631-643.
[23] MEINDL RS, LOVEJOY CO, MENSFORTH RP, et al. Accuracy and direction of error in the sexing of the skeleton: implications for paleodemography. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1985;68(1):79-85.
[24] TAGUE RG. Sexual dimorphism in the human bony pelvis, with a consideration of the Neandertal pelvis from Kebara Cave, Israel. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1992;88(1):1-21.
[25] LEWIS CL, LAUDICINA NM, KHUU A, et al. The Human Pelvis: Variation in Structure and Function During Gait. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017; 300(4):633-642.
[26] HU Y, ZHANG H, SU JC. Issues and thoughts on therapies of intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021; 34(10):891-894.
[27] SUERO EM, WESTPHAL R, CITAK M, et al. Robotic technique improves entry point alignment for intramedullary nailing of femur fractures compared to the conventional technique: a cadaveric study. J Robot Surg. 2018;12(2):311-315.
[28] BYUN YS, JUNG GH. Three-dimensional correlation between trochanteric fossa and the ideal entry point for antegrade femoral nailing. Injury. 2016;47(11):2539-2543.
[29] YAM M, CHAWLA A, KWEK E. Rewriting the tip apex distance for the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation. Injury. 2017;48(8):1843-1847.
[30] TAKIGAMI I, MATSUMOTO K, OHARA A, et al. Treatment of trochanteric fractures with the PFNA (proximal femoral nail antirotation) nail system - report of early results. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66(4):276-279.
[31] JIAMTON C, BOERNERT K, BABST R, et al. The nail-shaft-axis of the of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) is an important prognostic factor in the operative treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(3):339-349.
[32] GELLER JA, SAIFI C, MORRISON TA, et al. Tip-apex distance of intramedullary devices as a predictor of cut-out failure in the treatment of peritrochanteric elderly hip fractures. Int Orthop. 2010; 34(5):719-722.
[33] LORICH DG, GELLER DS, NIELSON JH. Osteoporotic pertrochanteric hip fractures: management and current controversies. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53:441-454.
[34] SARAI H, SCHMUTZ B, SCHUETZ M. Effects of ethnicity on proximal femoral intramedullary nail protrusion-a 3D computer graphical analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(5):845-853.
[35] SADAGATULLAH AN, NAZEEB MN, IBRAHIM S. Incidence of Varus Malalignment Post Interlocking Nail in Proximal Femur Shaft Fractures Comparing Two Types of Entry Points. Malays Orthop J. 2017;11(3):31-35.
[36] HUSSAIN N, HUSSAIN FN, SERMER C, et al. Antegrade versus retrograde nailing techniques and trochanteric versus piriformis intramedullary nailing entry points for femoral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Surg. 2017;60(1):19-29.
[37] TAO YL, MA Z, CHANG SM. Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(4):1393-1394.
[38] TURGUT A, KALENDERER O, KARAPINAR L, et al. Which factor is most important for occurrence of cutout complications in patients treated with proximal femoral nail antirotation? Retrospective analysis of 298 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(5):623-630.
[39] NIE B, CHEN X, LI J, et al. The medial femoral wall can play a more important role in unstable intertrochanteric fractures compared with lateral femoral wall: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):197.
[40] OSTERHOFF G, MORGAN EF, SHEFELBINE SJ, et al. Bone mechanical properties and changes with osteoporosis. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 2: S11-20.
[41] CHON CS, KANG B, KIM HS, et al. Implications of three-dimensional modeling of the proximal femur for cephalomedullary nailing: An Asian cadaver study. Injury. 2017;48(10):2060-2067.
[42] SINGH S. Proximal Femoral Nail versus Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation: Functional and Radiological Outcome in Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e19093.
[43] FISCHER CS, KUHN JP, VOLZKE H, et al. The neck-shaft angle: an update on reference values and associated factors. Acta Orthop. 2020; 91(1):53-57.
[44] ZHANG W, ANTONY XAVIER RP, DECRUZ J, et al. Risk factors for mechanical failure of intertrochanteric fractures after fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA II): a study in a Southeast Asian population. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(4):569-575.
[45] LV C, FANG Y, LIU L, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation-Asia: early results. Orthopedics. 2011;34(5):351.
[46] TYAGI V, YANG JH, OH KJ. A computed tomography-based analysis of proximal femoral geometry for lateral impingement with two types of proximal femoral nail anterotation in subtrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2010;41(8):857-861.
|