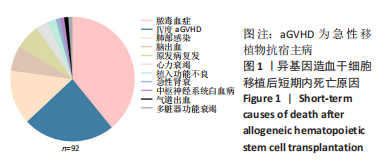
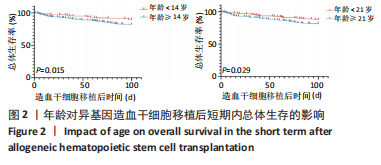
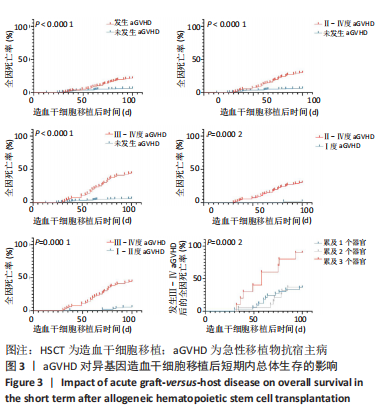
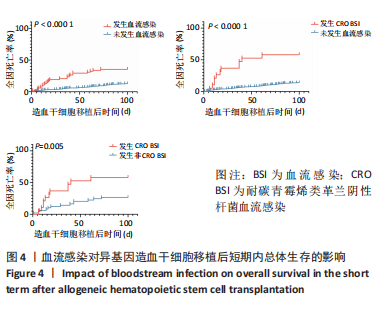
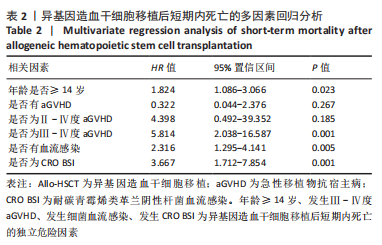
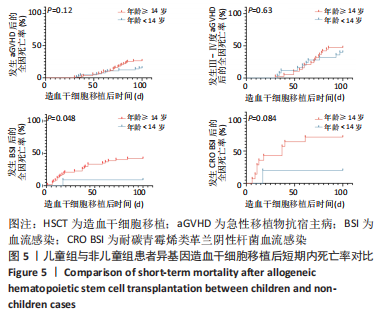
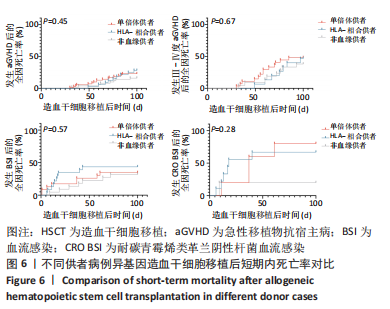
[1] WANG Y, HUANG XJ. Advances in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological disease. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2019;40(8):704-708.
[2] EHMANN MA, MEDINGER M, BODENMANN B, et al. Histologic features of hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy are best percepted in deep skin biopsies and renal biopsies, while showing a significant overlap with changes related to severe acute graft-versus-host disease in gastrointestinal biopsies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(9):1847-1850.
[3] MARTINEZ MT, BUCHER CH, STUSSI G, et al. Transplant-associated microangiopathy (TAM) in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005;36(11):993-1000.
[4] LUFT T, DIETRICH S, FALK C, et al. Steroid-refractory GVHD: T-cell attack within a vulnerable endothelial system. Blood. 2011;118(6):1685-1692.
[5] GIRMENIA C, BERTAINA A, PICIOCCHI A, et al. Incidence, Risk Factors and Outcome of Pre-engraftment Gram-Negative Bacteremia After Allogeneic and Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Italian Prospective Multicenter Survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11): 1884-1896.
[6] GATZA E, REDDY P, CHOI SW. Prevention and Treatment of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26(5):e101-e112.
[7] NIVISON-SMITH I, BARDY P, DODDS AJ, et al. A Review of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Australia and New Zealand, 2005 to 2013. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(2):284-291.
[8] PARK JH, LEE JH, LEE JH, et al. Incidence, Management, and Prognosis of Graft Failure and Autologous Reconstitution after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(23):e151.
[9] SAHIN U, TOPRAK SK, ATILLA PA, et al. An overview of infectious complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Infect Chemother. 2016;22(8):505-514.
[10] TOMBLYN M, CHILLER T, EINSELE H, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009; 15(10):1143-1238.
[11] MIKULSKA M, AVERBUCH D, TISSOT F, et al. Fluoroquinolone prophylaxis in haematological cancer patients with neutropenia: ECIL critical appraisal of previous guidelines. J Infect. 2018;76(1):20-37.
[12] WEISSER M, THEILACKER C, TSCHUDIN SUTTER S, et al. Secular trends of bloodstream infections during neutropenia in 15 181 haematopoietic stem cell transplants: 13-year results from a European multicentre surveillance study (ONKO-KISS). Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(11):854-859.
[13] 秦菁,张素平,李丽,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后带状疱疹病毒感染的危险因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(33):5292-5297.
[14] KERN WV, RIEG S. Burden of bacterial bloodstream infection-a brief update on epidemiology and significance of multidrug-resistant pathogens. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(2):151-157.
[15] YANG TT, LUO XP, YANG Q, et al. Different screening frequencies of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: which one is better? Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020;9(1):49.
[16] CHEN L, HAN X, LI Y, et al. Assessment of Mortality-Related Risk Factors and Effective Antimicrobial Regimens for Treatment of Bloodstream Infections Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021;65(9):e0069821.
[17] LI C, LI Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Treatment options and clinical outcomes for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae bloodstream infection in a Chinese university hospital. J Infect Public Health. 2019;12(1):26-31.
[18] CASTÓN JJ, LACORT-PERALTA I, MARTÍN-DÁVILA P, et al. Clinical efficacy of ceftazidime/avibactam versus other active agents for the treatment of bacteremia due to carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in hematologic patients. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;59:118-123.
[19] TANG Y, XU C, XIAO H, et al. Gram-Negative Bacteria Bloodstream Infections in Patients with Hematological Malignancies - The Impact of Pathogen Type and Patterns of Antibiotic Resistance: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Infect Drug Resist. 2021;14:3115-3124.
[20] SATLIN MJ, COHEN N, MA KC, et al. Bacteremia due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in neutropenic patients with hematologic malignancies. J Infect. 2016;73(4):336-345.
[21] World Health Organization. Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bac teria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics. http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/WHO-PPL-Short_Summary_25Feb-ET_NM_WHO.pdf.
[22] EL-JAWAHRI A, LI S, ANTIN JH, et al. Improved Treatment-Related Mortality and Overall Survival of Patients with Grade IV Acute GVHD in the Modern Years. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(5):910-918.
[23] JAGASIA MH, GREINIX HT, ARORA M, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(3):389-401.
[24] SCHOEMANS HM, LEE SJ, FERRARA JL, et al. EBMT-NIH-CIBMTR Task Force position statement on standardized terminology & guidance for graft-versus-host disease assessment. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(11):1401-1415.
[25] STEM CELL APPLICATION GROUP, CHINESE SOCIETY OF HEMATOLOGY, CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION. Chinese consensus of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological disease (Ⅲ) -acute graft-versus-host disease (2020). Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(7):529-536.
[26] 中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组.中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅰ)——适应证、预处理方案及供者选择(2014年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2014,35(8):775-780.
[27] MIŚKIEWICZ-BUJNA J, MIŚKIEWICZ-MIGOŃ I, SZMIT Z, et al. Short- and long-term outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in infants: A single-center experience over 20 years. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:956108.
[28] STYCZYŃSKI J, TRIDELLO G, KOSTER L, et al. Death after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: changes over calendar year time, infections and associated factors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(1):126-136.
[29] PENACK O, MARCHETTI M, RUUTU T, et al. Prophylaxis and management of graft versus host disease after stem-cell transplantation for haematological malignancies: updated consensus recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(2):e157-e167.
[30] 许慧敏,张素平,曹伟杰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗难治性急性移植物抗宿主病的单臂临床研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(31):4921-4927.
[31] 王卓,陶芳,唐威,等.儿童异基因造血干细胞移植后肠道急性移植物抗宿主病的临床研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2022,30(2): 600-606.
[32] WACHSMUTH LP, PATTERSON MT, ECKHAUS MA, et al. Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide prevents graft-versus-host disease by inducing alloreactive T cell dysfunction and suppression. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(6):2357-2373.
[33] CASTILLA-LLORENTE C, MARTIN PJ, MCDONALD GB, et al. Prognostic factors and outcomes of severe gastrointestinal GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014; 49(7):966-971.
[34] LIN C, SHEN H, ZHOU S, et al. Assessment of infection in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients: risk factors and main characteristics. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20(1):699.
[35] XU CH, SU Y, LYU YX, et al. Perianal swabs surveillance cultures of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae(CRE) can be hints for CRE bloodstream infection in patients with hematological diseases. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018;39(12):1021-1025.
[36] CAO W, ZHANG J, BIAN Z, et al. Active Screening of Intestinal Colonization of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae for Subsequent Bloodstream Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Infect Drug Resist. 2022;15:5993-6006.
[37] POUCH SM, SATLIN MJ. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in special populations: Solid organ transplant recipients, stem cell transplant recipients, and patients with hematologic malignancies. Virulence. 2017;8(4):391-402.
[38] GORRIE CL, MIRCETA M, WICK RR, et al. Gastrointestinal Carriage Is a Major Reservoir of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Intensive Care Patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(2):208-215.
[39] KUMAR A, MOHAPATRA S, BAKHSHI S, et al. Rectal Carriage of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A Menace to Highly Vulnerable Patients. J Glob Infect Dis. 2018;10(4):218-221.
[40] BALLO O, TARAZZIT I, STRATMANN J, et al. Colonization with multidrug resistant organisms determines the clinical course of patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing intensive induction chemotherapy. PLoS One. 2019;14(1):e0210991.
[41] 张成涛,康志杰,杨岩,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗骨髓增生异常综合征及其转化急性髓系白血病的疗效分析[J].大连医科大学学报,2023,45(1):25-31.
[42] 娄典,刘利,严学倩,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗难治/复发急性髓系白血病的疗效及预后因素分析[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2022,30(5):1577-1585.
[43] TODISCO E, CICERI F, BOSCHINI C, et al. Factors predicting outcome after allogeneic transplant in refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a retrospective analysis of Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(7):955-961.
[44] 宋晓露,王晓刚,彭也,等.中高危骨髓增生异常综合征及其转化急性髓系白血病异基因造血干细胞移植时机与疗效的临床研究[J].中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(10):867-872.
[45] CIFTCILER R, DEMIROGLU H, BUYUKASIK Y, et al. Efficacy and Feasibility of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019;19(3):177-182.
[46] CRADDOCK C, LABOPIN M, PILLAI S, et al. Factors predicting outcome after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation in primary refractory acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2011;25(5):808-813. |