中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (26): 4216-4220.doi: 10.12307/2024.433
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
普适性阶梯康复训练促进股骨转子间骨折术后股四头肌功能恢复
王春红,陆 明
- 上海市公共卫生临床中心,上海市 201508
Universal stepwise rehabilitation training promotes the functional recovery of quadriceps femoris after intertrochanteric femoral fracture surgery
Wang Chunhong, Lu Ming
- Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China
摘要:
文题释义:
运动康复的FITT原则:一个运动处方应包括运动频率(Frequency)、运动强度(Intensity)、运动时间(Time)和运动类型(Type)四个要素,即FITT原则。FITT原则体现了运动处方的可调整性,使其适合参加运动者的个体化特点。使用FITT原则制订运动处方时需要根据个体的身体状况(健康和体能)、需要、限制、运动适应性及运动计划的目的和目标进行修改。普适性(化):是指某一事物(特别是观念、制度和规律等)比较普遍适用于同类对象或事物的性质。事物普适性源于事物的共性和规律。普适性与针对性相对应。普适性(化)康复最早2009年开始在国内医学期刊上有报道。
背景:如果未对股四头肌进行有效的康复训练,股骨转子间骨折术后患者的股四头肌肌力会逐渐下降,甚至造成下肢肌肉萎缩,以至于术后患者患侧大腿疼痛,患侧髋、膝关节不灵活等并发症的发生。
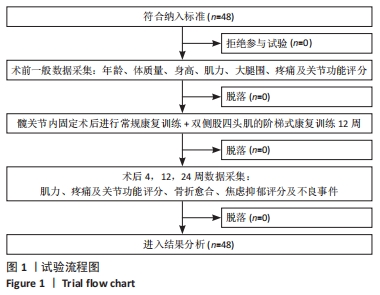
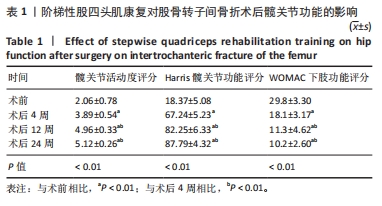
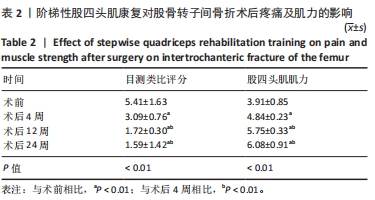
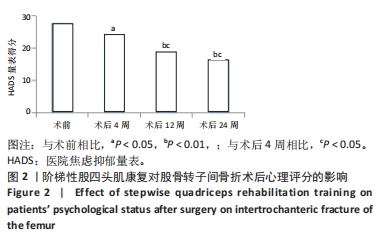
目的:评价股四头肌的普适性阶梯式康复训练在股骨转子间骨折术后康复的作用,探讨股四头肌康复在股骨转子间骨折术后的康复效果。方法:采用回顾性方法分析2016年10月至2022年2月间应用股四头肌康复方案复健的48例股骨转子间骨折手术患者的资料,康复训练包括股四头肌等张、等长收缩训练等,锻炼时间为术后第1-12周。采用Merle D’Aubigne and Postel评价系统中髋关节活动度评分、WOMAC下肢功能评分及Harris髋关节功能评分评价患者髋关节功能,目测类比评分评估疼痛,医院焦虑抑郁量表(HADS)评估患者心理状况,同时测量股四头肌肌力变化。
结果与结论:①患者骨折平均愈合时间为(9.78±1.65)周。②术后4周,患者髋关节功能较术前显著改善(P < 0.01),疼痛目测类比评分降低(P < 0.01),股四头肌肌力升高(P < 0.01),HADS 量表评分降低(P < 0.05)。术后12周,随着康复训练的持续,患者髋关节功能及疼痛症状较术后4周进一步改善(P < 0.05),肌力进一步恢复(P < 0.05),HADS 量表评分进一步降低(P < 0.01)。术后24周,虽然康复训练已经停止,但患者髋关节功能、肌力等得到了很好的维持,股四头肌没有明显的肌萎缩发生,与术后12周比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。③术后康复期间未发生并发症及不良事件。④结果提示在股骨转子间骨折术后早期进行普适性阶梯式股四头肌功能康复模式,有助于髋关节功能恢复,具有增加肌肉力量的作用还在一定程度上起到促进骨折愈合作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6444-0943(陆明)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: