[1] VERONESE N, MAGGI S. Epidemiology and social costs of hip fracture. Injury 2018;49(8):1458-1460.
[2] CHANG SM, HOU ZY, HU SJ, et al. Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Treatment in Asia: What We Know and What the World Can Learn. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(2):189-205.
[3] VAN DE REE CLP, DE JONGH MAC, PEETERS CMM, et al. Hip fractures in elderly people:surgery or no surgery?A systematic review and meta-analysis. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2017;8:173-180.
[4] 张全,曾勇,舒鑫.不同手术方法治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折效果及其生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2020,35(5):602-607.
[5] KASHIGAR A, VINCENT A, GUNTON MJ, et al. Predictors of failure for cephalomedullary nailing of proximal femoral fractures. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(8): 1029-1034.
[6] LIU JJ, SHAN LC, DENG BY, et al. Reason and treatment of failure of proximal femoral nail antirotation internal fixation for femoral intertrochanteric fractures of senile patients. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(3):5949-5956.
[7] KAMMERLANDER C, ERHART S, DOSHI H, et al. Principles of osteoporotic fracture treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27:757-769.
[8] 王勇,尤炯鸣,吴银生,等.标准骨水泥强化型与传统股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨转子间不稳定骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志, 2020,36(12):1077-1082.
[9] KAMMERLANDER C, DOSHI H, GEBHARD F, et al. Long-term results of the augmented PFNA: a prospective multicenter trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(3):343-349.
[10] ZYSSET P, QIN L, LANG T, et al. Clinical Use of Quantitative Computed Tomography-Based Finite Element Analysis of the Hip and Spine in the Management of Osteoporosis in Adults: the 2015 ISCD Official Positions-Part II. J Clin Densitom. 2015;18(3):359-392.
[11] SCHILEO E, TADDEI F. Finite Element Assessment of Bone Fragility from Clinical Images. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(6):688-698.
[12] ZHENG L, CHEN X, ZHENG Y, et al. Cement augmentation of the proximal femoral nail antirotation for the treatment of two intertrochanteric fractures - a comparative finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):1010.
[13] 陈心敏,罗斯嘉,夏卓伟,等.钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(27): 4265-4271.
[14] HONG CC, NASHI N, MAKANDURA MC, et al.The long and short of cephalomedullary nails in the treatment of osteo poroticpertrochanteric fracture. Singapore Med J. 2017;58(2):85-91.
[15] 蔡群斌,邹霞,胡剑涛,等.有限元法分析尖顶距与股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折稳定性的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6):831-836.
[16] GAO Z, LV Y, ZHOU F, et al. Risk factors for implant failure after fixation of proximal femoral fractures with fracture of the lateral femoral wall. Injury. 2018;49(2): 315-322.
[17] HELWIG P, FAUST G, HINDENLANG U, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the gliding nail in trochanteric fractures. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2006;144: 594e601.
[18] DHANOPIA A, BHARGAVA M. Finite element analysis of human fractured femur bone implantation with PMMA thermoplastic prosthetic plate. Proc Engin. 2017; 173:1658-1665.
[19] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ, et al. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit (finite-element analysis). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10):991-996.
[20] 朱兴华,宫赫,白雪飞,等.弹性模量与表观密度的分段函数关系用于股骨近端的结构模拟[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2003,22(3):250-257.
[21] 李家琼,王冬梅,孙璟川,等.骨水泥对椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松压缩性骨折的生物力学影响[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(1):6-12.
[22] SHAO Q, ZHANG Y, SUN GX, et al. Positive or negative anteromedial cortical support of unstable pertrochanteric femoral fractures: A finite element analysis study. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111473.
[23] NUÑO N, AMABILI M, GROPPETTI R, et al. Static coefcient of friction between Ti-6Al-4V and PMMA for cemented hip and knee implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;59(1):191-200.
[24] KARAGIANNIS A, PAPAKITSOU E, DRETAKIS K, et al. Mortality rates of patients with a hip fracture in a southwestern district of Greece: ten-year follow-up with reference to the type of fracture. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;78(2):72-77.
[25] ARCHIBECK MJ, CAROTHERS JT, TRIPURANENI KR, et al. Total hip arthroplasty after failed internal fixation of proximal femoral fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(1):168-171.
[26] LI J, HAN L,ZHANG H, et al. Medial sustainable nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation in treating AO/OTA 31-A2.3 fractures: Finite element analysis and biomechanical evaluation. Injury. 2019;50(3):648-656.
[27] HAN L, LIU JJ, HU YG, et al. Controlled study on Gamma nail and proximal femoral locking plate for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures with broken lateral wall. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11114.
[28] HOFFMANN MF, KHORIATY JD, SIETSEMA DL, et al. Outcome of intramedullary nailing treatment for intertrochanteric femoral fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):360.
[29] 赵晓涛,张殿英,郁凯,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗股骨转子间骨折的失效原因分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(3):202-208.
[30] 王勇,潘骏.标准骨水泥强化型PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间不稳定骨折[J].中国矫形外科志,2018,26(18):1653-1658.
[31] 田智勇,陈洪强,戴科晶,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉骨水泥增强固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(6):539-542.
[32] HANKE MS, BECKMANN NA, KEEL MJB, et al. Revision of a blade cut-out in PFN-A fixation: Blade exchange,cement augmentation and a cement plug as a successful salvage option. Trauma Case Rep. 2020;27:100303.
[33] ERHART S, SCHMOELZ W, BLAUTH M, et al. Biomechanical effect of bone cement augmentation on rotational stability and pull-out strength of the Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation. Injury. 2011;42(11):1322-1327.
[34] DONALDSON AJ, THOMSON HE, HARPER NJ, et al. Bone cement implantation syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 2009;102(1):12-22.
[35] BOOZ C, NOESKE J, ALBRECHT MH, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of quantitative dual-energy CT-based bone mineral density assessment in comparison to Hounsfield unit measurements using dual x-ray absorptiometry as standard of reference. Eur J Radiol. 2020;132:109321. |
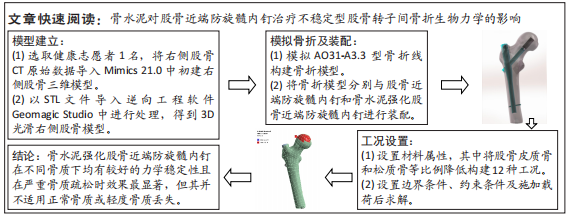
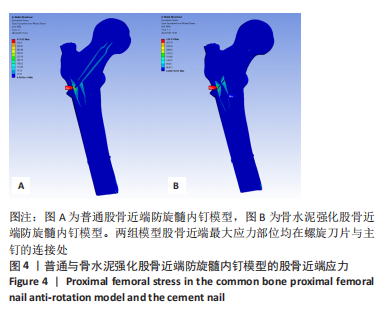
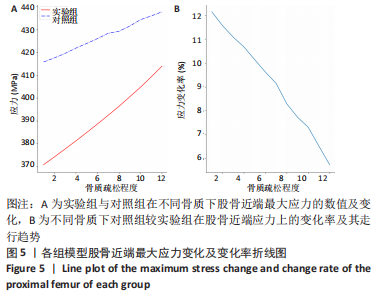
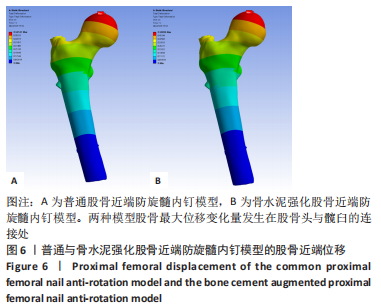
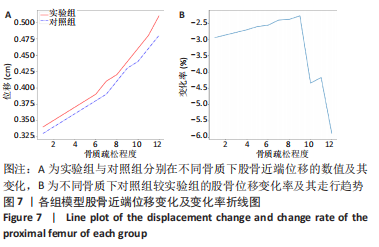
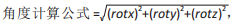 rotx代表x轴角度变化,roty代表y轴角度变化,rotz代表z轴角度变化。
rotx代表x轴角度变化,roty代表y轴角度变化,rotz代表z轴角度变化。