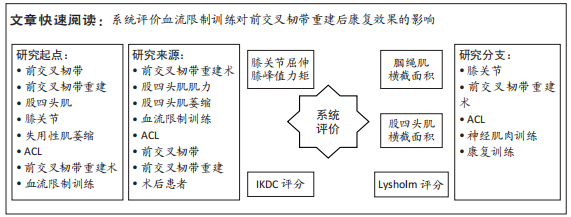
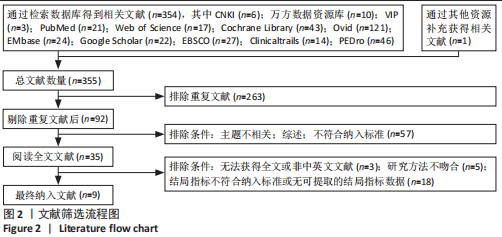
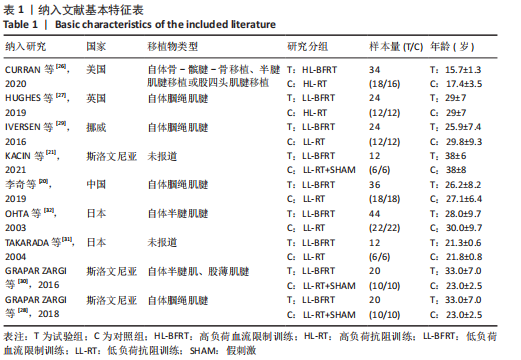
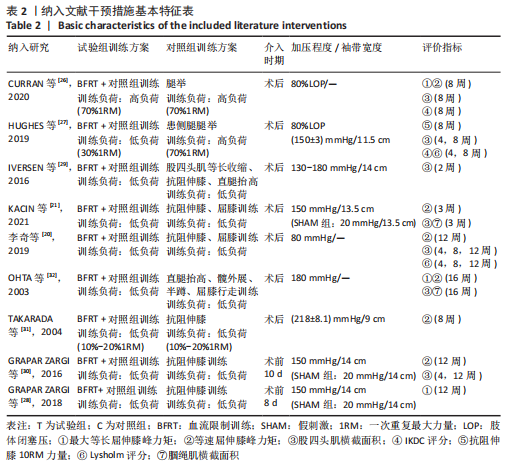
[1] FILBAY SR, GRINDEM H. Evidence-based recommendations for the management of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(1):33-47.
[2] LAI CCH, ARDERN CL, FELLER JA, et al. Eighty-three per cent of elite athletes return to preinjury sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review with meta-analysis of return to sport rates, graft rupture rates and performance outcomes. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(2):128-138.
[3] SANDERS TL, MARADIT KREMERS H, BRYAN AJ, et al. Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears and Reconstruction: A 21-Year Population-Based Study. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(6):1502-1507.
[4] PASCHOS NK, HOWELL SM. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: principles of treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;1(11):398-408.
[5] MALL NA, CHALMERS PN, MORIC M, et al. Incidence and trends of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in the United States. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(10):2363-2370.
[6] 陈连旭,付立功.前交叉韧带断裂和重建的临床流行病学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(24):3602-3608.
[7] HEWETT TE, DI STASI SL, MYER GD. Current concepts for injury prevention in athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(1):216-224.
[8] BIRCHMEIER T, LISEE C, KANE K, et al. Quadriceps Muscle Size Following ACL Injury and Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(3):598-608.
[9] VAN GRINSVEN S, VAN CINGEL RE, HOLLA CJ, et al. Evidence-based rehabilitation following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(8):1128-1144.
[10] MONK AP, DAVIES LJ, HOPEWELL S, et al. Surgical versus conservative interventions for treating anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;4(4):CD011166.
[11] THOMAS AC, WOJTYS EM, BRANDON C, et al. Muscle atrophy contributes to quadriceps weakness after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(1):7-11.
[12] PALMIERI-SMITH RM, THOMAS AC. A neuromuscular mechanism of posttraumatic osteoarthritis associated with ACL injury. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2009;37(3):147-153.
[13] KOCHMAN M, KASPRZAK M, KIELAR A. ACL Reconstruction: Which Additional Physiotherapy Interventions Improve Early-Stage Rehabilitation? A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(23):15893.
[14] CULVENOR AG, GIRDWOOD MA, JUHL CB, et al. Rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament and meniscal injuries: a best-evidence synthesis of systematic reviews for the OPTIKNEE consensus. Br J Sports Med. 2022;56(24):1445-1453.
[15] WORTMAN RJ, BROWN SM, SAVAGE-ELLIOTT I, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training for Athletes: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(7):1938-1944.
[16] PIGNANELLI C, CHRISTIANSEN D, BURR JF. Blood flow restriction training and the high-performance athlete: science to application. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021;130(4):1163-1170.
[17] 魏佳,李博,冯连世,等.血流限制训练的方法学因素及潜在安全性问题[J].中国体育科技, 2019,55(3):3-12.
[18] HUGHES L, PATON B, ROSENBLATT B, et al. Blood flow restriction training in clinical musculoskeletal rehabilitation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(13):1003-1011.
[19] 李新通,潘玮敏,覃华生,等.血流限制训练:加速肌肉骨骼康复的新方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(15):2415-2420.
[20] 李奇,李蕊,罗昌禄,等.血流限制性运动对前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节功能的影响[J].广东医学,2019,40(10):1405-1408.
[21] KACIN A, DROBNIČ M, MARŠ T, et al. Functional and molecular adaptations of quadriceps and hamstring muscles to blood flow restricted training in patients with ACL rupture. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(8):1636-1646.
[22] BOBES ÁLVAREZ C, ISSA-KHOZOUZ SANTAMARÍA P, FERNÁNDEZ-MATÍAS R, et al. Comparison of Blood Flow Restriction Training versus Non-Occlusive Training in Patients with Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction or Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2020;10(1):68.
[23] WENGLE L, MIGLIORINI F, LEROUX T, et al. The Effects of Blood Flow Restriction in Patients Undergoing Knee Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(10): 2824-2833.
[24] GIBSON W, WAND BM, O’CONNELL NE. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;9(9):CD011976.
[25] HAYDEN JA, ELLIS J, OGILVIE R, et al. Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;9(9):CD009790.
[26] CURRAN MT, BEDI A, MENDIAS CL, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training Applied With High-Intensity Exercise Does Not Improve Quadriceps Muscle Function After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(4):825-837.
[27] HUGHES L, ROSENBLATT B, HADDAD F, et al. Comparing the Effectiveness of Blood Flow Restriction and Traditional Heavy Load Resistance Training in the Post-Surgery Rehabilitation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Patients: A UK National Health Service Randomised Controlled Trial. Sports Med. 2019;49(11):1787-1805.
[28] ŽARGI T, DROBNIČ M, STRAŽAR K, et al. Short-Term Preconditioning With Blood Flow Restricted Exercise Preserves Quadriceps Muscle Endurance in Patients After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1150.
[29] IVERSEN E, RØSTAD V, LARMO A. Intermittent blood flow restriction does not reduce atrophy following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Sport Health Sci. 2016;5(1):115-118.
[30] GRAPAR ZARGI T, DROBNIC M, JKODER J, et al. The effects of preconditioning with ischemic exercise on quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a quasi-randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;52(3):310-320.
[31] TAKARADA Y, TSURUTA T, ISHII N. Cooperative effects of exercise and occlusive stimuli on muscular function in low-intensity resistance exercise with moderate vascular occlusion. Jpn J Physiol. 2004;54(6):585-592.
[32] Ohta H, Kurosawa H, Ikeda H, et al. Low-load resistance muscular training with moderate restriction of blood flow after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003; 74(1):62-68.
[33] PERRATON L, CLARK R, CROSSLEY K, et al. Impaired voluntary quadriceps force control following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: relationship with knee function. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(5):1424-1431.
[34] NEUMAN P, OWMAN H, MÜLLER G, et al. Knee cartilage assessment with MRI (dGEMRIC) and subjective knee function in ACL injured copers: a cohort study with a 20 year follow-up. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1):84-90.
[35] CENTNER C, WIEGEL P, GOLLHOFER A, et al. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training on Muscular Strength and Hypertrophy in Older Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(1):95-108.
[36] LIXANDRÃO ME, UGRINOWITSCH C, BERTON R, et al. Magnitude of Muscle Strength and Mass Adaptations Between High-Load Resistance Training Versus Low-Load Resistance Training Associated with Blood-Flow Restriction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):361-378.
[37] PECK BD, BRIGHTWELL CR, JOHNSON DL, et al. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear Promotes Skeletal Muscle Myostatin Expression, Fibrogenic Cell Expansion, and a Decline in Muscle Quality. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(6):1385-1395.
[38] NOEHREN B, ANDERSEN A, HARDY P, et al. Cellular and Morphological Alterations in the Vastus Lateralis Muscle as the Result of ACL Injury and Reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(18):1541-1547.
[39] HWANG PS, WILLOUGHBY DS. Mechanisms Behind Blood Flow-Restricted Training and its Effect Toward Muscle Growth. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33 Suppl 1:S167-S179.
[40] COUNTS BR, DANKEL SJ, BARNETT BE, et al. Influence of relative blood flow restriction pressure on muscle activation and muscle adaptation. Muscle Nerve. 2016;53(3):438-445.
[41] SPRANGER MD, KRISHNAN AC, LEVY PD, et al. Blood flow restriction training and the exercise pressor reflex: a call for concern. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(9):H1440-H1452.
[42] PANAGOPOULOS A, GIANNATOS V, MOROS G, et al. Isokinetic Muscle Strength and Knee Function in Anatomical Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction With Hamstring Autografts: A Prospective Randomized Comparative Study Between Suspensory and Expandable Femoral Fixation in Male Patients. Cureus. 2022;14(12): e32482.
[43] ITHURBURN MP, LONGFELLOW MA, THOMAS S, et al. Knee Function, Strength, and Resumption of Preinjury Sports Participation in Young Athletes Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2019; 49(3):145-153.
[44] GRINDEM H, SNYDER-MACKLER L, MOKSNES H, et al. Simple decision rules can reduce reinjury risk by 84% after ACL reconstruction: the Delaware-Oslo ACL cohort study. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(13):804-808.
[45] ITHURBURN MP, PATERNO MV, FORD KR, et al. Young Athletes With Quadriceps Femoris Strength Asymmetry at Return to Sport After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Demonstrate Asymmetric Single-Leg Drop-Landing Mechanics. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(11):2727-2737.
[46] LADLOW P, COPPACK RJ, DHARM-DATTA S, et al. Low-Load Resistance Training With Blood Flow Restriction Improves Clinical Outcomes in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Physiol. 2018; 9:1269.
[47] PTASINSKI AM, DUNLEAVY M, ADEBAYO T, et al. Returning Athletes to Sports Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022;15(6):616-628.
[48] JENKINS SM, GUZMAN A, GARDNER BB, et al. Rehabilitation After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: Review of Current Literature and Recommendations. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022;15(3):170-179.
[49] SALAGAS A, TSOUKOS A, TERZIS G, et al. Effectiveness of either short-duration ischemic pre-conditioning, single-set high-resistance exercise, or their combination in potentiating bench press exercise performance. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1083299.
[50] WAHLSTRØM KL, BJERRUM E, GÖGENUR I, et al. Effect of remote ischaemic preconditioning on mortality and morbidity after non-cardiac surgery: meta-analysis. BJS Open. 2021;5(2):zraa026.
[51] JIN Z, ZHENG E, SARELI C, et al. Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-Induced Protein 1 (MCPIP-1): A Key Player of Host Defense and Immune Regulation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:727861. |