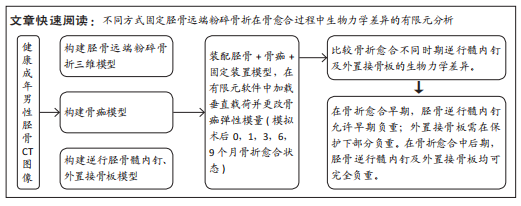
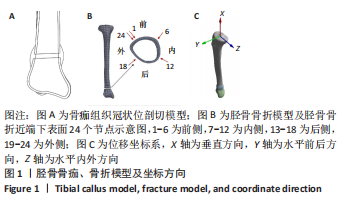
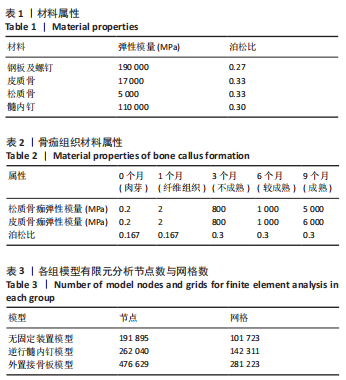
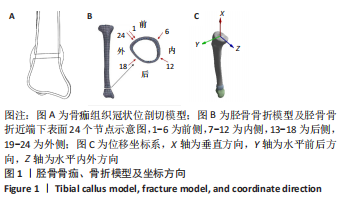
[1] RUSHDI I, CHE-AHMAD A, ABDUL-GHANI K, et al. Surgical Management of Distal Tibia Fracture: Towards An Outcome-based Treatment Algorithm. Malays Orthop J. 2020;14(3):57-65.
[2] QIU XS, YUAN H, ZHENG X, et al. Locking plate as a definitive external fixator for treating tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134:383-388.
[3] HIDAYAT L, TRIANGGA AFR, CEIN CR, et al. Low profile external fixation using locking compression plate as treatment option for management of soft tissue problem in open tibia fracture grade IIIA: A case series. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022;93:106882.
[4] KUHN S, APPELMANN P, PAIRON P, et al. The retrograde tibial nail: presentation and biomechanical evaluation of a new concept in the treatment of distal tibia fractures. Injury. 2014;45Suppl 1:S81-S86.
[5] BARUA E, DAS S, DEOGHAER AB. Development of computational Tibia model to investigate stress shielding effect at healing stages. Mater Today Proc. 2018;5(5):13267-13275.
[6] LIPPHAUS A, WITZEL U. Finite-Element Syntheses of Callus and Bone Remodeling: Biomechanical Study of Fracture Healing in Long Bones. Anat Rec (Hoboken, N.J. : 2007). 2018;301(12):2112-2121.
[7] PERREN SM, FERNANDEZ A, REGAZZONI P. Understanding Fracture Healing Biomechanics Based on the “Strain” Concept and its Clinical Applications. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015;82(4):253-260.
[8] ZHOU K, HE X, TAO X, et al. A biomechanical matched-pair comparison of two different locking plates for tibial diaphyseal comminuted fracture: carbon fiber-reinforced poly-ether-ether-ketone (CF-PEEK) versus titanium plates. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):558.
[9] AUGAT P, PENZKOFER R, NOLTE A, et al. Interfragmentary movement in diaphyseal tibia fractures fixed with locked intramedullary nails. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22:30-36.
[10] ELKINS J, MARSH JL, LUJAN T, et al. Motion Predicts Clinical Callus Formation: Construct-Specific Finite Element Analysis of Supracondylar Femoral Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(4):276-284.
[11] LI J, ZHAO X, HU X, et al. A theoretical analysis and finite element simulation of fixator-bone system stiffness on healing progression.J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2018;16(3):115-125.
[12] 王明明,张中,孙建华,等.胫骨远端骨折伴软组织损伤3种不同微创固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(6): 879-885.
[13] 刘晨东,胡孙君,张世民.三种新型内固定方式治疗胫骨平台双髁四象限骨折的有限元研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(3): 290-295.
[14] 董衍生,王永清,董黎敏,等.可吸收锁钉鞘预防股骨带锁髓内钉应力遮挡的有限元分析[J].天津理工大学学报,2018,34(3):42-47.
[15] BYRNE DP, LACROIX D, PRENDERGAST PJ. Simulation of fracture healing in the tibia: mechanoregulation of cell activity using a lattice modeling approach. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(10):1496-1503.
[16] 贾军锋,唐承杰,乐劲涛,等.胫骨远端骨折3种不同固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5188-5194.
[17] SOUZA JCM, PINHO SS, BRAZ MP, et al. Carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK in implant dentistry: A scoping review on the finite element method. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(12):1355-1367.
[18] ZHOU K, YANG H. Effects of Bone-Plate Material on the Predicted Stresses in the Tibial Shaft Comminuted Fractures: A Finite Element Analysis.J Invest Surg. 2022;35(1):132-140.
[19] 杨卫强,赵永明,丁童,等.动态锁定螺钉固定胫骨远端骨折的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(9):835-838.
[20] LIU B, LV Y, LI X, et al. Influence of different fixation modes on biomechanical conduction of 3D printed prostheses for treating critical diaphyseal defects of lower limbs: A finite element study. Front Surg. 2022;9:959306.
[21] ZHAO X, LI J, CHEN Y, et al. Investigation of load transfer process between external fixator and bone model by experimental and finite element methods. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2019;17(1): 2280800019826512.
[22] MARONGIU G, DOLCI A, VERONA M, et al. The biology and treatment of acute long-bones diaphyseal fractures: Overview of the current options for bone healing enhancement. Bone Rep. 2020;12:100249.
[23] PERREN SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(8): 1093-1110.
[24] EPARI DR, GURUNG R, HOFMANN-FLIRI L, et al. Biphasic plating improves the mechanical performance of locked plating for distal femur fractures. J Biomech. 2021;115:110192.
[25] 史金友,肖玉周,吴敏,等. 微动本质及骨折愈合生物力学分期的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(9):1205-1211.
[26] GARDNER MJ, VAN DER MEULEN MC, DEMATRAKOPOULOS D, et al. In vivo cyclic axial compression affects bone healing in the mouse tibia. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:1679-1686.
[27] BETTS DC, MULLER R. Mechanical regulation of bone regeneration: theories, models, and experiments. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:211.
[28] SAMIEZADEH S, AVVAL PT, FAWAZ Z, et al. On optimization of a composite bone plate using the selective stress shielding approach. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015;42:138-153.
[29] MEHBOOB A, MEHBOOB H, KIM J, et al. Influence of initial biomechanical environment provided by fibrous composite intramedullary nails on bone fracture healing. Compos Struct. 2017; 175:123-134.
[30] 丁晓红,徐世鹏,段朋云,等.骨折内固定接骨板生物力学评价及结构设计方法研究进展[J].上海理工大学学报,2022,44(5): 429-439+472. |