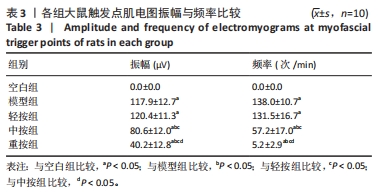
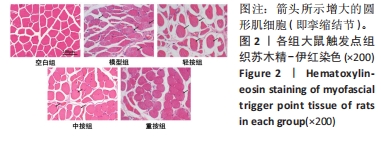
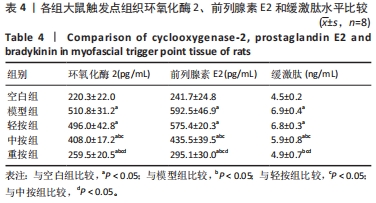
[1] 克莱尔•戴维斯,安伯•戴维斯.触发点疗法[M].北京:北京科学技术出版社,2018.
[2] FLECKENSTEIN J, ZAPS D, RÜGER LJ, et al. Discrepancy between prevalence and perceived effectiveness of treatment methods in myofascial pain syndrome: results of a cross-sectional, nationwide survey. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010; 11:32.
[3] 徐安乐,黄强民,荣积峰,等.缺血性按压肌筋膜触发点对非特异性颈痛治疗效果的系统评价与meta分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2022,37(11):1541-1550.
[4] XU A, HUANG Q, RONG J, et al. Effectiveness of ischemic compression on myofascial trigger points in relieving neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(4):783-798.
[5] JIANG Q, FENG X, LIU D, et al. Pressing Intervention Promotes the Skeletal Muscle Repair of Traumatic Myofascial Trigger Points in Rats. J Pain Res. 2021;14:3267-3278.
[6] 蒋全睿,刘丹,潘杰灵,等.不同部位按法对慢性疼痛激痛点大鼠模型的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2023,46(7):1008-1019.
[7] 冯熹文.缺血性按压与针刺激痛点镇痛机理与临床应用[J].中国实用医药, 2023,18(7):155-159.
[8] LEE S, MOON H, RYU Y, et al. Sensory and emotional responses to deep pressure stimulation at myofascial trigger points: a pilot study. Front Neurosci. 2023;17: 1197302.
[9] SHAH JP, DANOFF JV, DESAI MJ, et al. Biochemicals associated with pain and inflammation are elevated in sites near to and remote from active myofascial trigger points. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(1):16-23.
[10] LV H, LI Z, HU T, et al. The shear wave elastic modulus and the increased nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB/p65) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in the area of myofascial trigger points activated in a rat model by blunt trauma to the vastus medialis. J Biomech. 2018;66:44-50.
[11] 蒋全睿,李江山,陈四红,等.不同参数和方式按压心俞穴对局部温度影响的正交试验[J].针灸推拿医学(英文版),2019,17(3):147-154.
[12] 蒋全睿.不同参数和方式按压心俞穴对局部温度影响的实验研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2018.
[13] 韩蓓,黄强民,谭树生,等.大鼠肌筋膜疼痛触发点自发肌电现象和病理组织学研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2011,30(6):532-535+531.
[14] 吕娇娇,黄强民,汤莉.大鼠慢性肌筋膜疼痛触发点的电生理和病理组织学研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(7):621-628.
[15] 周理,罗和平,李义凯,等.肌筋膜痛扳机点模型与造模方法研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(8):789-792.
[16] TSUGE K, INAZUMI T, SHIMAMOTO A, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying prostaglandin E2-exacerbated inflammation and immune diseases. Int Immunol. 2019;31(9):597-606.
[17] ZIEGLGÄNSBERGER W. Substance P and pain chronicity. Cell Tissue Res. 2019; 375(1):227-241.
[18] SHIGEMATSU S, ISHIDA S, GUTE DC, et al. Bradykinin-induced proinflammatory signaling mechanisms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283(6):H2676-H2686.
[19] INOUE A, IWASA M, NISHIKURA Y, et al. The long-term exposure of rat cultured dorsal root ganglion cells to bradykinin induced the release of prostaglandin E2 by the activation of cyclooxygenase-2. Neurosci Lett. 2006;401(3):242-247.
[20] CHENG H, HUANG H, GUO Z, et al. Role of prostaglandin E2 in tissue repair and regeneration. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8836-8854.
[21] NAKANISHI M, ROSENBERG DW. Multifaceted roles of PGE2 in inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(2):123-137.
[22] GRABAUSKAS G, WU X, GAO J, et al. Prostaglandin E2, Produced by Mast Cells in Colon Tissues From Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Contributes to Visceral Hypersensitivity in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(8):2195-2207.e6.
[23] LEMOS HP, GRESPAN R, VIEIRA SM, et al. Prostaglandin mediates IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil migration in inflammation by inhibiting IL-12 and IFNgamma production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(14):5954-5959.
[24] 卢悦.推拿按压致大鼠骨骼肌损伤的时间-压强曲线研究[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2022.
[25] 李武,蒋全睿,艾坤,等.力度和按压时间对按法热效应影响的实验研究[J].针灸推拿医学(英文版),2018,16(5):303-309.
[26] 李晶晶,沈世辉,蒋全睿,等.不同力度按压心俞对局部血流速度和温度的影响[J].新中医,2021,53(2):122-125.
[27] SEO BR, PAYNE CJ, MCNAMARA SL, et al. Skeletal muscle regeneration with robotic actuation-mediated clearance of neutrophils. Sci Transl Med. 2021; 13(614):eabe8868.
[28] 匡小霞.基于AMPK调节骨骼肌能量代谢研究按法对激痛点去活化效应机制[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2022.
[29] 蒋全睿,吴琼,匡小霞,等.按压对大鼠肌筋膜激痛点软组织张力的影响及其作用机制研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(5):335-341.
[30] 姚泰,赵志奇,朱大年,等.人体生理学(第4版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2015.
[31] 张宇星,冯祥,危威,等.基于指按法及针刺作用于手三里的痛温觉诱发电位探讨经络小纤维神经感传效应[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2020,27(4):23-27.
[32] 张宇星,冯祥,危威,等.观察按法作用于正常人手三里产生的痛温觉诱发电位探析经络理论的神经传导效应[J].辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(9):150-152.
[33] 朱兵.弥漫性伤害抑制性控制研究进展[J].生理科学进展,1992(1):88-94.
[34] GE HY, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Arendt-Nielsen L. Sympathetic facilitation of hyperalgesia evoked from myofascial tender and trigger points in patients with unilateral shoulder pain. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;117(7):1545-1550.
[35] CAO L, GAO Y, WU K, et al. Sympathetic hyperinnervation in myofascial trigger points. Med Hypotheses. 2020;139:109633.
[36] 袁仕国,颜丽满,武凯,等.化学性交感神经切除对肌筋膜激痛点炎症和肌卫星细胞成肌分化的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2020,36(15):2059-2065.
[37] MORIKAWA Y, TAKAMOTO K, NISHIMARU H, et al. Compression at Myofascial Trigger Point on Chronic Neck Pain Provides Pain Relief through the Prefrontal Cortex and Autonomic Nervous System: A Pilot Study. Front Neurosci. 2017; 11:186.
[38] KODAMA K, TAKAMOTO K, NISHIMARU H, et al. Analgesic Effects of Compression at Trigger Points Are Associated With Reduction of Frontal Polar Cortical Activity as Well as Functional Connectivity Between the Frontal Polar Area and Insula in Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized Trial. Front Syst Neurosci. 2019;13:68.
[39] DIEGO MA, FIELD T. Moderate pressure massage elicits a parasympathetic nervous system response. Int J Neurosci. 2009;119(5):630-638.
[40] 刘阅阅,郑林遥,陈佳彦,等.电针干预远近端穴位对肌筋膜疼痛综合征模型大鼠致痛物质、巨噬细胞及相关炎症因子的影响[J].中医杂志,2023, 64(17):1799-1806.
|