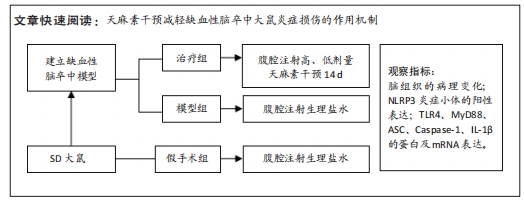
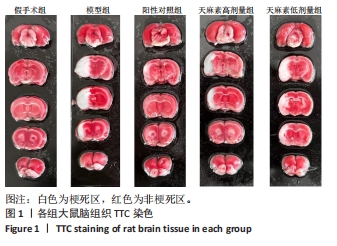
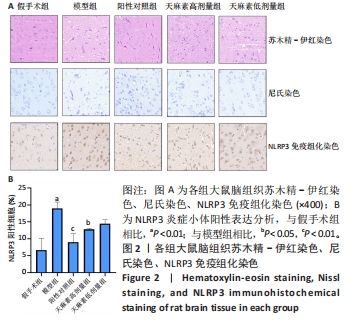
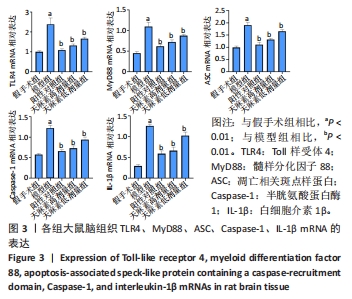
[1] PAUL S, CANDELARIO-JALIL E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp Neurol. 2021;335:113518.
[2] KATAN M, LUFT A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018;38(2):208-211.
[3] FESKE SK. Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med. 2021;134(12):1457-1464.
[4] SU XT, WANG L, MA SM, et al. Mechanisms of Acupuncture in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:7875396.
[5] QIU CW, LIU ZY, ZHANG FL, et al. Post-stroke gastrodin treatment ameliorates ischemic injury and increases neurogenesis and restores the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 2019;1712:7-15.
[6] 秦文秀,许军峰,高莹,等.中药干预腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶相关信号通路防治缺血性脑卒中的研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2023,34(8):1156-1163.
[7] THIANKHAW K, CHATTIPAKORN N, CHATTIPAKORN SC. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on the brain with middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(3):1677-1694.
[8] SU Z, YANG Y, CHEN S, et al. The processing methods, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Gastrodia elata Bl.: A comprehensive review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;314:116467.
[9] WU MY, YIANG GT, LIAO WT, et al. Current Mechanistic Concepts in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(4):1650-1667.
[10] ZHU T, WANG L, FENG Y, et al. Classical Active Ingredients and Extracts of Chinese Herbal Medicines: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Molecular Mechanisms for Ischemic Stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8868941.
[11] LUO Y, CHEN P, YANG L, et al. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on molecular targets and mechanisms of Gastrodia elata Blume in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(6):742.
[12] LIU Y, GAO J, PENG M, et al. A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:24.
[13] ZHU T, WANG L, WANG LP, et al. Therapeutic targets of neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke: Applications for natural compounds from medicinal herbs. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;148:112719.
[14] 徐焕昌,王雪梅.系统免疫炎症指数与急性缺血性脑卒中相关性研究进展[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2023,30(4):277-281.
[15] WANG X, LI S, MA J, et al. Effect of Gastrodin on Early Brain Injury and Neurological Outcome After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(3):461-470.
[16] YANG F, LI G, LIN B, et al. Gastrodin suppresses pyroptosis and exerts neuroprotective effect in traumatic brain injury model by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J Integr Neurosci. 2022;21(2):72.
[17] 苏晶,刘立明,丁盈月,等.中药干预脑卒中后细胞焦亡的研究进展[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-8[2023-08-20].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20230816.0942.004.html
[18] MAIDA CD, NORRITO RL, DAIDONE M, et al. Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6454.
[19] GROSLAMBERT M, PY BF. Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J Inflamm Res. 2018;11:359-374.
[20] QIN Y, LI Q, LIANG W, et al. TRIM28 SUMOylates and stabilizes NLRP3 to facilitate inflammasome activation. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4794.
[21] GHAFOURI-FARD S, SHOOREI H, POORNAJAF Y, et al. NLRP3: Role in ischemia/reperfusion injuries. Front Immunol. 2022;13:926895.
[22] LI Y, ZHANG J. Animal models of stroke. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021;4(3):204-219.
[23] GUO P, JIN Z, WU H, et al. Effects of irisin on the dysfunction of blood-brain barrier in rats after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Behav. 2019;9(10):e01425.
[24] 刘书涵.迷迭香酸通过调节小胶质细胞极化表型减轻缺血性脑卒中损伤的机制研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022.
[25] CHEN GH, LI XL, DENG YQ, et al. The Molecular Mechanism of EPO Regulates the Angiogenesis after Cerebral Ischemia through AMPK-KLF2 Signaling Pathway. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(2):105-112.
[26] GUO S, LEI Q, GUO H, et al. Edaravone Attenuates Aβ 1-42-Induced Inflammatory Damage and Ferroptosis in HT22 Cells. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(2):570-578.
[27] ZHANG N, KOMINE-KOBAYASHI M, TANAKA R, et al. Edaravone reduces early accumulation of oxidative products and sequential inflammatory responses after transient focal ischemia in mice brain. Stroke. 2005;36(10):2220-2225.
[28] FENG YS, TAN ZX, WANG MM, et al. Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome: A Prospective Target for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:155.
[29] TIRANDI A, SGURA C, CARBONE F, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers of ischemic stroke.Intern Emerg Med. 2023;18(3):723-732.
[30] 秦文秀,许军峰,杨婷,等.丹参酮ⅡA治疗缺血性脑卒中后神经损伤的信号通路研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2023,28(6):705-713.
[31] PANG YQ, YANG J, JIA CM, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning reduces NLRP3 inflammasome expression and protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(2):395-400.
[32] COLL RC, SCHRODER K, PELEGRÍN P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(8):653-668.
[33] SHAO A, FEI J, FENG S, et al. Chikusetsu saponin IVa alleviated sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment by blocking NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Pharmacol Rep. 2020;72(4):833-845.
[34] ALISHAHI M, FARZANEH M, GHAEDRAHMATI F, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke: As possible therapeutic target. Int J Stroke. 2019;14(6):574-591.
[35] 林兰明,宋征宇,胡瑾.金合欢素调节TLR4/NLRP3信号通路对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠的保护作用[J/OL].中国中药杂志:1-9[2023-08-20].DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230719.401.
[36] 高毅,冷玉芳,张保朝,等.基于Keap1/Nrf2/NLRP3炎症小体和p62途径探讨右美托咪定改善脑卒中后损伤的内在机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2023, 39(7):1362-1366.
[37] LEITNER GR, WENZEL TJ, MARSHALL N, et al. Targeting toll-like receptor 4 to modulate neuroinflammation in central nervous system disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23(10):865-882.
[38] DURÁN-LAFORET V, PEÑA-MARTÍNEZ C, GARCÍA-CULEBRAS A, et al. Pathophysiological and pharmacological relevance of TLR4 in peripheral immune cells after stroke. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;228:107933.
[39] YE X, KONG D, WANG J, et al. MyD88 contributes to neuroinflammatory responses induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;480(1):69-74.
[40] BAYER AL, ALCAIDE P. MyD88: At the heart of inflammatory signaling and cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021;161:75-85.
[41] SUN Y, CHEN H, LIN Y. Rehabilitation training inhibits neuronal apoptosis by down-regulation of TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in mice with cerebral ischemic stroke. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(4):2213-2223.
[42] HAN D, LI F, ZHANG H, et al. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor restores blood-brain barrier integrity of aged mice after ischaemic stroke/reperfusion through anti-inflammation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. J Drug Target. 2022;30(4):430-441.
[43] LI Z, ZHAO M, ZHANG X ,et al. TJ-M2010-5, a novel CNS drug candidate, attenuates acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the MyD88/NF-κB and ERK pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1080438.
[44] MANGAN MSJ, OLHAVA EJ, ROUSH WR, et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17(9):688.
[45] HUANG Y, XU W, ZHOU R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(9):2114-2127.
[46] ZAHID A, LI B, KOMBE AJK, et al. Pharmacological Inhibitors of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2538.
[47] WANG L, HAUENSTEIN AV. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Mechanism of action, role in disease and therapies. Mol Aspects Med. 2020;76:100889.
[48] LI Z, GUO J, BI L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110542.
[49] LI Y, LIANG W, GUO C, et al. Renshen Shouwu extract enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway following ischemic stroke in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;253:112616.
[50] BRODERICK L, HOFFMAN HM. IL-1 and autoinflammatory disease: biology, pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(8):448-463.
[51] CAI Y, XUE F, QUAN C, et al. A Critical Role of the IL-1β-IL-1R Signaling Pathway in Skin Inflammation and Psoriasis Pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(1): 146-156.
[52] ZHU H, HU S, LI Y, et al. Interleukins and Ischemic Stroke. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:828447.
[53] ZHA H, MIAO W, RONG W, et al. Remote ischaemic perconditioning reduces the infarct volume and improves the neurological function of acute ischaemic stroke partially through the miR-153-5p/TLR4/p65/IkBa signalling pathway. Folia Neuropathol. 2021;59(4):335-349.
[54] 全宏娟,何旭丽,夏明万,等.针刺治疗结合康复训练改善缺血性卒中急性期大鼠神经损伤的作用及与TLR4通路相关的机制研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2023,21(14):2607-2612.
[55] 徐倩倩,钱旭东,孙凡,等.西红花苷对缺血性脑卒中后抑郁大鼠炎症反应及TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(2):179-185.
[56] DURÁN-LAFORET V, PEÑA-MARTÍNEZ C, GARCÍA-CULEBRAS A, et al. Role of TLR4 in Neutrophil Dynamics and Functions: Contribution to Stroke Pathophysiology. Front Immunol. 2021;12:757872.
[57] 黎艳,王世栋,黄文川.薯蓣皂苷元对缺血性脑卒中大鼠神经运动功能及TLR4-MyD88/TRIF信号通路调节作用研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2021,38(12): 2319-2324.
[58] 阳晶晶,罗政,刘艺璇,等.基于TLR4/MyD88/NF-KB通路探讨中医超声药透电疗改善脑缺血大鼠炎症反应的实验研究[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2022, 17(12):2409-2415+2434.
[59] 王瑜,梁超,王宝爱,等.白藜芦醇激活PI3K/Akt信号通路与老年缺血性脑卒中大鼠血清IL-6、IL-1β含量的分子机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(3): 656-660. |