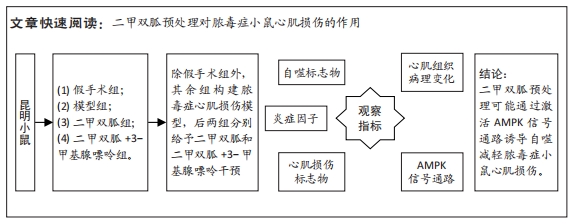
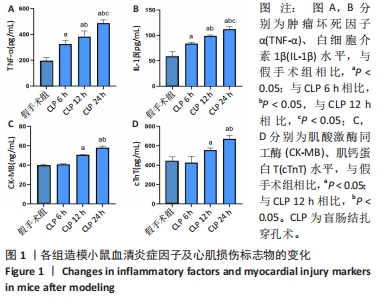
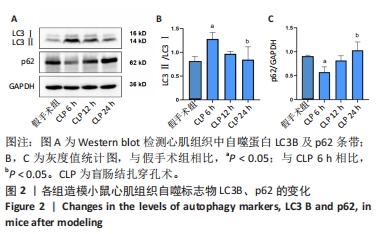
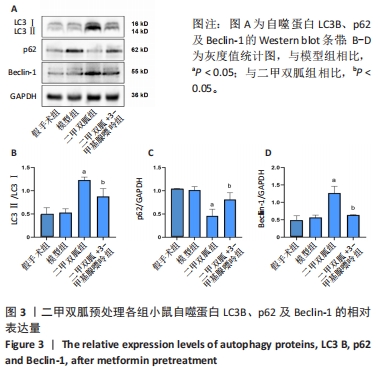
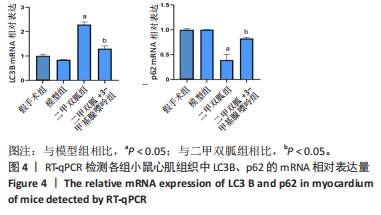
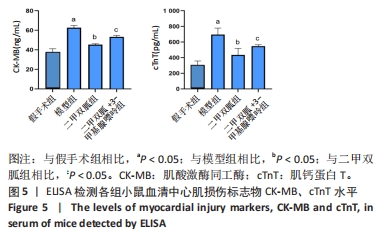
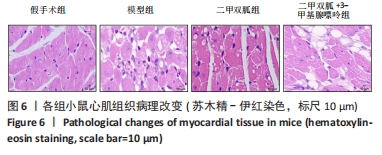
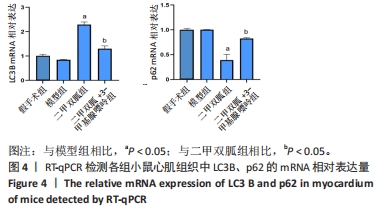
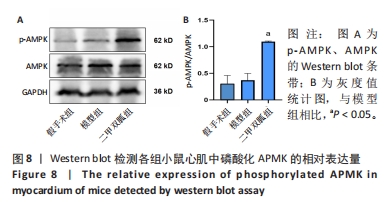
[1] ZHANG YY, NING BT. Signaling pathways and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):407.
[2] ZHOU B, ZHANG J, CHEN Y, et al. Puerarin protects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury through AMPK-mediated ferroptosis signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(8):3617-3632.
[3] LI Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG P, et al. Dehydrocorydaline Protects Against Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury Through Modulating the TRAF6/NF-κB Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:709604.
[4] BI CF, LIU J, YANG LS, et al. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:4275-4290.
[5] SUN Y, CAI Y, ZANG QS. Cardiac Autophagy in Sepsis. Cells. 2019; 8(2):141.
[6] ISMAIL HASSAN F, DIDARI T, KHAN F, et al. A Review on The Protective Effects of Metformin in Sepsis-Induced Organ Failure. Cell J. 2020;21(4): 363-370.
[7] KOLAHDOUZMOHAMMADI M, PAHLAVAN S, SOTOODEHNEJADNEMATALAHI F, et al. Activation of AMPK promotes cardiac differentiation by stimulating the autophagy pathway. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Apr 11. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00744-z.
[8] LI Q, WANG L, JI D, et al. Metformin attenuates cadmium-induced degeneration of spiral ganglion neuron via restoring autophagic flux in primary culture. J Inorg Biochem. 2022;234:111901.
[9] LI W, HE P, HUANG Y, et al. Selective autophagy of intracellular organelles: recent research advances. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):222-256.
[10] HUANG M, CAI S, SU J. The Pathogenesis of Sepsis and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(21):5376.
[11] GROSS AS, GRAEF M. Mechanisms of Autophagy in Metabolic Stress Response. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(1):28-52.
[12] LIU C, LIU Y, CHEN H, et al. Myocardial injury: where inflammation and autophagy meet. Burns Trauma. 2023;11:tkac062.
[13] 蒋大军,蒋万威,周颖,等.NLRC4炎症小体介导自噬反应在脓毒症心肌功能障碍小鼠中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(23): 3667-3673.
[14] JINPIAO Z, ZONGZE Z, QIUYUE Y, et al. Metformin attenuates sevoflurane-induced neurocognitive impairment through AMPK-ULK1-dependent autophagy in aged mice. Brain Res Bull. 2020;157:18-25.
[15] LI T, CHEN Y, LI Y, et al. FAM134B-mediated endoplasmic reticulum autophagy protects against sepsis myocardial injury in mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(10):13535-13547.
[16] EVANS L, RHODES A, ALHAZZANI W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47(11):1181-1247.
[17] PÓVOA P, COELHO L, DAL-PIZZOL F, et al. How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians. Intensive Care Med. 2023;49(2):142-153.
[18] LIU C, ZOU Q, TANG H, et al. Melanin nanoparticles alleviate sepsis-induced myocardial injury by suppressing ferroptosis and inflammation. Bioact Mater. 2022;24:313-321.
[19] 杭成文,崔鸣.脓毒症致心肌损伤模型的研究进展[J].中国心血管杂志,2020,25(5):485-488.
[20] HO J, YU J, WONG SH, et al. Autophagy in sepsis: Degradation into exhaustion? Autophagy. 2016;12(7):1073-1082.
[21] ALA M, ALA M. Metformin for Cardiovascular Protection, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Osteoporosis, Periodontitis, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, Neurodegeneration, Cancer, Inflammation and Senescence: What Is Next? ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021;4(6):1747-1770.
[22] CEJUELA M, MARTIN-CASTILLO B, MENENDEZ JA, et al. Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2705.
[23] LIU G, WU K, ZHANG L, et al. Metformin attenuated endotoxin-induced acute myocarditis via activating AMPK. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47:166-172.
[24] ZHANG M, SUN W, DU J, et al. Protective Effect of Metformin on Sepsis Myocarditis in Zebrafish. Dose Response. 2020;18(3): 1559325820938543.
[25] LIANG H, SONG H, ZHANG X, et al. Metformin attenuated sepsis-related liver injury by modulating gut microbiota. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022;11(1):815-828.
[26] ZHAO H, LYU Y, ZHAI R, et al. Metformin Mitigates Sepsis-Related Neuroinflammation via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Front Immunol. 2022;13:797312.
[27] GHAVIMI H, SHEIDAEI S, VAEZ H, et al. Metformin-attenuated sepsis-induced oxidative damages: a novel role for metformin. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018;21(5):469-475.
[28] TANG G, YANG H, CHEN J, et al. Metformin ameliorates sepsis-induced brain injury by inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):97977-97989.
[29] 高婷,陈忠.二甲双胍对脂多糖诱导的大鼠心肌细胞H9C2损伤的保护机制[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(9):1298-1303.
[30] LI M, GOU Y, YU H, et al. Mechanism of Metformin on LPS-Induced Bacterial Myocarditis. Dose Response. 2019;17(2):1559325819847409.
[31] WU B, SONG H, FAN M, et al. Luteolin attenuates sepsis‑induced myocardial injury by enhancing autophagy in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(5):1477-1487.
[32] TANG R, JIA L, LI Y, et al. Narciclasine attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by modulating autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 2021; 13(11):15151-15163.
[33] WANG X, XIE D, DAI H, et al. Clemastine protects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury in vivo and in vitro. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):7134-7146.
[34] WU S, ZHANG H, CHEN N, et al. Metformin protects cardiomyocytes against oxygen-glucose deprivation injury by promoting autophagic flux through AMPK pathway. J Drug Target. 2021;29(5):551-561.
[35] WEN X, XIE B, YUAN S, et al. The “Self-Sacrifice” of ImmuneCells in Sepsis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:833479.
[36] QIU P, LIU Y, ZHANG J. Review: the Role and Mechanisms of Macrophage Autophagy in Sepsis. Inflammation. 2019;42(1):6-19.
[37] LU G, WU Z, SHANG J, et al. The effects of metformin on autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111286.
[38] HUANG KY, QUE JQ, HU ZS, et al. Metformin suppresses inflammation and apoptosis of myocardiocytes by inhibiting autophagy in a model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2559-2579.
[39] WANG Y, YANG Z, ZHENG G, et al. Metformin promotes autophagy in ischemia/reperfusion myocardium via cytoplasmic AMPKα1 and nuclear AMPKα2 pathways. Life Sci. 2019;225:64-71.
[40] WANG Y, AN H, LIU T, et al. Metformin Improves Mitochondrial Respiratory Activity through Activation of AMPK. Cell Rep. 2019;29(6): 1511-1523.e5.
[41] BU Y, PENG M, TANG X, et al. Protective effects of metformin in various cardiovascular diseases: Clinical evidence and AMPK-dependent mechanisms. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(19):4886-4903.
[42] TURCO E, FRACCHIOLLA D, MARTENS S. Recruitment and Activation of the ULK1/Atg1 Kinase Complex in Selective Autophagy. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(1):123-134.
[43] LI SX, LI C, PANG XR, et al. Metformin Attenuates Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:719589.
[44] SONG H, ZHANG X, ZHAI R, et al. Metformin attenuated sepsis-associated liver injury and inflammatory response in aged mice. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):4598-4609.
[45] LI Y, CHEN Y. AMPK and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:85-108.
[46] LAMOIA TE, SHULMAN GI. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin Action. Endocr Rev. 2021;42(1):77-96.
[47] TZANAVARI T, VARELA A, THEOCHARIS S, et al. Metformin protects against infection-induced myocardial dysfunction. Metabolism. 2016; 65(10):1447-1458.
[48] DI MAURO S, FILIPPELLO A, SCAMPORRINO A, et al. Metformin: When Should We Fear Lactic Acidosis? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8320.
[49] L’HEUREUX M, STERNBERG M, BRATH L, et al. Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: a Comprehensive Review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020; 22(5):35.
[50] CHEN P, AN Q, HUANG Y, et al. Prevention of endotoxin-induced cardiomyopathy using sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate: Involvement of augmented autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome suppression. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;909:174438.
[51] 迪丽热巴•吐尔逊,杨春波,王毅,等.脓毒性心肌损伤机制及治疗的研究进展[J].中华危重病急救医学,2022,34(10):1112-1115.
[52] NIKOUEE A, KIM M, DING X, et al. Beclin-1-Dependent Autophagy Improves Outcomes of Pneumonia-Induced Sepsis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:706637. |