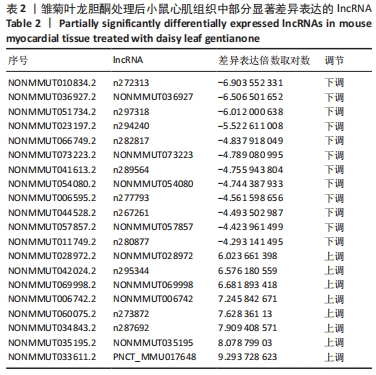
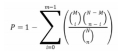1.1 设计 完全随机设计动物实验,组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用Tukey Test 检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2021年3月至2022年6月在河北中医学院完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 SPF级雄性C57小鼠48只,8周龄,体质量18-22 g,购自河北伊维沃生物科技有限公司,许可证号:SCXK(冀)2020-002。所有小鼠均饲养于标准动物房,分笼饲养,6只/笼,活动空间自由,食物和饮水充足,通风状况良好,12 h昼夜节律,环境温度控制在20-25 ℃,相对湿度保持在40%-70%。
实验已获得河北中医学院实验动物管理和伦理委员会审核批准,批准号:DWLL202212032。动物实验部分的设计和方案充分考虑了安全性和公平性原则,研究过程中涉及的实验动物和实验条件均符合国家对医学实验动物的相关要求,并且满足伦理学标准。
1.3.2 主要实验试剂 阿霉素购于默克 Merck公司;雏菊叶龙胆酮单体购于上海源叶生物科技有限公司;卡托普利购于上海源叶生物科技有限公司;苏木精-伊红染色试剂盒、Masson三色染色试剂盒和天狼猩红染色试剂盒均购于北京索莱宝生物科技有限公司;RNAsolid™组织RNA稳定保存液购于Servicebio 公司;RNA抽提试剂盒购于北京天漠科技开发有限公司;3%戊巴比妥钠(1030001,默克Merck公司);Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100(Agilent technologies,Santa Clara,CA,US);Qubit®3.0 Fluorometer(Life Technologies,CA,USA);Nanodrop One spectrophotometer(Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc,USA)。
1.3.3 主要实验仪器 安捷伦技术 2100 生物分析仪(Agilent 2100,安捷伦科技有限公司);QubitTM荧光计(Qubit4.0,Thermo Fisher);热循环仪应用生物系统(Applied Biosystems 2720,Thermo Fisher);高速低温离心机(5424R,Eppendorf);-80 ℃超低温冰箱(DW-86L828ST,中国海尔集团)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 实验分组与干预 采用随机数字表法将48只小鼠分为正常组、模型组、雏菊叶龙胆酮组和阳性药组,每组12只。模型组、雏菊叶龙胆酮组和阳性药组小鼠通过腹腔注射2.5 mg/kg阿霉素建立心肌损伤模型,正常组小鼠腹腔注射5 mL/kg的生理盐水,隔日一次,共8次[14]。通过心电图检查与心肌组织病理染色判断造模是否成功。在注射阿霉素的基础上,雏菊叶龙胆酮组小鼠灌胃给予 50 mg/(kg•d)的雏菊叶龙胆酮单体悬浊液[3],阳性药组小鼠灌胃给予3.61 mg/(kg•d)的卡托普利溶液,连续给药21 d。正常组小鼠每天灌胃给予5 mL/kg的生理盐水,连续21 d。

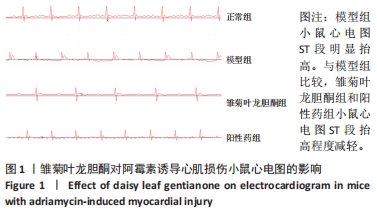
1.4.2 心电图检查 给药结束后,腹腔注射3%戊巴比妥钠50 mg/kg麻醉小鼠,仰卧位固定于实验台上,按照右上肢红色,左上肢黄色,左下肢绿色,右下肢黑色的连接方式,四肢皮下连接BL-420S生物机能实验系统,观察标准Ⅱ导联心电图,心电图监测60-120 s,进行心电图记录。
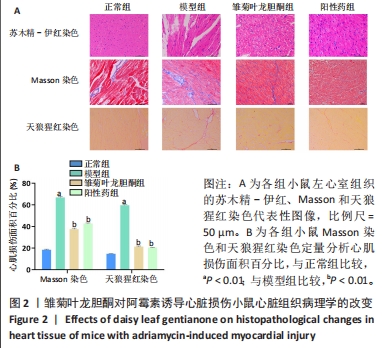
1.4.3 心肌组织病理形态学观察 完成心电图检查后,采用颈椎脱臼法处死小鼠,迅速摘除心脏,取左心室前壁组织,置于体积分数4%中性甲醛溶液中固定备用。固定后,将心肌组织常规脱水并石蜡包埋,之后将蜡块切为厚度为4 μm的连续切片。将切片置于45 ℃温水中展片,避免起皱,用载玻片捞出并将捞出的载玻片置于架子上。将捞出的组织切片置于40 ℃恒温箱中烘烤30 min,备用。
苏木精-伊红染色:将心肌组织的石蜡切片依次按照二甲苯Ⅰ(15 min)、二甲苯Ⅱ(15 min)、无水乙醇(5 min)、体积分数95%乙醇(5 min)、体积分数85%乙醇(5 min)、体积分数70%乙醇(5 min)、蒸馏水(5 min)顺序处理,常规脱蜡至水。擦干切片上的水分,苏木精染细胞核,切片入Harris苏木精染3-8 min,流水冲洗,1%盐酸乙醇分化数秒,流水冲洗,0.6%氨水返蓝,流水冲洗。伊红染细胞质,切片入伊红染液中染色1-3 min。之后将切片依次放入体积分数95%乙醇Ⅰ (5 min)、体积分数95%乙醇Ⅱ (5 min)、无水乙醇Ⅰ(5 min)、无水乙醇Ⅱ(5 min)、二甲苯Ⅰ(5 min)、二甲苯Ⅱ(5 min)中脱水透明,从二甲苯溶液中取出后稍晾干,中性树胶封固。于光学显微镜下观察,Leica图像采集系统采集图像。
Masson 染色:将心肌组织的石蜡切片常规脱蜡至水,然后将重铬酸钾滴加在组织切片上,4 ℃过夜,次日流水冲洗。铁苏木精A液与B液按1∶1混合成铁苏木精染液,将铁苏木精染液滴加在组织切片上,染色3 min,流水冲洗。用Masson 丽春红酸性复红液浸染5-10 min,流水漂洗。1%磷钼酸水溶液分化3-5 min,不经水洗,直接用苯胺蓝或光绿液染5 min。切片用1%冰醋酸分化数秒,无水乙醇脱水2次。切片再次放入无水乙醇5 min,二甲苯透明5 min,中性树胶封固。于光学显微镜下观察,Leica图像采集系统采集图像,利用Image-J图像分析系统分析蓝色胶原纤维分布情况及面积。
天狼猩红染色:将心肌组织的石蜡切片常规脱蜡至水,weigert铁苏木精染色液染色10-20 min;酸性分化液分化数秒;自来水洗5-10 min,蒸馏水洗一次;天狼猩红染色液滴染1 h,流水稍冲洗,去除切片表面染液;常规脱水透明,中性树胶封固。显微镜镜检,图像采集分析猩红色胶原纤维分布情况及面积。
1.4.4 心肌组织RNA抽提与质检
RNA的抽提与纯化:采用Tianmo#TR205-200试剂盒进行心肌组织的RNA抽提,抽提时严格遵循试剂盒生产厂商提供的标准操作流程手册进行,抽提得到的为样本总RNA。
RNA质检:抽提的总RNA采用Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100进行检验检测RNA的完整性,并使用Qubit®3.0 Fluorometer和Nanodrop One spectrophotometer来对总RNA进行浓度及纯度检测。
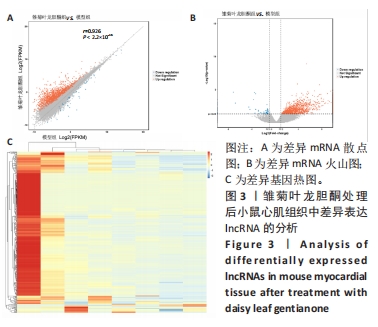
1.4.5 差异基因筛选 采用edgeR软件包对样本间/组间基因表达进行差异分析。计算得到P值后进行多重假设检验校正,通过控制FDR(False Discovery Rate)来决定P值的阈值,校正后的P值被称为Q 值。同时,根据FPKM值计算差异表达倍数,即fold change,简称FC,常常用log2(FC)来表示。使用这些参数来统计筛选差异基因。
一般情况下,FPKM数值0.1或者1作为判断基因是否表达的阈值,不同的文献所采用的阈值不同,差异基因分析默认对比较组中任意一组FPKM > 1的结果进行保留。
差异筛选标准为q或P < 0.05,此外FC2倍(|log2 Fold change|≥1)也是一个常用的标准,即表达值变化倍数为上调2倍(FC≥2/log2FC > 1)或下调2倍(FC≤0.5/ log2FC < -1)。
差异基因筛选标准为在比较组中任意一组FPKM > 1条件下: P < 0.05且FC2。
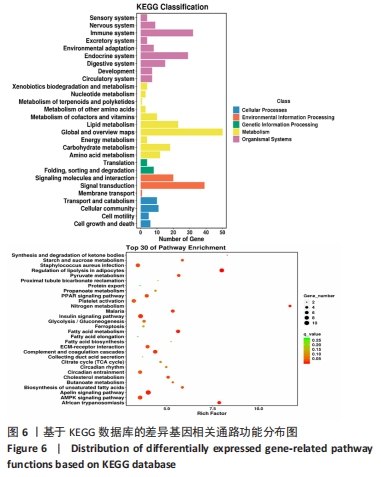
1.4.6 生物信息学分析 将差异表达的lncRNA 母源基因和 mRNA进行GO功能及KEGG通路富集分析,并利用cytoscape可视化软件进行mRNA-miRNA- LncRNA转录网络的构建。
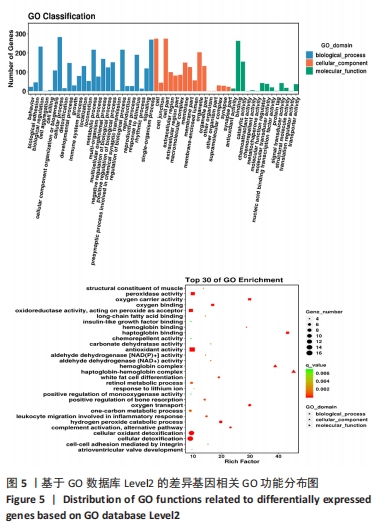
(1)差异基因GO富集:GO(gene ontology)是基因本体联合会(Gene Onotology Consortium)建立的数据库(http://geneontology.org/),目的在于建立对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述,可以适用于各个物种,并且随着研究不断深入而更新的语言词汇标准。
当研究的物种有相关GO注释数据库,直接使用该数据库进行GO的分析;若没有,则利用Blast2GO,得到每个基因对应的GO条目。针对GO数据库中的二级条目[直属于3个GO大类的条目:细胞组分(cellular component)、生物学过程(biological process)、分子功能(molecular function)],统计差异表达基因在该条目里的个数。
进一步还需要对差异基因进行GO富集分析。具体原理是把差异基因进行GO数据库条目内的注释映射,计算每个GO条目中的差异基因数目,再使用超几何检验进行统计,将注释结果与基因组背景相比,筛选在差异基因中显著富集的GO条目。
富集因子计算公式为:(该通路的差异基因/所有的差异基因)/(该通路的所有基因/所有通路的所有基因)。
富集显著性P值计算公式为:
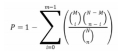
其中,N为所有基因中具有GO注释的基因数目;n为N中差异表达基因的数目;M为所有基因中注释为某特定GO条目的基因数目;m为注释为某特定GO条目的差异表达基因数目。P值通过多重假设检验校正之后,以q ≤ 0.05为阈值,满足此条件的GO条目定义为在差异表达基因中显著富集的GO条目。
(2)差异基因KEGG富集:KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,京都基因与基因组百科全书)是一个整合了基因组、化学和系统功能信息的数据库(http://geneontology.org/),旨在揭示生命现象的遗传与化学蓝图。KEGG具有强大的图形功能,它利用图形来介绍众多的代谢途径以及各途径之间的关系。
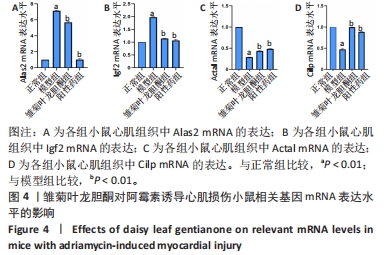
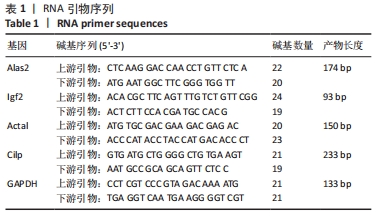
1.4.7 RT-PCR验证实验 取小鼠心肌组织,按提取试剂盒方法提取小鼠心脏总RNA,测定总RNA浓度和纯度,根据反转录试剂盒方法合成cDNA,低温保存。在NCBI数据库查询C57小鼠 Alas2、Igf2、Actal和Cilp的基因序列,由武汉赛维尔生物科技有限公司设计合成,各引物序列见表1。进行RT-PCR检测,分析结果并计算待测目的基因相对表达量。
1.5 主要观察指标 各组小鼠心电图与心肌组织病理形态观察结果,以及模型组与雏菊叶龙胆酮组小鼠心肌组织差异表达lncRNA筛选结果。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 21.0软件对数据进行统计分析。计数数据以百分率(%)表示,两组间比较采用卡方检验。计量数据以x±s表示,若满足正态性分布,采用Levene’s Test 检验进行两组间方差齐性检验,若方差齐则采用Tukey Test检验进行组间两两比较,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),若方差不齐则采用非参数秩和检验。所有假设均以α=0.05为水准。文章统计学方法已经河北中医学院基础医学院统计学专家审核。