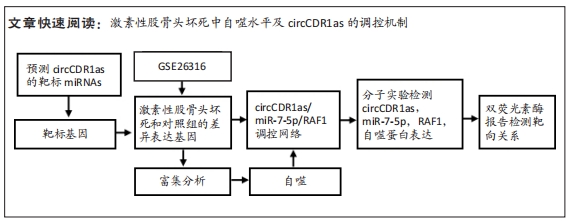
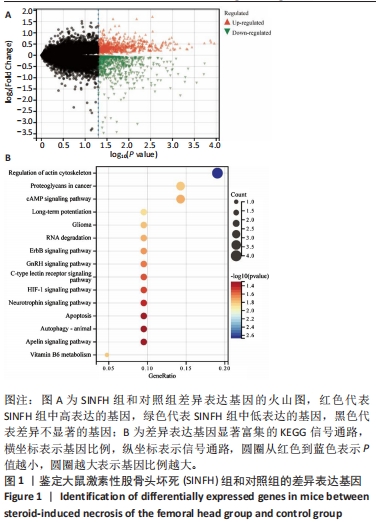
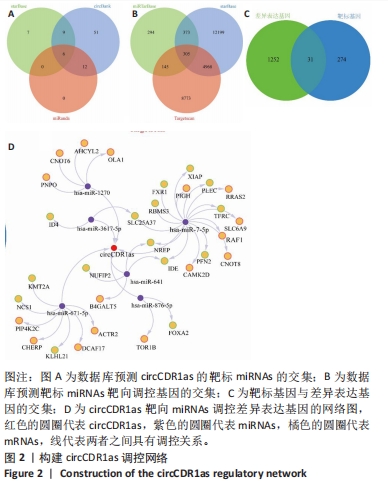
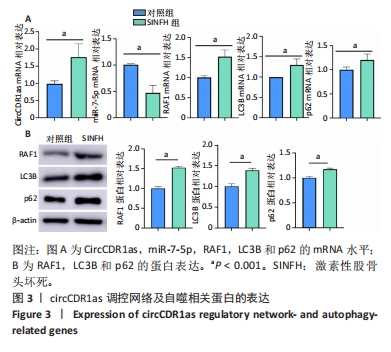
[1] FU D, QIN K, YANG S, et al. Proper mechanical stress promotes femoral head recovery from steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rats through the OPG/RANK/RANKL system. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21:281.
[2] REN GW, WEN SB, HAN J, et al. Network-Based Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Study on the Mechanism of Action of Gujiansan in the Treatment of Steroid-Induced Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8080679.
[3] LIU J, LI C, YANG F, et al. Effects of angiotensin II combined with asparaginase and dexamethasone on the femoral head in mice: A model of steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:975879.
[4] ZHANG F, PENG W, WANG T, et al. Lnc Tmem235 promotes repair of early steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting hypoxia-induced apoptosis of BMSCs. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54:1991-2006.
[5] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110.
[6] LI Z, SHAO W, LV X, et al. Advances in experimental models of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Translat. 2023;39:88-99.
[7] LIN T, CAI K, YANG P, et al. Composite indices of femoral neck strength predicts the collapse of steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23:722.
[8] LU C, QI H, XU H, et al. Global research trends of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A 30-year bibliometric analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1027603.
[9] LIU B, GAO F, XIU X, et al.Denosumab Can Prevent Collapse in Patients with Early-Stage Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Inhibiting Osteoclasts and Autophagy. Orthop Surg. 2023;15:256-265.
[10] 刘树义, 李凯, 兰凯, 等. 细胞自噬在激素性股骨头缺血坏死大鼠发病中的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(4):896-900.
[11] KRISTENSEN LS, ANDERSEN MS, STAGSTED LVW, et al.The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20: 675-691.
[12] 成衍男, 潘振宇. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J].临床外科杂志,2023,31(4):301-304.
[13] CHEN G, WANG Q, LI Z, et al. Circular RNA CDR1as promotes adipogenic and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone. 2020;133:115258.
[14] IRIZARRY RA, HOBBS B, COLLIN F, et al. Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 2003;4:249-264.
[15] LIANG C, LI W, HUANG Q, et al. CircFKBP5 Suppresses Apoptosis and Inflammation and Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation. Int Dent J. 2023;73:377-386.
[16] PAN X, CEN X, ZHANG B, et al. Circular RNAs as potential regulators in bone remodeling: a narrative review. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:1505.
[17] 艾克热木江•阿尔肯, 日夏提•帕尔哈提, 张峥, 等. 敲低CircCDR1as在糖皮质激素诱导的骨微血管内皮细胞活性及血管生成中的作用研究[J]河北医学,2022,28(12):1937-1943.
[18] KYEI B, LI L, YANG L, et al.CDR1as/miRNAs-related regulatory mechanisms in muscle development and diseases. Gene. 2020;730:144315.
[19] HUANG C, WEN Z, NIU J, et al. Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Novel Insight Into the Roles of Bone Endothelial Cells in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:777697.
[20] JIANG B, ZHU SH, ZENG JY, et al. Plasma and local expressions of CircRNA CDR1as are linked with disease severity in patients with non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15:592.
[21] 高岭, 郅克谦. 低氧微环境下circCDR1as通过AKT/ERK?/mTOR通路调控自噬促进口腔鳞状细胞存活的实验研究[C]. 2019第一届全国口腔颌面-头颈肿瘤学术大会——聚合引领、协同发展论文汇编, 上海:2019.
[22] CUI L, HUANG C, ZHOU D. Overexpression of circCDR1as drives oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. Oral Dis. 2023;29:957-967.
[23] TANG X, WANG J, XIA X, et al. Elevated expression of ciRS-7 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Diagn Pathol. 2019;14(1):11.
[24] MO L, WANG Z, HUANG H, et al. Integrated Analysis of Crucial Genes and miRNAs Associated with Osteoporotic Fracture of Type 2 Diabetes. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:3921570.
[25] HAN J, LUO Z, WANG Y, et al. LncRNA ZFAS1 protects chondrocytes from IL-1beta-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation via regulating miR-7-5p/FLRT2 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18:320.
[26] LIU C, LIU J, CHEN H. Overexpression of miR-7-5p Promoted Fracture Healing Through Inhibiting LRP4 and Activating Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2023:15347346231157443.
[27] WANG C, TANG Z, ZHANG Z, et al. MiR-7-5p suppresses invasion via downregulation of the autophagy-related gene ATG7 and increases chemoresistance to cisplatin in BCa. Bioengineered. 2022;13:7328-7339.
[28] MA C, GU R, WANG X, et al. circRNA CDR1as Promotes Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification by Upregulating CAMK2D and CNN3 via Sponging miR-7-5p. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:530-541.
[29] LIANG XZ, LUO D, CHEN YR, et al. Identification of potential autophagy-related genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17:86.
[30] ZHANG B, LI F, ZHU Z, et al. CircRNA CDR1as/miR-1287/Raf1 Axis Modulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through MEK/ERK Pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:8951-8964.
[31] ZHANG P, ZHENG Z, LING L, et al. w09, a novel autophagy enhancer, induces autophagy-dependent cell apoptosis via activation of the EGFR-mediated RAS-RAF1-MAP2K-MAPK1/3 pathway. Autophagy. 2017;13: 1093-1112.
[32] 马海龙, 赵振群, 刘万林, 等. 自噬基因微管相关蛋白1轻链3参与模型兔激素性股骨头缺血坏死的发生与发展[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5167-5172.
|