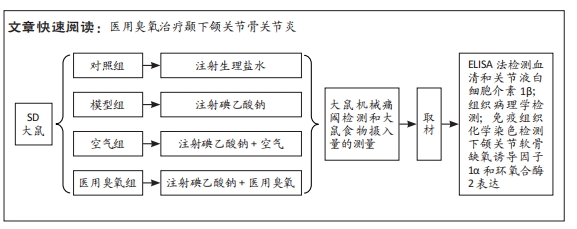
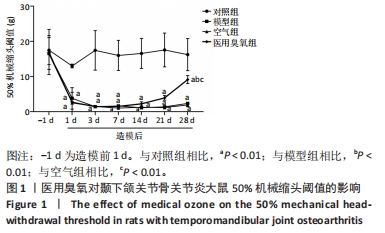
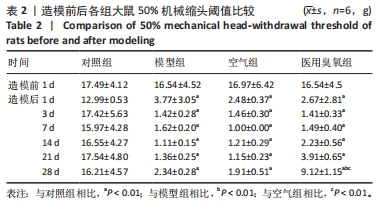
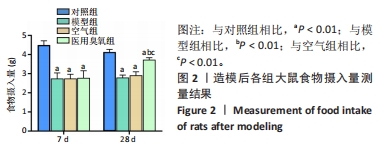
[1] LIU X, ZHAO J, JIANG H, et al. ALPK1 Aggravates TMJOA Cartilage Degradation via NF-kappaB and ERK1/2 Signaling. J Dent Res. 2022;101(12):1499-509.
[2] CHEN XY, HAO YR, WANG Z, et al. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on aggrecan and type II collagen expression in rat articular chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(11):3359-3364.
[3] DERWICH M, MITUS-KENIG M, PAWLOWSKA E. Interdisciplinary Approach to the Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis-Review of the Literature. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(5):225.
[4] 李飞,崔雪英,王利刚,等.颞下颌关节紊乱患者慢性疼痛与自我调节疲劳的关系[J].中国心理卫生杂志,2019,33(8):583-586.
[5] GROSS TS, KING KA, RABAIA NA, et al. Upregulation of osteopontin by osteocytes deprived of mechanical loading or oxygen. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(2):250-256.
[6] XU Z, KE T, ZHANG Y, et al. Danshensu inhibits the IL-1beta-induced inflammatory response in chondrocytes and osteoarthritis possibly via suppressing NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Med. 2021;27(1): 80.
[7] SHARMA V, BHATIA P, ALAM O, et al. Recent advancement in the discovery and development of COX-2 inhibitors: Insight into biological activities and SAR studies (2008-2019). Bioorg Chem. 2019;89:103007.
[8] ZENG CY, WANG XF, HUA FZ. HIF-1alpha in Osteoarthritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:927126.
[9] GAO P, RAO ZW, LI M, et al. Erratum to: Tetrandrine Represses Inflammation and Attenuates Osteoarthritis by Selective Inhibition of COX-2. Curr Med Sci. 2023; 43(4):845-846.
[10] LU J, ZHANG H, PAN J, et al. Fargesin ameliorates osteoarthritis via macrophage reprogramming by downregulating MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):142.
[11] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[12] 刘庆华.音频和电脑脉冲超短波治疗颞下颌关节紊乱症对比研究[J].吉林医学,2013,34(10):1843-1844.
[13] 董亚炜,李述文,贾雁,等.《中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021版)》中医药相关内容解读[J].世界中医药,2023,18(16):2377-2381.
[14] 阳越,王志刚,毛田,等.富血小板血浆与玻璃酸钠治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床疗效对比[J].现代诊断与治疗,2023,34(1):78-80.
[15] 胡宇奇,王仁伟,王北洋,等.医用臭氧治疗膝骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2023,45(2):283-287.
[16] 任芹,赵序利,万燕杰.医用臭氧治疗膝骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].实用疼痛学杂志,2006,2(2):67-69.
[17] 张婉霞,尼加提·努尔穆罕默德,买斯吐热木·黒力力,等.关节腔内注射医用臭氧治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎模型大鼠的合适剂量[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3700-3705.
[18] SHEN Q, HUANG W, QIU Y, et al. Bergapten exerts a chondroprotective effect in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by combining intestinal flora alteration and reactive oxygen species reduction. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;167:115525.
[19] 李棋,毛云鹤,李箭.玻璃酸钠在骨科和运动医学相关疾病中的应用专家共识(2017年修订版)解读 [J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2017,9(11):9-13.
[20] BOCCI V. Ozone as Janus: this controversial gas can be either toxic or medically useful. Mediators Inflamm. 2004;13(1):3-11.
[21] 曹兴,李建福,雷涛,等.玻璃酸钠腔内注射联合臭氧治疗对膝骨关节炎患者膝关节功能及疼痛程度的影响[J].按摩与康复医学,2022,13(12):29-32.
[22] HASSAN TA, SUHAIL ZA. The Efficacy of Ozonized Water Versus Ringer Lactate Arthrocentesis for the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Internal Derangement. J Craniofac Surg. 2023;34(3):e238-e241.
[23] WANG D, QI Y, WANG Z, et al. Recent Advances in Animal Models, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023;29(1):62-77.
[24] WANG MN, LIU L, ZHAO LP, et al. Research of inflammatory factors and signaling pathways in knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020;33(4):388-392.
[25] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257.
[26] VINCENT TL. IL-1 in osteoarthritis: time for a critical review of the literature. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000.
[27] SAMAD TA, MOORE KA, SAPIRSTEIN A, et al. Interleukin-1beta-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature. 2001;410(6827):471-475.
[28] FAN HW, LIU GY, ZHAO CF, et al. Differential expression of COX-2 in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(4):12872-12879.
[29] HSIAO HT, LIN YC, WANG JC, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha inhibition produced anti-allodynia effect and suppressed inflammatory cytokine production in early stage of mouse complex regional pain syndrome model. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(3):355-359.
[30] QING L, LEI P, LIU H, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in synovial fluid and articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(1):63-68.
[31] FRAISL P, ARAGONES J, CARMELIET P. Inhibition of oxygen sensors as a therapeutic strategy for ischaemic and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(2): 139-152.
[32] 廖超.臭氧注射、小针刀联合中药封包治疗在膝关节炎治疗中的应用[J].按摩与康复医学,2023,14(8):38-41.
[33] 杨文骞,王宇泽,孟志超,等.活性氧抑制剂对骨关节炎进展的影响[J].国际骨科学杂志,2023,44(4):247-250,255.
[34] VEGA RB, HORTON JL, KELLY DP. Maintaining ancient organelles: mitochondrial biogenesis and maturation. Circ Res. 2015;116(11):1820-1834.
[35] STUART JA, BROWN MF. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance and bioenergetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1757(2):79-89.
[36] ZHOU F, MEI J, YANG S, et al. Modified ZIF-8 Nanoparticles Attenuate Osteoarthritis by Reprogramming the Metabolic Pathway of Synovial Macrophages. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(2):2009-2022.
[37] YAMAMOTO N, OYAIZU T, ENOMOTO M, et al. VEGF and bFGF induction by nitric oxide is associated with hyperbaric oxygen-induced angiogenesis and muscle regeneration. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2744.
[38] 熊翱,魏小雨,许建中,等.碘乙酸单钠诱导SD大鼠膝骨关节炎后HIF-1α、OPN、IL-1β、TNF-α、MMP-13和NGF蛋白表达及意义[J].中国实验动物学报, 2023,31(5):643-652.
[39] WARBRICK I, RABKIN SW. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1alpha) as a factor mediating the relationship between obesity and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Obes Rev. 2019;20(5):701-712.
[40] TAKEDA K, ICHIKI T, NARABAYASHI E, et al. Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(12):2132-2137.
|