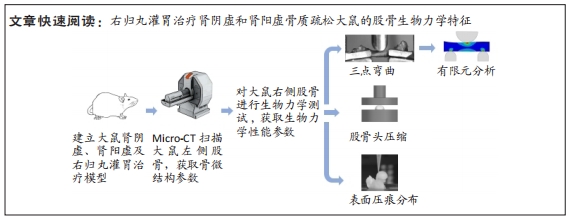
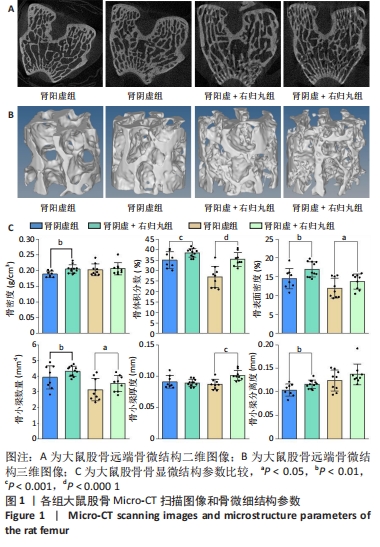
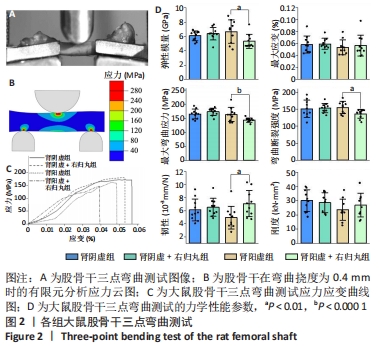
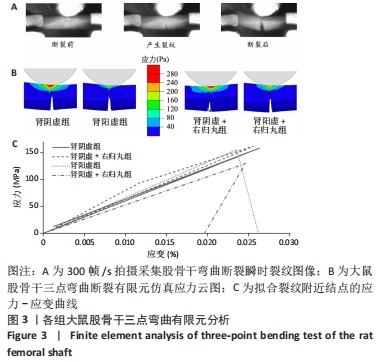
[1] LIN X, XIONG D, PENG YQ, et al. Epidemiology and management of osteoporosis in the People’s Republic of China: current perspectives. Clin Interv Aging. 2015; 10:1017-1033.
[2] WANG Y, TAO Y, HYMAN ME, et al. Osteoporosis in china. Osteoporosis Int. 2009; 20(10):1651-1662.
[3] LI L, LIU H, SHI W, et al. Insights into the Action Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017; 2017:5190986.
[4] PENG Z, XU R, YOU Q. Role of traditional Chinese medicine in bone regeneration and osteoporosis. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2022;10:911326.
[5] LU J, HU D, MA C, et al. Advances in Our Understanding of the Mechanism of Action of Drugs (including Traditional Chinese Medicines) for the Intervention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:938447.
[6] WANG ZQ, LI JL, SUN YL, et al. Chinese Herbal Medicine for Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trails. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:356260.
[7] CHEN R, WANG J, ZHAN R, et al. Fecal metabonomics combined with 16S rRNA gene sequencing to analyze the changes of gut microbiota in rats with kidney-yang deficiency syndrome and the intervention effect of You-gui pill. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;244:112139.
[8] WENXIONG L, KUAIQIANG Z, ZHU L, et al. Effect of Zuogui pill and Yougui pill on osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. J Tradit Chin Med. 2018;38(1):33-42.
[9] GU F, JIANG J, WANG S, et al. An experimental research into the potential therapeutic effects of Anti-Osteoporosis Decoction and Yougui Pill on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:6032-6039.
[10] COOK RB, CURWEN C, TASKER T, et al. Fracture toughness and compressive properties of cancellous bone at the head of the femur and relationships to non-invasive skeletal assessment measurements. Med Eng Phys. 2010;32(9):991-997.
[11] BURGERS TA, MASON J, NIEBUR G, et al. Compressive properties of trabecular bone in the distal femur. J Biomech. 2008;41(5):1077-1085.
[12] NAZARIAN A, ARAIZA ARROYO FJ, ROSSO C, et al. Tensile properties of rat femoral bone as functions of bone volume fraction, apparent density and volumetric bone mineral density. J Biomech. 2011;44(13):2482-2488.
[13] DUPARC F, THOMINE JM, SIMONET J, et al. Femoral and tibial bone torsions associated with medial femoro-tibial osteoarthritis. Index of cumulative torsions. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(1):69-74.
[14] MENG X, QIN Q, QU C. Tensile and compressive strain evolutions of bovine compact bone under four-point bending fatigue loading. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2021;123:104774.
[15] ARIAS-MORENO AJ, ITO K, VAN RIETBERGEN B. Accuracy of beam theory for estimating bone tissue modulus and yield stress from 3-point bending tests on rat femora. J Biomech. 2020;101:109654.
[16] WANG Y, MA Z, ZHENG Y, et al. Establishment of an osteoporosis model in tree shrews by bilateral ovariectomy and comprehensive evaluation. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(5):3644-3654.
[17] PANG WY, WANG XL, MOK SK, et al. Naringin improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts oestrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(8):1693-1703.
[18] VAN LENTHE GH, VOIDE R, BOYD SK, et al. Tissue modulus calculated from beam theory is biased by bone size and geometry: implications for the use of three-point bending tests to determine bone tissue modulus. Bone. 2008;43(4):717-723.
[19] SCHRIEFER JL, ROBLING AG, WARDEN SJ, et al. A comparison of mechanical properties derived from multiple skeletal sites in mice. J Biomech. 2005;38(3): 467-475.
[20] ROBLING AG, TURNER CH. Mechanotransduction in bone: genetic effects on mechanosensitivity in mice. Bone. 2002;31(5):562-569.
[21] RITCHIE RO, KOESTER KJ, IONOVA S, et al. Measurement of the toughness of bone: a tutorial with special reference to small animal studies. Bone. 2008;43(5): 798-812.
[22] KOMORI T. Animal models for osteoporosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;759:287-294.
[23] SIM S, LAVOIE JF, MOREAU A, et al. Novel technique to map the biomechanical properties of entire mice articular surfaces using indentation. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2014;22:S310-S311.
[24] ZHANG L, WANG PE, YING J, et al. Yougui Pills Attenuate Cartilage Degeneration via Activation of TGF-β/Smad Signaling in Chondrocyte of Osteoarthritic Mouse Model. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:1-11.
[25] 张悦,李运峰.骨质疏松症动物模型研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020, 26(1): 152-156.
[26] 何兴鹏,郑利钦,李鹏飞,等.两种肾虚证型去势模型大鼠骨小梁微观结构及骨代谢的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3768-3772.
[27] SIRIS ES, ADLER R, BILEZIKIAN J, et al. The clinical diagnosis of osteoporosis: a position statement from the National Bone Health Alliance Working Group. Osteoporosis Int. 2014;25(5):1439-1443.
[28] COUGHLAN T, DOCKERY F. Osteoporosis and fracture risk in older people. Clin Med (Lond). 2014;14:187-191.
[29] BLACK DM, SOLOMON CG, ROSEN CJ. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. New Engl J Med. 2016;374(3):254-262.
[30] POLZONETTI V, PUCCIARELLI S, VINCENZETTI S, et al. Dietary Intake of Vitamin D from Dairy Products Reduces the Risk of Osteoporosis. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1743.
[31] ARNOLD M, RAJAGUKGUK YV, GRAMZA-MICHAŁOWSKA A. Functional Food for Elderly High in Antioxidant and Chicken Eggshell Calcium to Reduce the Risk of Osteoporosis—A Narrative Review. Foods. 2021;10(3):656.
[32] KENDLER DL, COSMAN F, STAD RK, et al. Denosumab in the Treatment of Osteoporosis: 10 Years Later: A Narrative Review. Adv Ther. 2022;39(1):58-74.
[33] ZAHEER S, LEBOFF M, LEWIECKI EM. Denosumab for the treatment of osteoporosis. Expert Opin Drug Met. 2015;11(3):461-470.
[34] 刘瑞琦,王东凯.双膦酸盐类抗骨质疏松药物研究进展[J].中国药剂学杂志(网络版),2023,21(2):103-115.
[35] ORYAN A, SAHVIEH S. Effects of bisphosphonates on osteoporosis: Focus on zoledronate. Life Sci. 2021;264:118681.
[36] REID IR. Stopping osteoporosis medications. J Intern Med. 2021;290(6):1102-1104.
[37] SHU B, SHI Q, WANG YJ. Shen (Kidney)-tonifying principle for primary osteoporosis: to treat both the disease and the Chinese medicine syndrome. Chin J Integr Med. 2015;21(9):656-661.
[38] GU F, JIANG J, WANG S, et al. An experimental research into the potential therapeutic effects of Anti-Osteoporosis Decoction and Yougui Pill on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:6032-6039.
|