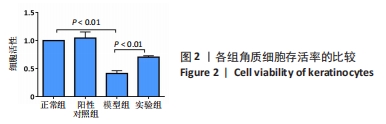
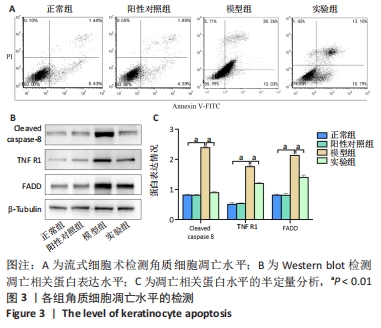
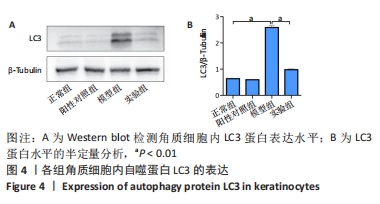
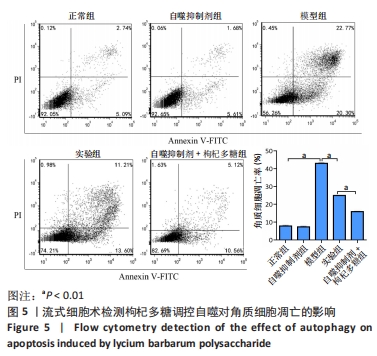
[1] 陈孝平,汪建平.外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2013.
[2] ORYAN A, ALEMZADEH E, MOSHIRI A. Burn wound healing: present concepts, treatment strategies and future directions. J Wound Care. 2017;26(1):5-19.
[3] SARKOZYOVA N, DRAGUNOVA J, BUKOVCAN P, et al. Preparation and processing of human allogenic dermal matrix for utilization in reconstructive surgical procedures. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2020;121(6):386-394.
[4] SHAKHAKARMI K, SEO JE, LAMICHHANE S, et al. EGF, a veteran of wound healing: highlights on its mode of action, clinical applications with focus on wound treatment, and recent drug delivery strategies. Arch Pharm Res. 2023;46(4):299-322.
[5] JING S, LI H, XU H. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Therapy in Diabetic Wound Repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:2707-2720.
[6] ZHAO D, XIAO J, QIANG L, et al. Walnut ointment promotes full-thickness burning wound healing: role of linoleic acid. Acta Cir Bras. 2022;37(9):e370902.
[7] LIU J. A new way of repairing special wounds. Heliyon. 2023;9(5): e15755.
[8] MARKS R. Seeing through the stratum corneum. Keio J Med. 2000; 49(2):80-83.
[9] NORLÉN L. Skin barrier structure and function: the single gel phase model. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117(4):830-836.
[10] VOEGELI R, RAWLINGS AV, BRETERNITZ M, et al. Increased stratum corneum serine protease activity in acute eczematous atopic skin. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161(1):70-77.
[11] FOLDVARI M, KUMAR P, KING M, et al. Gene delivery into human skin in vitro using biphasic lipid vesicles. Curr Drug Deliv. 2006;3(1):89-93.
[12] HORVÁTH D, SIPOS A, MAJOR E, et al. Myosin phosphatase accelerates cutaneous wound healing by regulating migration and differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes via Akt signaling pathway in human and murine skin. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(10):3268-3280.
[13] MORIYAMA M, MORIYAMA H, UDA J, et al. Beneficial Effects of the Genus Aloe on Wound Healing, Cell Proliferation, and Differentiation of Epidermal Keratinocytes. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0164799.
[14] GRIEB G. Basic and Clinical Research in Wound Healing. Biomedicines. 2023;11(5):1380.
[15] YU MS, LEUNG SK, LAI SW, et al. Neuroprotective effects of anti-aging oriental medicine Lycium barbarum against beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Exp Gerontol. 2005;40(8-9):716-727.
[16] CHEN L, LI W, QI D, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects against LPS-induced ARDS by inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation in pulmonary endothelial cells. Free Radic Res. 2018;52(4):480-490.
[17] ZHANG M, TANG X, WANG F, et al. Characterization of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and its effect on human hepatoma cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;61:270-275.
[18] NIU Y, ZHANG G, SUN X, et al. Distinct Role of Lycium barbarum L. Polysaccharides in Oxidative Stress-Related Ocular Diseases. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(2):215.
[19] RAJKOWSKA K, OTLEWSKA A, BRONCEL N, et al. Microbial Diversity and Bioactive Compounds in Dried Lycium barbarum Fruits (Goji): A Comparative Study. Molecules. 2023;28(10):4058.
[20] LI H, LI Z, PENG L, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects human keratinocytes against UVB-induced photo-damage. Free Radic Res. 2017;51(2):200-210.
[21] XIAO J, LIONG EC, CHING YP, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect rat liver from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-induced injury. Nutr Diabetes. 2013;3(7):e81.
[22] LAM CS, TIPOE GL, SO KF, et al. Neuroprotective mechanism of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides against hippocampal-dependent spatial memory deficits in a rat model of obstructive sleep apnea. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0117990.
[23] LENG H, PU L, XU L, et al. Effects of aloe polysaccharide, a polysaccharide extracted from Aloe vera, on TNF-α-induced HaCaT cell proliferation and the underlying mechanism in psoriasis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(3):3537-3543.
[24] XIAO M, LI L, LI C, et al. Role of autophagy and apoptosis in wound tissue of deep second-degree burn in rats. Acad Emerg Med. 2014; 21(4):383-391.
[25] SINSUEBPOL C, BURAPAPADH K, CHOWJAROEN V, et al. The radical scavenging activity of vanillin and its impact on the healing properties of wounds. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2023;14(2):99-104.
[26] GALLEGOS-ALCALÁ P, JIMÉNEZ M, CERVANTES-GARCÍA D, et al. Glycomacropeptide Protects against Inflammation and Oxidative Stress, and Promotes Wound Healing in an Atopic Dermatitis Model of Human Keratinocytes. Foods. 2023;12(10):1932.
[27] WOO YK, PARK J, RYU JH, et al. The anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of advanced anti-inflammation composition (AAIC) in heat shock-induced human HaCaT keratinocytes. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19(8):2114-2124.
[28] DONG Y, CHEN H, GAO J, et al. Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;136:27-41.
[29] CAO Y, LI Q, LIU L, et al. Modafinil protects hippocampal neurons by suppressing excessive autophagy and apoptosis in mice with sleep deprivation. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176(9):1282-1297.
[30] YOUNG TM, REYES C, PASNIKOWSKI E, et al. Autophagy protects tumors from T cell-mediated cytotoxicity via inhibition of TNFα-induced apoptosis. Sci Immunol. 2020;5(54):eabb9561.
[31] ZHU B, JIANG Q, QUE G, et al. Role of autophagy and apoptosis in atrophic epithelium in oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Sci. 2020;62(2): 184-188.
[32] ZHANG P, WANG H, CHEN Y, et al. DR5 related autophagy can promote apoptosis in gliomas after irradiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;522(4):910-916.
[33] ZHU S, LI X, DANG B, et al. Lycium Barbarum polysaccharide protects HaCaT cells from PM2.5-induced apoptosis via inhibiting oxidative stress, ER stress and autophagy. Redox Rep. 2022;27(1):32-44.
[34] WAJANT H. The Fas signaling pathway: more than a paradigm. Science. 2002;296(5573):1635-1636.
[35] KISCHKEL FC, HELLBARDT S, BEHRMANN I, et al. Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 1995;14(22):5579-5588.
[36] DJAVAHERI-MERGNY M, AMELOTTI M, MATHIEU J, et al. NF-kappaB activation represses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(41):30373-30382.
[37] DING R, LIU Z, TAN J, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products mediate human keratinocytes apoptosis by inducing cell autophagy through the mTOR-Beclin-1 pathway. Cell Biochem Funct. 2022;40(8): 880-887.
[38] TANG SC, KO JL, LU CT, et al. Chloroquine alleviates the heat-induced to injure via autophagy and apoptosis mechanisms in skin cell and mouse models. PLoS One. 2022;17(8):e0272797.
[39] FERNANDO PDSM, PIAO MJ, KANG KA, et al. Hesperidin Protects Human HaCaT Keratinocytes from Particulate Matter 2.5-Induced Apoptosis via the Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Autophagy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(7):1363.
[40] YOUNCE CW, KOLATTUKUDY PE. MCP-1 causes cardiomyoblast death via autophagy resulting from ER stress caused by oxidative stress generated by inducing a novel zinc-finger protein, MCPIP. Biochem J. 2010;426(1):43-53.
|