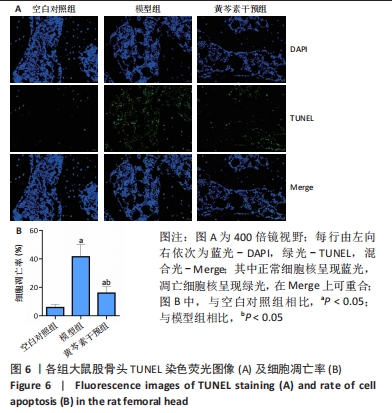
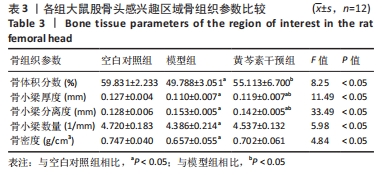
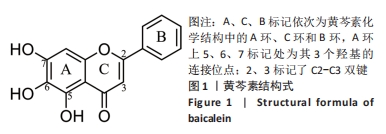
[1] KURODA T, TANABE N, WAKAMATSU A, et al. High triglyceride is a risk factor for silent osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34(12):2071-2077.
[2] HOUDEK MT, WYLES CC, PACKARD BD, et al. Decreased Osteogenic Activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Corticosteroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(4):893-898.
[3] XIE XH, WANG XL, YANG HL, et al. Steroid-associated osteonecrosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, animal model, prevention, and potential treatments (an overview). J Orthop Translat. 2015;3(2):58-70.
[4] KIM HJ. Glucocorticoids suppress bone formation via the osteoclast. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(8):2152-2160.
[5] CHEN K, LIU Y, HE J, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head reveals enhanced reactive oxygen species and hyperactive osteoclasts. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(11):1888-1900.
[6] JIA D, O’BRIEN CA, STEWART SA, et al. Glucocorticoids Act Directly on Osteoclasts to Increase Their Life Span and Reduce Bone Density. Endocrinology. 2006;147(12):5592-5599.
[7] ZHAN J, YAN Z, ZHAO M, et al. Allicin inhibits osteoblast apoptosis and steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head progression by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct. 2020;11(9):7830-7841.
[8] JIA YB, JIANG DM, REN YZ, et al. Inhibitory effects of vitamin E on osteocyte apoptosis and DNA oxidative damage in bone marrow hemopoietic cells at early stage of steroid-induced femoral head necrosis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):1585-1592.
[9] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020; 102(12):1084-1099.
[10] LEE Y J, CUI Q, KOO KH. Is There a Role of Pharmacological Treatments in the Prevention or Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head?: A Systematic Review. J Bone Metab. 2019;26(1):13.
[11] FU F, HUANG Z, YE H, et al. Mechanisms and Molecular Targets of the Tao-Hong-Si-Wu-Tang Formula for Treatment of Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head: A Network Pharmacology Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1-13.
[12] ZHANG P, XU H, WANG P, et al. Yougui pills exert osteoprotective effects on rabbit steroid-related osteonecrosis of the femoral head by activating β-catenin. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;120:109520.
[13] MEI R, CHEN D, ZHONG D, et al. Metabolic Profiling Analysis of the Effect and Mechanism of Gushiling Capsule in Rabbits With Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:845856.
[14] HUANG Z, FU F, YE H, et al. Chinese herbal Huo-Gu formula for the treatment of steroid-associated osteonecrosis of femoral head: A 14-year follow-up of convalescent SARS patients. J Orthop Translat. 2020;23:122-131.
[15] LI H, JIANG Y, CHEN F. Separation methods used for Scutellaria baicalensis active components. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004; 812(1):277-290.
[16] CHA MH, KIM IC, LEE BH, et al. Baicalein Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation by Enhancing COX-2 Expression. J Med Food. 2006;9(2):145-153.
[17] SEO MJ, CHOI HS, JEON HJ, et al. Baicalein inhibits lipid accumulation by regulating early adipogenesis and m-TOR signaling. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;67:57-64.
[18] RAHIMI VB, ASKARI VR, HOSSEINZADEH H. Promising influences of Scutellaria baicalensis and its two active constituents, baicalin, and baicalein, against metabolic syndrome: A review. Phytother Res. 2021;35(7):3558-3574.
[19] CAI P, LU Y, YIN Z, et al. Baicalein ameliorates osteoporosis via AKT/FOXO1 signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(13):17370-17379.
[20] JIN D, LI S, TANG J, et al. Regulation of bone formation by baicalein via the mTORC1 pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:5169-5183.
[21] KIM JM, LEE SU, KIM YS, et al. Baicalein stimulates osteoblast differentiation via coordinating activation of MAP kinases and transcription factors. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104(5):1906-1917.
[22] KIM MH, RYU SY, BAE MA, et al. Baicalein inhibits osteoclast differentiation and induces mature osteoclast apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46(11): 3375-3382.
[23] ZHANG X, ZHU Y, CHEN X, et al. Baicalein ameliorates inflammatory-related apoptotic and catabolic phenotypes in human chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;21(2):301-308.
[24] YI N, MI Y, XU X, et al. Baicalein Alleviates Osteoarthritis Progression in Mice by Protecting Subchondral Bone and Suppressing Chondrocyte Apoptosis Based on Network Pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:788392.
[25] YUNE TY, LEE JY, CUI CM, et al. Neuroprotective effect of Scutellaria baicalensis on spinal cord injury in rats . J Neurochem. 2009;110(4):1276-1287.
[26] DONG Q, CHU F, WU C, et al. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi extract protects against alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice and affects the mechanism of ER stress. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(4):3052-3062.
[27] DONG Y, LI Y, HUANG C, et al. Systemic application of teriparatide for steroid induced osteonecrosis in a rat model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:163.
[28] BAEK SH, KIM KH, LEE WK, et al. Abnormal Lipid Profiles in Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Comparison with Osteoarthritis Using Propensity Score Matching. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(Suppl 2):19-24.
[29] WU X, GENG C, SUN W, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors of Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head in Multiple Myeloma Patients Undergoing Dexamethasone-Based Regimens. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1-7.
[30] SAAD B, GHAREEB B, KMAIL A. Metabolic and Epigenetics Action Mechanisms of Antiobesity Medicinal Plants and Phytochemicals. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:1-19.
[31] WANG XH, GUO YW, TOLBA E, et al. Two-Armed Activation of Bone Mineral Deposition by the Flavones Baicalin and Baicalein, Encapsulated in Polyphosphate Microparticles. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(3):533-555.
[32] SAUL D, GLEITZ S, NGUYEN HH, et al. Effect of the lipoxygenase-inhibitors baicalein and zileuton on the vertebra in ovariectomized rats. Bone. 2017; 101:134-144.
[33] 桂林源, 刘世宇, 邱新毓, 等. 黄芩小分子化合物对雌激素缺乏骨质疏松的预防和治疗作用[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2016,26(5):294-300.
[34] 付方胜, 丁佳昕, 邵思远, 等. 黄芩素抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化和功能[J]. 锦州医科大学学报,2019,40(2):18-20+118-119.
[35] MAZUR CM, ANDRADE CDC, TOKAVANICH N, et al. Partial prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteocyte deterioration in young male mice with osteocrin gene therapy. iScience. 2022;25(9):105019.
[36] O’BRIEN CA, JIA D, PLOTKIN LI, et al. Glucocorticoids Act Directly on Osteoblasts and Osteocytes to Induce Their Apoptosis and Reduce Bone Formation and Strength. Endocrinology. 2004;145(4):1835-1841.
[37] MOUTSATSOU P, KASSI E, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in bone cells. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(6):348-359.
[38] FENG Z, ZHENG W, TANG Q, et al. Fludarabine inhibits STAT1-mediated up-regulation of caspase-3 expression in dexamethasone-induced osteoblasts apoptosis and slows the progression of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in rats. Apoptosis. 2017;22(8):1001-1012.
[39] TAO SC, YUAN T, RUI BY, et al. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):733-750.
[40] XUE X, FENG Z, LI Z, et al. Salidroside inhibits steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies. Mol Med Rep. 2017;17(3):3751-3757.
[41] ZHANG S, YE J, DONG G. Neuroprotective effect of baicalein on hydrogen peroxide-mediated oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in PC12 cells. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;40(3):311-320.
[42] JIN S, YANG L, MENG C, et al. Sequential Epiphyseal Cartilage Changes of Femoral Heads in C57BL/6 Female Mice Treated with Excessive Glucocorticoids. Cartilage. 2020;13(2_suppl):453S-464S.
[43] LU C, QI H, XU H, et al. Global research trends of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A 30-year bibliometric analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1027603.
[44] LU BB, LI KH. Lipoic acid prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatol Int. 2011;32(6):1679-1683.
[45] IUCHI T, AKAIKE M, MITSUI T, et al. Glucocorticoid Excess Induces Superoxide Production in Vascular Endothelial Cells and Elicits Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Circ Res. 2003;92(1):81-87.
[46] 周年, 刘波, 徐彭. 氧化应激与骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(12):1485-1489.
[47] 代重山, 汤树生, 张青杰, 等. 黄芩苷和黄芩素的生物学功能及其在动物生产中的应用[J]. 中国饲料,2015(8):11-14+18.
[48] DOK-GO H, LEE KH, KIM HJ, et al. Neuroprotective effects of antioxidative flavonoids, quercetin, (+)-dihydroquercetin and quercetin 3-methyl ether, isolated from Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Brain Res. 2003;965(1-2): 130-136.
[49] GRIGALIUS I, PETRIKAITE V. Relationship between Antioxidant and Anticancer Activity of Trihydroxyflavones. Molecules. 2017;22(12):2169.
[50] 李东, 宋启春, 赵研, 等. 白藜芦醇对兔激素诱导股骨头缺血性坏死抗氧化应激和抗凋亡作用的实验研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022, 37(12):1276-1280.
[51] 刘靖丽, 崔莹超. 黄芩素和黄芩苷抗氧化活性与结构关系的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 云南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2017,26(6):461-464.
[52] JIANG WB, ZHAO W, CHEN H, et al. Baicalin protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress through activation of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;45(3):303-311. |