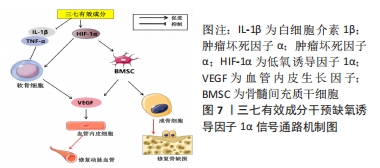
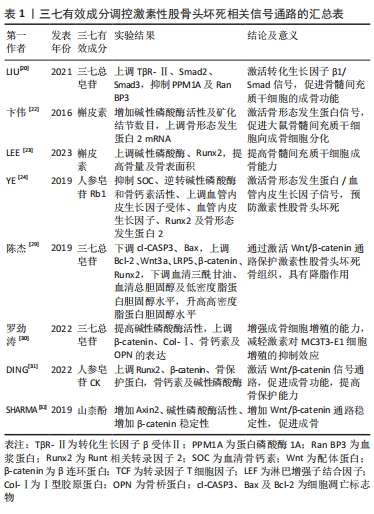
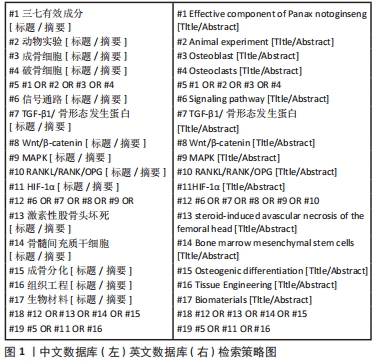
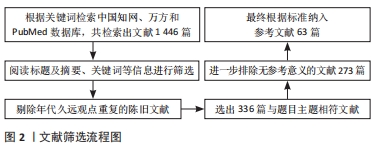
[1] MOTTA F, TIMILSINA S, GERSHWIN ME, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100168.
[2] TAN B, LI W, ZENG P, et al. Epidemiological study based on china osteonecrosis of the femoral head database. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(1):153-160.
[3] LU C, QI H, XU H, et al. Global research trends of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a 30-year bibliometric analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1027603.
[4] EXPERT PANEL ON MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING; HA AS, CHANG EY, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Osteonecrosis: 2022 Update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2022;19(11S):S409-S416.
[5] WANG A, REN M, WANG J. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109.
[6] HE P, CHEN J, YUE C,et al. Effectiveness and safety of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of steroid-osteonecrosis of femoral head: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(30):e26811.
[7] 蔡飞,王鹤,秦崇涛,等.血府逐瘀胶囊与血管内皮生长因子促血管新生差异研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2018,38(4):441-446.
[8] 张子龙,王文全.三七本草研究概述[J].世界科学技术(中医药现代化), 2010,12(2):271-276.
[9] WANG T, GUO R, ZHOU G, et al. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: a review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;188:234-258.
[10] 杨娟,袁一怔,尉广飞,等.三七植物化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].世界科学技术(中医药现代化),2017,19(10):1641-1647.
[11] QIANG H, LIU H, LING M, et al. Early steroid-induced osteonecrosis of rabbit femoral head and panax notoginseng saponins: mechanism and protective effects. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:719370.
[12] QIN L, YAO D, ZHENG L, et al. Phytomolecule icaritin incorporated PLGA/TCP scaffold for steroid-associated osteonecrosis: proof-of-concept for prevention of hip joint collapse in bipedal emus and mechanistic study in quadrupedal rabbits. Biomaterials. 2015;59:125-143.
[13] LOU P, ZHOU G, WEI B, et al. Bone grafting for femoral head necrosis in the past decade: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2023;109(3):412-418.
[14] MORIKAWA M, DERYNCK R, MIYAZONO K. TGF-β and the TGF-β family: context-dependent roles in cell and tissue physiology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8(5):a021873.
[15] LARSON C, ORONSKY B, CARTER CA, et al. TGF-beta: a master immune regulator. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020;24(5):427-438.
[16] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288.
[17] GARCIA J, DELANY AM. MicroRNAs regulating TGFβ and BMP signaling in the osteoblast lineage. Bone. 2021;143:115791.
[18] YANG X, CHEN Z, CHEN C, et al. Bleomycin induces fibrotic transformation of bone marrow stromal cells to treat height loss of intervertebral disc through the TGFβR1/Smad2/3 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):34.
[19] 陈镇秋,何伟,魏秋实,等.激素性股骨头坏死患者骨组织中骨代谢相关因子的表达[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(2):183-188.
[20] LIU D, ZHAO Z, JIANG W, et al. Panax notoginseng saponin promotes bone regeneration in distraction osteogenesis via the TGF-β1 signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:2895659.
[21] 韩杰,王世鑫,莫坚,等.三七总皂苷对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死模型兔骨组织血管内皮生长因子和骨形态形成蛋白2 mRNA表达的影响[J].广西医学,2016,38(5):611-614.
[22] 卞伟,杨丽,孙宏,等.槲皮素对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和骨向分化的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2016,32(5):27-30.
[23] LEE S, PARK H, OH JS, et al. Hydroxyapatite microbeads containing BMP2 and quercetin fabricated via electrostatic spraying to encourage bone regeneration. Biomed Eng Online. 2023;22(1):15.
[24] YE J, WEI D, PENG L, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents steroid induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head through the bone morphogenetic protein 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3175-3181.
[25] SHEN G, REN H, SHANG Q, et al. Foxf1 knockdown promotes BMSC osteogenesis in part by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. EBioMedicine. 2020;52:102626.
[26] LIU J, XIAO Q, XIAO J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):3.
[27] GAO J, XIANG S, WEI X, et al. Icariin promotes the osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through regulating sclerostin and activating the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6666836.
[28] ZHANG P, TAO F, LI Q, et al. 5-azacytidine and trichostatin a enhance the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells isolated from steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in rabbit. J Biosci. 2019;44(4):87.
[29] 陈杰,张堃,孔令俊,等.三七总皂苷通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路减轻家兔股骨头坏死[J].中药药理与临床,2019,35(4):95-99.
[30] 罗劲涛. 三七总皂苷对激素诱导的MC3T3-E1成骨前体细胞成骨分化影响的研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2022.
[31] DING L, GU S, ZHOU B, et al. Ginsenoside compound K enhances fracture healing via promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:855393.
[32] SHARMA AR, NAM JS. Kaempferol stimulates WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway to induce differentiation of osteoblasts. J Nutr Biochem. 2019;74: 108228.
[33] BIAN W, XIAO S, YANG L, et al. Quercetin promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation through the H19/miR-625-5p axis to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021;21(1):243.
[34] GUO YJ, PAN WW, LIU SB, et al. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(3):1997-2007.
[35] ROBERTS PJ, DER CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3291-3310.
[36] DROSTEN M, BARBACID M. Targeting the MAPK pathway in KRAS-driven tumors. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(4):543-550.
[37] LEE CH, HUANG YL, LIAO JF, et al. Ugonin K promotes osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization by activation of p38 MAPK- and ERK-mediated expression of Runx2 and osterix. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;668(3): 383-399.
[38] PENG P, NIE Z, SUN F, et al. Glucocorticoids induce femoral head necrosis in rats through the ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(1):312-321.
[39] GREENBLATT MB, SHIM JH, ZOU W, et al. The p38 MAPK pathway is essential for skeletogenesis and bone homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(7):2457-2473.
[40] ZENG HC, BAE Y, DAWSON BC, et al. MicroRNA miR-23a cluster promotes osteocyte differentiation by regulating TGF-beta signalling in osteoblasts. Nat Comms. 2017;8:15000.
[41] WANG C, SUN H, ZHONG Y. Notoginsenoside R1 promotes MC3T3-E1 differentiation by up-regulating miR-23a via MAPK and JAK1/STAT3 pathways. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):603-609.
[42] LIU Y, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Incorporation of NGR1 promotes bone regeneration of injectable HA/nHAp hydrogels by anti-inflammation regulation via a MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:992961.
[43] ZHAO S, YAN L, LI X, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 suppresses wear particle-induced osteolysis and RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47:118-125.
[44] LI XD, LIU ZY, CHANG B, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through the ERK and P38 MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28(2):367-76.
[45] YASUDA H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):2-11.
[46] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway: a mechanism involved in exercise-induced bone remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6910312.
[47] 陈锋,任国武,章晓云,等.核因子κB受体活化因子信号转导机制与破骨细胞的活化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):293-299.
[48] CHEN K, LIU Y, HE J, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head reveals enhanced reactive oxygen species and hyperactive osteoclasts. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(11):1888-1900.
[49] CONG F, LIU J, WANG C, et al. Ginsenoside Rb2 inhibits osteoclast differentiation through nuclear factor-kappaB and signal transducer and activator of transcription protein 3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;92:927-934.
[50] 方姝晨,邹季,史政康,等.三七总皂苷对股骨头坏死大鼠股骨头成骨作用影响的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(6):6-9, 15.
[51] 刘昭明,关智宇,蒋太平,等.由“从瘀论治”理论探讨三七中槲皮素对破骨细胞分化的自噬调控机制[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,12:1740-1744,1749.
[52] 王大伟,卢培根,贾永龙,等.三七总皂苷干预酒精性股骨头缺血坏死模型兔的超微结构[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(27):4277-4281.
[53] XU WN, ZHENG HL, YANG RZ, et al. HIF-1α regulates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through PDK1/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;10:922.
[54] LI HS, ZHOU YN, LI L, et al. HIF-1α protects against oxidative stress by directly targeting mitochondria. Redox Biol. 2019;25:101109.
[55] YING C, WANG R, WANG Z, et al. BMSC-exosomes carry mutant HIF-1α for improving angiogenesis and osteogenesis in critical-sized calvarial defects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:565561.
[56] WU J, YAO L, WANG B, et al. Tao-Hong-Si-Wu decoction ameliorates steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by regulating the HIF-1α pathway and cell apoptosis. Biosci Trends. 2016;10(5):410-417.
[57] HAN J, CHAI Y, ZHANG XY, et al. Gujiansan ameliorates avascular necrosis of the femoral head by regulating autophagy via the HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:6683007.
[58] ZHENG H, LIU C, OU Y, et al. Total saponins of Panax notoginseng enhance VEGF and relative receptors signals and promote angiogenesis derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013; 147(3):595-602.
[59] 伍海军,吴静澜,杨欣,等.基于网络药理学三七治疗缺血性脑卒中的作用机制研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2021,50(9):814-819.
[60] GAO J, YAO M, ZHANG W, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins alleviates inflammation induced by microglial activation and protects against ischemic brain injury via inhibiting HIF-1α/PKM2/STAT3 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;155:113479.
[61] 孙诗艺,颜炎,吴子轩,等.基于网络药理学和分子对接技术分析健脾活骨方治疗股骨头坏死的作用机制[J].中药新药与临床药理,2022, 33(10):1357-1365.
[62] REN GW, WEN SB, HAN J, et al. Network-based pharmacology and bioinformatics study on the mechanism of action of gujiansan in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8080679.
[63] FENG G, ZHANG P, HUANG J, et al. Sequential release of panax notoginseng saponins and osteopractic total flavone from Poly (-Lactic Acid) scaffold for treating glucocorticoid-associated osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(1):31. |