[1] GBD 2019 DISEASES AND INJURIES COLLABORATORS. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020; 396(10258):1204-1222.
[2] KNEZEVIC NN, CANDIDO KD, VLAEYEN JWS, et al. Low back pain. Lancet. 2021; 398(10294):78-92.
[3] Hooten WM, Cohen SP. Evaluation and Treatment of Low Back Pain. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90(12):1699-1718.
[4] ZHAO L, MANCHIKANTI L, KAYE AD, et al. Treatment of Discogenic Low Back Pain: Current Treatment Strategies and Future Options-a Literature Review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(11):86.
[5] BINCH AL, COLE AA, BREAKWELL LM, et al. Class 3 semaphorins expression and association with innervation and angiogenesis within the degenerate human intervertebral disc. Oncotarget. 2015;6(21):18338-18354.
[6] TOLOFARI SK, RICHARDSON SM, FREEMONT AJ, et al. Expression of semaphorin 3A and its receptors in the human intervertebral disc: potential role in regulating neural ingrowth in the degenerate intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010; 12(1):R1.doi: 10.1186/ar2898.
[7] VADASZ Z, TOUBI E. Semaphorin3A: A potential therapeutic tool in immune-mediated diseases. Eur J Rheumatol. 2018;5(1):58-61.
[8] 李瑶,孙中仪,戴健,等.椎间盘退变IL-1β激活NF-κB信号通路增强ADAMTS-4的表达[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(23):2177-2181.
[9] MIMA Y, SUZUKI S, FUJII T, et al. Potential involvement of semaphorin 3A in maintaining intervertebral disc tissue homeostasis. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(4): 972-980.
[10] CHEN F, JIANG G, LIU H, et al. Melatonin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by disrupting the IL-1β/NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammasome positive feedback loop. Bone Res. 2020;8:10.
[11] ZHONGYI S, SAI Z, CHAO L, et al. Effects of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(4):224-232.
[12] URITS I, BURSHTEIN A, SHARMA M, et al. Low Back Pain, a Comprehensive Review: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(3):23.
[13] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7.
[14] WEI A, BRISBY H, CHUNG SA, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 protects human intervertebral disc cells in vitro from apoptosis. Spine J. 2008;8(3):466-474.
[15] CAZZANELLI P, WUERTZ-KOZAK K. MicroRNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3601.
[16] LIAN C, GAO B, WU Z, et al. Collagen type II is downregulated in the degenerative nucleus pulposus and contributes to the degeneration and apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):4730-4736.
[17] MIYAGI M, MILLECAMPS M, DANCO AT, et al. ISSLS Prize winner: Increased innervation and sensory nervous system plasticity in a mouse model of low back pain due to intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39(17):1345-1354.
[18] BINCH A, CROSS AK, MAITRE CL. The regulation of nerve and blood vessel ingrowth in aneural and avascular intervertebral disc and articular cartilage. OA Arthritis. 2014;2(1):4.
[19] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356-2367.
[20] MOHD ISA IL, TEOH SL, MOHD NOR NH, et al. Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatments of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):208.
[21] AGILLI M, EKINCI S. Response to ‘increase of nerve growth factor levels in the human herniated intervertebral disc: can annular rupture trigger discogenic back pain?’. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):106.
[22] ROZBESKY D, VERHAGEN MG, KARIA D, et al. Structural basis of semaphorin-plexin cis interaction. EMBO J. 2020;39(13):e102926.
[23] YIN P, LV H, ZHANG L, et al. Semaphorin 3A: A Potential Target for Low Back Pain. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015;7:216.
[24] LI Z, HAO J, DUAN X, et al. The Role of Semaphorin 3A in Bone Remodeling. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:40.
[25] ADI SD, EIZA N, BEJAR J, et al. Semaphorin 3A Is Effective in Reducing Both Inflammation and Angiogenesis in a Mouse Model of Bronchial Asthma. Front Immunol. 2019;10:550.
[26] SUMI C, HIROSE N, YANOSHITA M, et al. Semaphorin 3A Inhibits Inflammation in Chondrocytes under Excessive Mechanical Stress. Mediators Inflamm. 2018; 2018:5703651.
[27] LEE JM, SONG JY, BAEK M, et al. Interleukin-1β induces angiogenesis and innervation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(2): 265-269.
[28] KIM H, HONG JY, LEE J, et al. IL-1β promotes disc degeneration and inflammation through direct injection of intervertebral disc in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. Spine J. 2021;21(6):1031-1041.
[29] YANG G, LIAO W, SHEN M, et al. Insight into neural mechanisms underlying discogenic back pain. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(11):4427-4436.
[30] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019; 11(22):10499-10512.
[31] RIVERA JC, SITARAS N, NOUEIHED B, et al. Microglia and Interleukin-1 in Ischemic Retinopathy Elicit Microvascular Degeneration Through Neuronal Semaphorin-3A. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(8):1881-1891.
[32] WU B, YANG L, PENG B. Ingrowth of Nociceptive Receptors into Diseased Cervical Intervertebral Disc Is Associated with Discogenic Neck Pain. Pain Med. 2019;20(6):1072-1077.
|
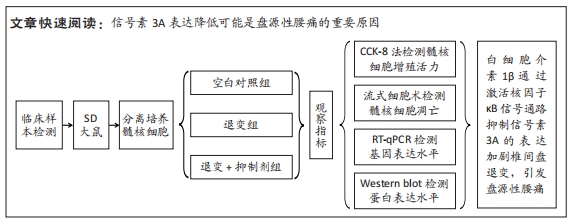
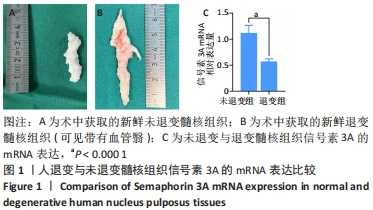
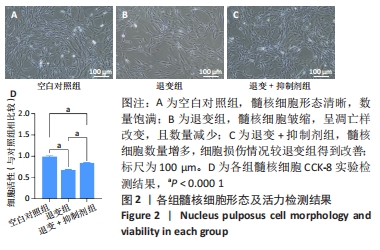
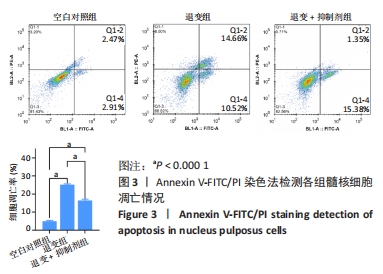
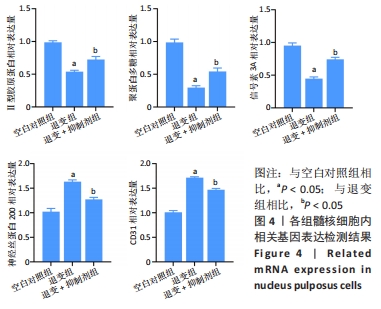
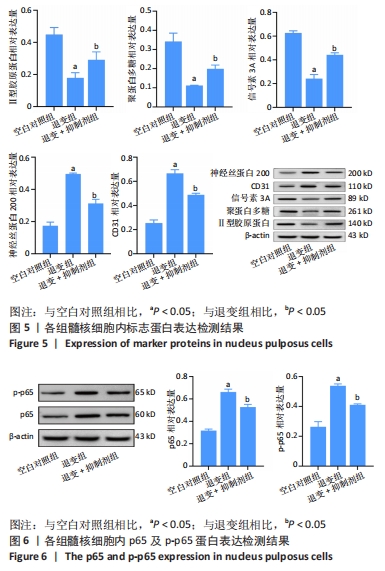
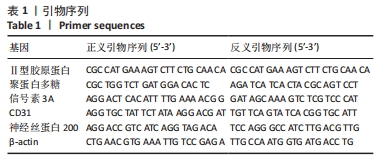
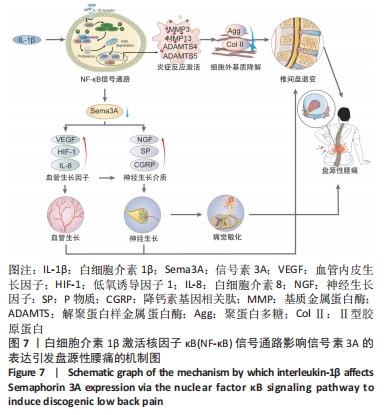 综上所述,促炎性因子白细胞介素1β通过诱导核因子κB信号通路的活化抑制信号素3A的表达;信号素3A的表达量下降在细胞外基质降解及诱导血管神经在退变椎间盘的分布过程中发挥关键作用,加剧椎间盘的退变;核因子κB通路抑制剂可以上调信号素3A的表达,进而有效延缓椎间盘退变的进程,为防治盘源性腰痛提供新的靶点和理论依据。
综上所述,促炎性因子白细胞介素1β通过诱导核因子κB信号通路的活化抑制信号素3A的表达;信号素3A的表达量下降在细胞外基质降解及诱导血管神经在退变椎间盘的分布过程中发挥关键作用,加剧椎间盘的退变;核因子κB通路抑制剂可以上调信号素3A的表达,进而有效延缓椎间盘退变的进程,为防治盘源性腰痛提供新的靶点和理论依据。