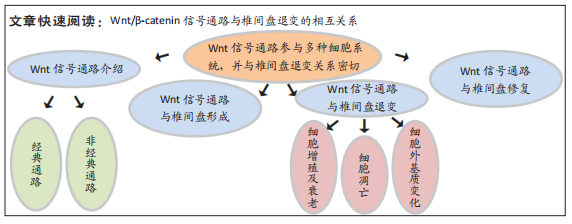
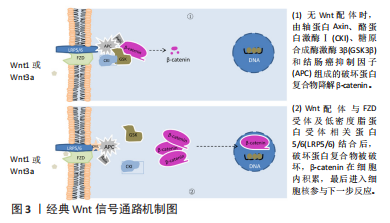
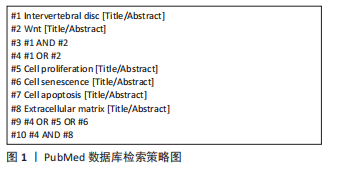
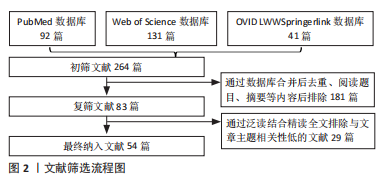
[1] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: the antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978.
[2] DISEASE GBD, INJURY I, PREVALENCE C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[3] BINCH ALA, FITZGERALD JC, GROWNEY EA, et al. Cell-based strategies for IVD repair: clinical progress and translational obstacles. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(3):158-175.
[4] OICHI T, TANIGUCHI Y, OSHIMA Y, et al. Pathomechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine. 2020;3(1):e1076.
[5] YANG F, LIU W, HUANG Y, et al. Regulated cell death: implications for intervertebral disc degeneration and therapy. J Orthop Translat. 2022;37: 163-172.
[6] LORZADEH S, KOHAN L, GHAVAMI S, et al. Autophagy and the Wnt signaling pathway: a focus on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021;1868(3):118926.
[7] MACDONALD BT, TAMAI K, HE X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling:components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17(1):9-26.
[8] GAJOS-MICHNIEWICZ A, CZYZ M. WNT Signaling in Melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4852.
[9] ZHAO H, MING T, TANG S, et al. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):144.
[10] ROUTLEDGE D, SCHOLPP S. Mechanisms of intercellular Wnt transport. Development. 2019;146(10):dev176073.
[11] FAN J, WEI Q, LIAO J, et al. Noncanonical Wnt signaling plays an important role in modulating canonical Wnt-regulated stemness, proliferation and terminal differentiation of hepatic progenitors. Oncotarget. 2017;8(16):27105-27119.
[12] CLARK CE, NOURSE CC, COOPER HM. The tangled web of non-canonical Wnt signalling in neural migration. Neurosignals. 2012;20(3):202-220.
[13] FRENQUELLI M, TONON G. WNT signaling in hematological malignancies. Front Oncol. 2020;10:615190.
[14] MCCANN MR, SéGUIN CA. Notochord cells in intervertebral disc development and degeneration. J Dev Biol. 2016;4(1):3.
[15] UKITA K, HIRAHARA S, OSHIMA N, et al. Wnt signaling maintains the notochord fate for progenitor cells and supports the posterior extension of the notochord. Mech Dev. 2009;126(10):791-803.
[16] KONDO N, YUASA T, SHIMONO K, et al. Intervertebral disc development is regulated by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(8): E513-E518.
[17] HIYAMA A, SAKAI D, RISBUD MV, et al. Enhancement of intervertebral disc cell senescence by WNT/β-catenin signaling-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(10):3036-3047.
[18] MARLAR S, JENSEN HH, LOGIN FH, et al. Aquaporin-3 in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2106.
[19] LI SB, YANG KS, ZHANG YT. Expression of aquaporins 1 and 3 in degenerative tissue of the lumbar intervertebral disc. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(4):8225-8233.
[20] XIE H, JING Y, XIA J, et al. Aquaporin 3 protects against lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2016; 37(3):859-864.
[21] HIYAMA A, MORITA K, SAKAI D, et al. CCN family member 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) is regulated by Wnt-β-catenin signaling in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):217.
[22] XIE D, ZHANG H, HU X, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA Taurine Up-Regulated 1 inhibited doxorubicin resistance of bladder urothelial carcinoma via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(51):88689-88696.
[23] CHEN J, JIA YS, LIU GZ, et al. Role of LncRNA TUG1 in intervertebral disc degeneration and nucleus pulposus cells via regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;491(3):668-674.
[24] LEHMANN M, HU Q, HU Y, et al. Chronic WNT/β-catenin signaling induces cellular senescence in lung epithelial cells. Cell Signal. 2020;70:109588.
[25] DING L, JIANG Z, WU J, et al. β‑catenin signalling inhibits cartilage endplate chondrocyte homeostasis in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(1):567-572.
[26] LIU C, LIU L, YANG M, et al. A positive feedback loop between EZH2 and NOX4 regulates nucleus pulposus cell senescence in age-related intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Div. 2020;15:2.
[27] WANG X, ZOU M, LI J, et al. LncRNA H19 targets miR-22 to modulate H2O2 - induced deregulation in nucleus pulposus cell senescence, proliferation, and ECM synthesis through Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(6):4990-5002.
[28] TREJO-SOLIS C, ESCAMILLA-RAMIREZ A, JIMENEZ-FARFAN D, et al. Crosstalk of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the induction of apoptosis on cancer cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(9):871.
[29] ZHU D, WANG Z, ZHANG G, et al. Periostin promotes nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2022;36(7):e22369.
[30] PENG Y, XIONG RP, ZHANG ZH, et al. Ski promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in fibroblasts under high-glucose conditions via the FoxO1 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(2):e12971.
[31] WU Z L, CHEN Y J, ZHANG G Z, et al. SKI knockdown suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and ameliorates disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 2022;27(1-2):133-148.
[32] HAO Y, REN Z, YU L, et al. p300 arrests intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the FOXO3/Sirt1/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Aging Cell. 2022;21(8):e13677.
[33] SHI Z, HE J, HE J, et al. High hydrostatic pressure (30 atm) enhances the apoptosis and inhibits the proteoglycan synthesis and extracellular matrix level of human nucleus pulposus cells via promoting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):3070-3081.
[34] RAN R, LIAO HY, WANG ZQ, et al. Mechanisms and functions of long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;235:153959.
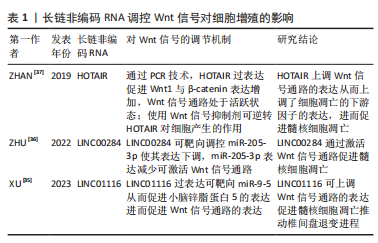
[35] XU S, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. LINC01116 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through miR-9-5p-mediated ZIC5 and the Wnt pathway and affects the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(7):979-992.
[36] ZHU M, YAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. lncRNA LINC00284 promotes nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and ECM synthesis via regulation of the miR‑205‑3p/Wnt/β‑catenin axis. Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(5):179.
[37] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201.
[38] YUN Z, WANG Y, FENG W, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-185 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration through inactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and downregulation of Galectin-3. Mol Pain. 2020;16:1744806920902559.
[39] SUN Z, JIAN Y, FU H, et al. MiR-532 downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling via targeting Bcl-9 and induced human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;138(4):263-270.
[40] ROUGHLEY PJ. Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(23): 2691-2699.
[41] SIVAN SS, HAYES AJ, WACHTEL E, et al. Biochemical composition and turnover of the extracellular matrix of the normal and degenerate intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J. 2014;23 Suppl 3:S344-S353.
[42] SONG Q, ZHANG F, WANG K, et al. MiR-874-3p plays a protective role in intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing MMP2 and MMP3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;895:173891.
[43] YE S, WANG J, YANG S, et al. Specific inhibitory protein Dkk-1 blocking Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway improve protectives effect on the extracellular matrix. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011;31(5):657.
[44] LIU H, SHEN J, ZHOU H, et al. Resveratrol regulate the extracellular matrix expression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32(4):476-483.
[45] XU Y, HE J, HE J. Cyanidin attenuates the high hydrostatic pressure-induced degradation of cellular matrix of nucleus pulposus cell via blocking the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Tissue Cell. 2022;76:101798.
[46] WANG X, WANG B, ZOU M, et al. CircSEMA4B targets miR-431 modulating IL-1β-induced degradative changes in nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc degeneration via Wnt pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(11):3754-3768.
[47] ZHANG F, LIN F, XU Z, et al. Circular RNA ITCH promotes extracellular matrix degradation via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(10):14185-14197.
[48] WINKLER T, MAHONEY EJ, SINNER D, et al. Wnt signaling activates Shh signaling in early postnatal intervertebral discs, and re-activates Shh signaling in old discs in the mouse. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e98444.
[49] COLOMBIER P, HALGAND B, CHéDEVILLE C, et al. NOTO transcription factor directs human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesendoderm progenitors to a notochordal fate. Cells. 2020;9(2):509.
[50] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, CHEN P, et al. Directed differentiation of notochord-like and nucleus pulposus-like cells using human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2020;30(8):2791-2806.e5.
[51] LUO L, GONG J, ZHANG H, et al. Cartilage endplate stem cells transdifferentiate into nucleus pulposus cells via autocrine exosomes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:648201.
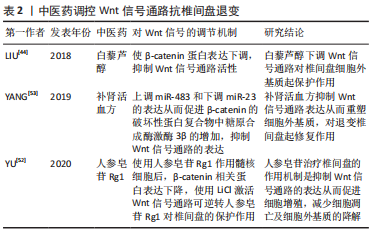
[52] YU L, HAO Y, PENG C, et al. Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on the intervertebral disc degeneration rats and the degenerative pulposus cells and its mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;123:109738.
[53] YANG S, LI L, ZHU L, et al. Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue-Fang modulates nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and extracellular matrix remodeling in intervertebral disk degeneration through miR-483 regulation of Wnt pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(12):19318-19329.
[54] PIZZUTE T, HE F, ZHANG XB, et al. Impact of Wnt signals on human intervertebral disc cell regeneration. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(12):3196-1207. |