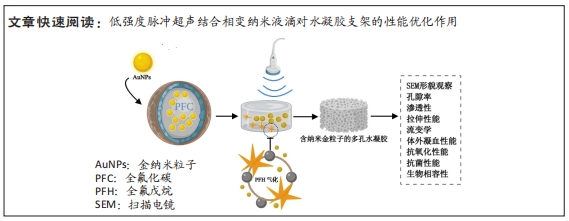
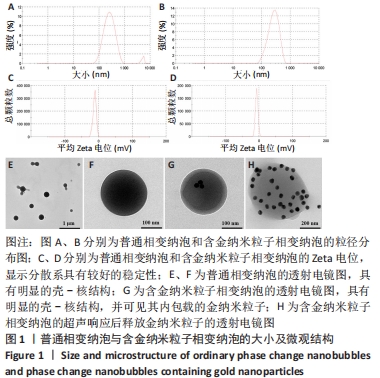
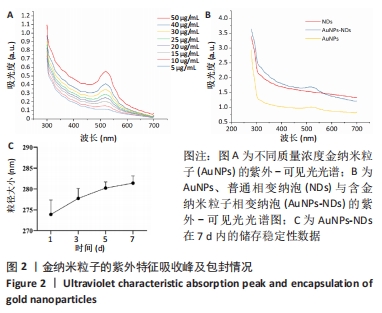
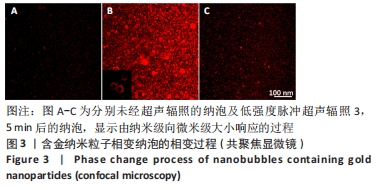
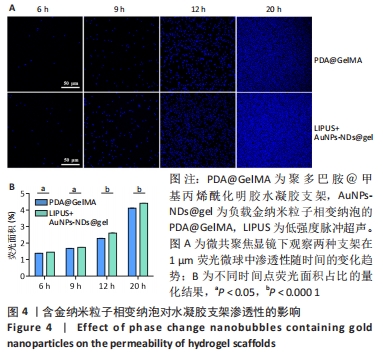
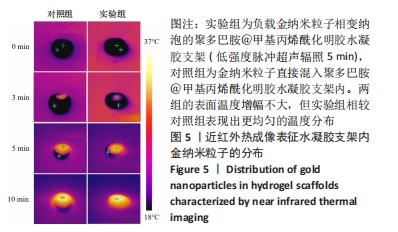
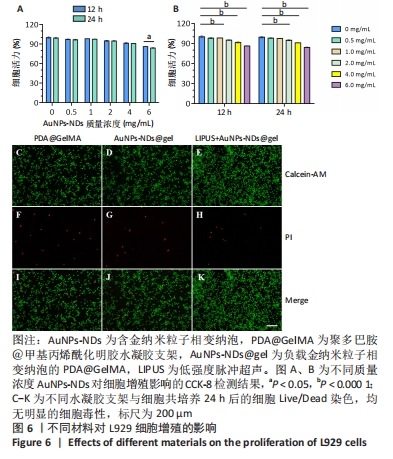
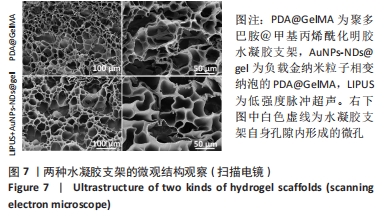
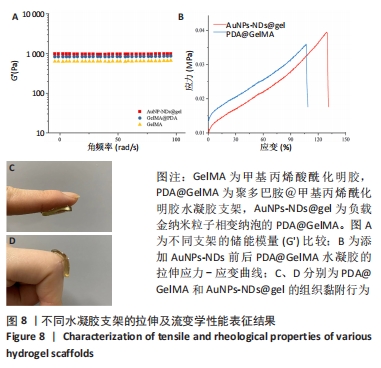
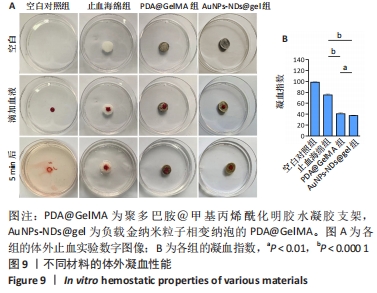
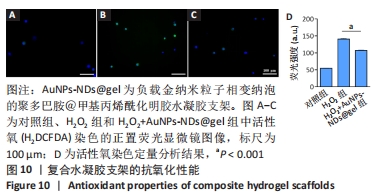
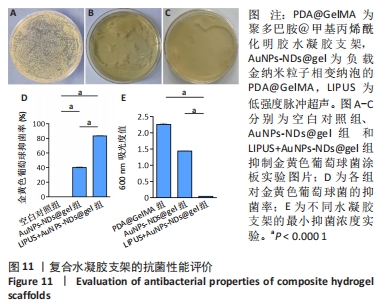
[1] GUNGOR S, KAHRAMAN E. Nanocarriers Mediated Cutaneous Drug Delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;158:105638.
[2] FENG X, CHEN Y. Drug delivery targets and systems for targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Drug Target. 2018;26(10):845-857.
[3] CHEN Y, FENG X. Gold nanoparticles for skin drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2022;625:122122.
[4] LABOUTA HI, LIU DC, LIN LL, et al. Gold nanoparticle penetration and reduced metabolism in human skin by toluene. Pharm Res. 2011; 28(11):2931-2944.
[5] FABIILLI ML, WILSON CG, PADILLAF, et al. Acoustic droplet-hydrogel composites for spatial and temporal control of growth factor delivery and scaffold stiffness. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7399-7409.
[6] 陈丹丹,靳巧锋,谢明星,等.超声响应性纳米载体的研究进展[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2020,29(6):548-552.
[7] CHOWDHURY SM, ABOU-ELKACEM L, LEE T, et al. Ultrasound and microbubble mediated therapeutic delivery: Underlying mechanisms and future outlook. J Control Release. 2020;326:75-90.
[8] AKTURK O, KISMET K, YASTI AC, et al. Collagen/gold nanoparticle nanocomposites: A potential skin wound healing biomaterial. J Biomater Appl. 2016;31(2):283-301.
[9] JIANG X, SAVCHENKO O, LI Y, et al. A Review of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound for Therapeutic Applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2019; 66(10):2704-2718.
[10] MA W, DONG W, ZHAO S, et al. An injectable adhesive antibacterial hydrogel wound dressing for infected skin wounds. Biomater Adv. 2022;134:112584.
[11] ZHANG Z, KUANG G, ZONG S, et al. Sandwich-Like Fibers/Sponge Composite Combining Chemotherapy and Hemostasis for Efficient Postoperative Prevention of Tumor Recurrence and Metastasis. Adv Mater. 2018;30(49):e1803217.
[12] SHI W, HASS B, KUSS MA, et al. Fabrication of versatile dynamic hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115803.
[13] WIEGAND I, HILPERT K, HANCOCK RE. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(2):163-175.
[14] ANNABI N, RANA D, SHIRZAEI SANI E, et al. Engineering a sprayable and elastic hydrogel adhesive with antimicrobial properties for wound healing. Biomaterials. 2017;139:229-243.
[15] 缪伟伟,王志雄,张俊利,等.聚羟基脂肪酸酯和聚酰胺-胺树状高分子构筑的经皮给药系统[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(52): 8433-8437.
[16] KIM YJ, KIM B, KIM JW, et al. Combination of nanoparticles with photothermal effects and phase-change material enhances the non-invasive transdermal delivery of drugs. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;135:324-331.
[17] BESSAR H, VENDITTI I, BENASSI L, et al. Functionalized gold nanoparticles for topical delivery of methotrexate for the possible treatment of psoriasis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;141:141-147.
[18] MAHMOUD NN, AL-QAOUD KM, AL-BAKRI AG, et al. Colloidal stability of gold nanorod solution upon exposure to excised human skin: Effect of surface chemistry and protein adsorption. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;75:223-231.
[19] 任超宇,薛鹏程,焦雄,等.超声波作用下SiO2纳米颗粒的分离[J].高压物理学报,2018,32(4):60-66.
[20] ANIRUDHAN TS, NAIR SS. Development of voltage gated transdermal drug delivery platform to impose synergistic enhancement in skin permeation using electroporation and gold nanoparticle. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:437-446.
[21] ZHANG Y, YU J, KAHKOSKA AR, et al. Advances in transdermal insulin delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;139:51-70.
[22] CHENG CY, PHO QH, WU XY, et al. PLGA Microspheres Loaded with beta-Cyclodextrin Complexes of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate for the Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Activated Microglial Cells. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(5):519.
[23] SHI NQ, ZHOU J, WALKER J, et al. Microencapsulation of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist in poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres by spray-drying. J Control Release. 2020;321:756-772.
[24] JOYCE P, PRESTIDGE CA. Synergistic effect of PLGA nanoparticles and submicron triglyceride droplets in enhancing the intestinal solubilisation of a lipophilic weak base. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;118:40-48.
[25] LARESE FILON F, MAURO M, ADAMI G, et al. Nanoparticles skin absorption: New aspects for a safety profile evaluation. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;72(2):310-322.
[26] DUL M, NIKOLIC T, STEFANIDOU M, et al. Conjugation of a peptide autoantigen to gold nanoparticles for intradermally administered antigen specific immunotherapy. Int J Pharm. 2019;562:303-312.
[27] CHANDAN R, MEHTA S, BANERJEE R. Ultrasound-Responsive Carriers for Therapeutic Applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(9):4731-4747.
[28] RAHALI K, BEN MESSAOUD G, KAHN CJF, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanofunctionalized Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2675.
[29] GAN D, XU T, XING W, et al. Mussel-inspired dopamine oligomer intercalated tough and resilient gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels for cartilage regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(10):1716-1725.
[30] ALIABOUZAR M, ZHANG LG, SARKAR K. Lipid Coated Microbubbles and Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Enhance Chondrogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in 3D Printed Scaffolds. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 37728.
[31] HAMEED S, WANG Y, ZHAO L, et al. Shape-dependent significant physical mutilation and antibacterial mechanisms of gold nanoparticles against foodborne bacterial pathogens (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus) at lower concentrations. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;108:110338.
[32] LEUNG K. Poly(ethylene glycol)-coated gold nanocages bioconjugated with [Nle(4),d-Phe(7)]-alpha-melanotropin-stimulating hormone. Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD), Bethesda (MD), 2004.
[33] CHI YF, QIN JJ, LI Z, et al. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of 5-aminolevulinic acid-gold nanoparticles-mediated photodynamic therapy in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020;53(5):e8457.
|