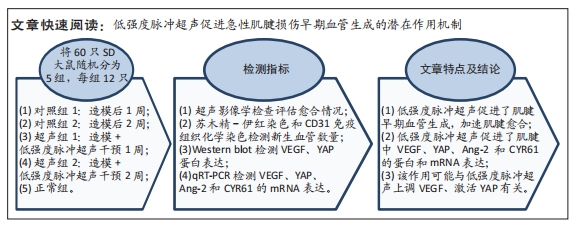
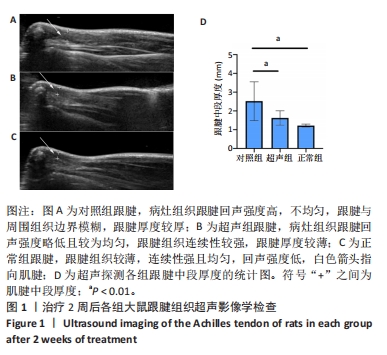
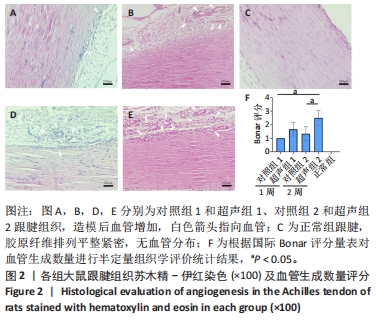
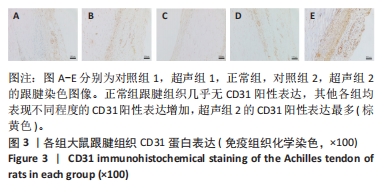
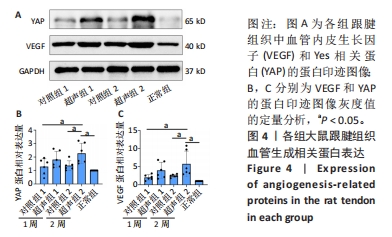
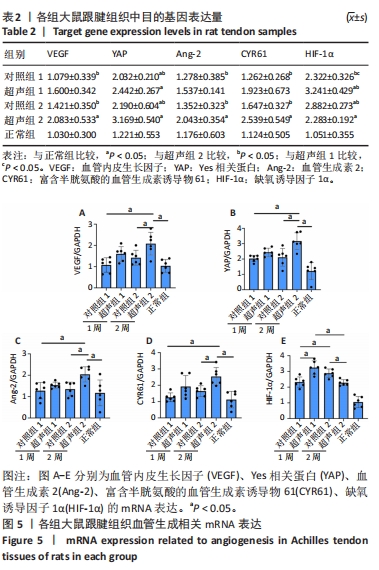
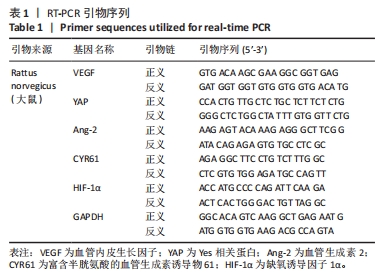
[1] NOURISSAT G, BERENBAUM F, DUPREZ D. Tendon injury: From biology to tendon repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11:223-233.
[2] RIBBANS WJ, SEPTEMBER AV, COLLINS M. Tendon and Ligament Genetics: How Do They Contribute to Disease and Injury? A Narrative Review. Life (Basel). 2022;12(5):663.
[3] SNEDEKER JG, FOOLEN J. Tendon injury and repair - A perspective on the basic mechanisms of tendon disease and future clinical therapy. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:18-36.
[4] ACKERMAN JE, BEST KT, MUSCAT SN, et al. Metabolic Regulation of Tendon Inflammation and Healing Following Injury. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(3):15.
[5] LIU X, ZHU B, LI Y, et al. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Tendon Healing. Front Physiol. 2021;12:766080.
[6] YING ZM, LIN T, YAN SG. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound therapy: a potential strategy to stimulate tendon-bone junction healing. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2012;13(12):955-963.
[7] ZHANG N, CHOW SK, LEUNG KS, et al. Ultrasound as a stimulus for musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Translat. 2017;9:52-59.
[8] LU H, CHEN C, QU J, et al. Initiation Timing of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation for Tendon-Bone Healing in a Rabbit Model. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(10):2706-2715.
[9] DE OLIVEIRA PERRUCINI PD, POLI-FREDERICO RC, DE ALMEIDA PIRES-OLIVEIRA DA, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Healing Effects of Pulsed Ultrasound Therapy on Fibroblasts. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;99(1):19-25.
[10] LAI WC, IGLESIAS BC, MARK BJ, et al. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Augments Tendon, Ligament, and Bone-Soft Tissue Healing in Preclinical Animal Models: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy. 2021; 37(7):2318-2333.
[11] LI Y, LI W, LIU X, et al. Effects of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound in Tendon Injuries. J Ultrasound Med. 2023;42(9):1923-1939.
[12] APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264.
[13] AZAD T, JANSE VAN RENSBURG HJ, LIGHTBODY ED, et al. A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1061.
[14] BOOPATHY GTK, HONG W. Role of Hippo Pathway-YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:49.
[15] HUANG Y, PAN M, SHU H, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances tendon-bone healing by activating Yes-associated protein for angiogenesis induction and rotator cuff reconstruction in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(3):2343-2353.
[16] DELCOMBEL R, JANSSEN L, VASSY R, et al. New prospects in the roles of the C-terminal domains of VEGF-A and their cooperation for ligand binding, cellular signaling and vessels formation. Angiogenesis. 2013;16(2):353-371.
[17] SOLCHAGA LA, BENDELE A, SHAH V, et al. Comparison of the effect of intra-tendon applications of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB, platelet-rich plasma, steroids in a rat achilles tendon collagenase model. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(1):145-150.
[18] TORRES-SILVA R, LOPES-MARTINS RA, BJORDAL JM, et al. The low level laser therapy (LLLT) operating in 660 nm reduce gene expression of inflammatory mediators in the experimental model of collagenase-induced rat tendinitis. Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(7):1985-1990.
[19] TSAI YP, CHANG CW, LEE JS, et al. Direct radiofrequency application improves pain and gait in collagenase-induced acute achilles tendon injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:402692.
[20] UEDA Y, INUI A, MIFUNE Y, et al. Molecular changes to tendons after collagenase-induced acute tendon injury in a senescence-accelerated mouse model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):120.
[21] MAFFULLI N, LONGO UG, FRANCESCHI F, et al. Movin and Bonar scores assess the same characteristics of tendon histology. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1605-1611.
[22] LIMA KMME, COSTA JÚNIOR JFS, PEREIRA WCA, et al. Assessment of the mechanical properties of the muscle-tendon unit by supersonic shear wave imaging elastography: a review. Ultrasonography. 2018; 37(1):3-15.
[23] ZABRZYŃSKA M, GRZANKA D, ZIELIŃSKA W, et al. The Bonar Score in the Histopathological Assessment of Tendinopathy and Its Clinical Relevance-A Systematic Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(4):367.
[24] KING CM, VARTIVARIAN M. Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair: Simple to Complex. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2023;40(1):75-96.
[25] GORICK CM, CHAPPELL JC, PRICE RJ. Applications of Ultrasound to Stimulate Therapeutic Revascularization. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12): 3081.
[26] KORNTNER S, LEHNER C, GEHWOLF R, et al. Limiting angiogenesis to modulate scar formation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146:170-189.
[27] WU F, NERLICH M, DOCHEVA D. Tendon injuries: Basic science and new repair proposals. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(7):332-342.
[28] ZHANG F, LIU H, STILE F, et al. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on rat Achilles tendon healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;112(6): 1613-1619.
[29] HALL K, RAN S. Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by the local environment. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010;15(1):195-212.
[30] COPELAND K, PURVIS AR. A Retrospective Chart Review of Chronic Wound Patients Treated with Topical Oxygen Therapy. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2017;6(5):143-152.
[31] TEMPFER H, TRAWEGER A. Tendon Vasculature in Health and Disease. Front Physiol. 2015;6:330.
[32] 王增涛,郝丽文,李桂石. Wistar大鼠解剖图谱[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社,2009.
[33] FARCIC TS, BALDAN CS, CATTAPAN CG, et al. Treatment time of ultrasound therapy interferes with the organization of collagen fibers in rat tendons. Braz J Phys Ther. 2013;17(3):263-271.
[34] FARCIC TS, BALDAN CS, MACHADO AFP, et al. Collagen Fibers in the Healing Process of Rat Achilles Tendon Rupture Using Different Times of Ultrasound Therapy. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2018; 7(4):114-120.
[35] JEREMIAS JÚNIOR SL, CAMANHO GL, BASSIT AC, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates healing in rat calcaneus tendon injuries. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41(7):526-531.
[36] PEACH CJ, MIGNONE VW, ARRUDA MA, et al. Molecular Pharmacology of VEGF-A Isoforms: Binding and Signalling at VEGFR2. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1264.
[37] LAI F, WANG J, TANG H, et al. VEGF promotes tendon regeneration of aged rats by inhibiting adipogenic differentiation of tendon stem/progenitor cells and promoting vascularization. FASEB J. 2022;36(8): e22433.
[38] WU JB, TANG YL, LIANG XH. Targeting VEGF pathway to normalize the vasculature: an emerging insight in cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:6901-6909.
[39] BUDEL SJ, PENNING MM, PENNING LC. Hippo signaling pathway in companion animal diseases, an under investigated signaling cascade. Vet Q. 2021;41(1):172-180.
[40] DEY A, VARELAS X, GUAN KL. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(7):480-494.
[41] WU Z, GUAN KL. Hippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and Development. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021;46(1):51-63.
|