中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (20): 3272-3280.doi: 10.12307/2024.291
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇
去铁胺在骨组织再生中的应用进展
汪饶开卷1,2,赵立星1,2,3
- 1口腔疾病研究国家重点实验室/国家口腔疾病临床研究中心,四川省成都市 610041;2四川大学华西口腔医学院,四川省成都市 610041;3四川大学华西口腔医院正畸科,四川省成都市 610041
-
收稿日期:2023-03-24接受日期:2023-05-11出版日期:2024-07-18发布日期:2023-09-11 -
通讯作者:赵立星,医学博士,副教授,副主任医师,硕士生导师,口腔疾病研究国家重点实验室/国家口腔疾病临床研究中心,四川省成都市 610041;四川大学华西口腔医学院,四川省成都市 610041;四川大学华西口腔医院正畸科,四川省成都市 610041 -
作者简介:汪饶开卷,女,1997年生,汉族,四川大学华西口腔医学院在读硕士,主要从事高分子复合材料优化骨组织工程的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31670992),项目负责人:赵立星
Application of deferoxamine in bone tissue regeneration
Wang Raokaijuan1, 2, Zhao Lixing1, 2, 3
- 1State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases/National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2West China School of Stomatology Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Orthodontics, West China School of Somatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-24Accepted:2023-05-11Online:2024-07-18Published:2023-09-11 -
Contact:Zhao Lixing, MD, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases/National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; West China School of Stomatology Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Orthodontics, West China School of Somatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wang Raokaijuan, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases/National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; West China School of Stomatology Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31670992 (to ZLX)
摘要:
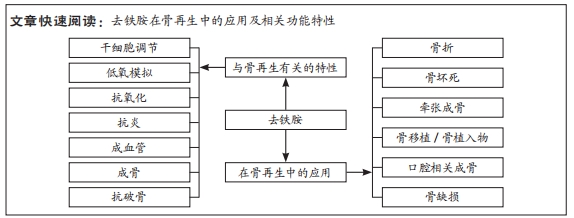
文题释义:
去铁胺:是一种被美国食品和药物管理局批准的铁络合剂,属羟肟酸络合剂。在体内,去铁胺的羟肟酸基团对三价铁离子具有高亲和力并形成水溶性铁胺复合物后主要由尿排出,常用于铁超载或铁中毒的临床治疗。骨组织再生:此过程通常将生物活性物质或药物局部注射,或利用生物材料、生物活性物质及药物制备组织工程支架植入骨缺损部位,改善损伤区域局部微环境以促进相关细胞归巢及生物活性因子表达形成新生骨,加速病变或缺损骨组织的再生及功能恢复。
背景:除了铁络合作用外,去铁胺还被认为是一种有效的低氧模拟剂及缺氧诱导因子1α稳定剂,近年的基础及临床研究中去铁胺也表现出良好的骨再生效应。去铁胺溶液或负载去铁胺的生物支架被局部应用于骨组织工程中,其对骨再生的促进涉及多种功能特性及分子机制,但尚未完全明确,且其在骨再生中的研究进展缺乏有效总结。
目的:对去铁胺应用于骨再生的功能特性、优缺点及其在基础研究及临床实践中的进展进行综述,以期为后续相关研究提供参考及策略。方法:以“deferoxamine OR desferrioxamine OR desferal OR DFO”“bone tissue engineering OR bone regeneration OR bone remodeling OR bone repair OR bone healing OR osteogenesis”“angiogenesis OR vascularized bone regeneration OR angiogenic-osteogenic coupling”为英文检索词检索PubMed数据库,以“去铁胺”“骨组织工程,骨再生,骨重建,骨修复,骨愈合”“成血管,血管化成骨,成骨-成血管偶联”为中文检索词检索万方和中国知网数据库,最终纳入88篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①去铁胺能招募干细胞并调节干细胞功能,激活相关信号通路提高细胞的低氧适应能力,发挥抗炎抗氧化特性改善局部炎性环境,并通过偶联成骨-成血管及抑制骨吸收来促进骨再生。②相较于传统骨组织工程中加载的生长因子或多肽,去铁胺作为小分子药物具有独特的优势,同时也存在毒性反应及应用局限,因此优化载药形式及剂量是必要的。③去铁胺独特的成血管-成骨偶联能力,在不同类型的骨损伤如骨折、骨坏死、牵张成骨、骨移植、口腔相关成骨及骨缺损中,因对骨愈合过程中血管生成的加强而更能适应和解决复杂多变的临床情况及个体差异下造成的骨修复困难;但同时也需要对去铁胺的应用方式及安全剂量加以对比和优化,利于其应用范围的扩大及临床价值的提升。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8185-7273(汪饶开卷);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9870-6436(赵立星)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
汪饶开卷, 赵立星. 去铁胺在骨组织再生中的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(20): 3272-3280.
Wang Raokaijuan, Zhao Lixing. Application of deferoxamine in bone tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3272-3280.
2.1.1 干细胞调节 拥有再生潜力的干细胞和祖细胞会在需要时分化出后代以取代老化或受损细胞,保持体内的动态平衡和完整性。体内干细胞存活于复杂、动态、专门的低氧压微环境中,低氧在保持干细胞干性的同时还具有促进干细胞存活、增殖、分化和细胞因子分泌的能力[5]。作为研究最多的间充质干细胞预处理剂之一,与低氧相比,去铁胺引起的代谢改变对间充质干细胞的损害较小、安全性相对较高[6]。研究显示,去铁胺对多种干细胞具有不同的调节作用[7-21],见表1,除促进干细胞存活、增殖和迁移外,还能诱导分化及分泌有利于血管生成、神经再生、创口愈合和组织再生的活性因子[7]。
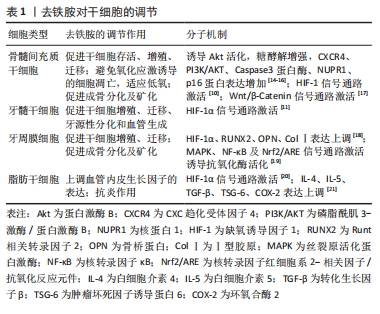
在骨再生研究中,去铁胺主要通过影响间充质干细胞及内皮祖细胞的行为及功能来促进成骨。其一,去铁胺能增强体内间充质干细胞和内皮细胞的归巢能力[8];其二,去铁胺能促进间充质干细胞活性的维持和旁分泌因子的释放,使其具有向内皮样细胞分化的趋势并促进血管形成[9];其三,去铁胺在激活Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路诱导间充质的成骨分化的同时,还能保护细胞免受氧化应激诱导的凋亡[10]。另外,去铁胺对牙髓干细胞(dental pulp stem cells,DPSCs)和牙周膜细胞(periodontal ligament cells,PDLCs)的活性调节和分化影响展现了其促进牙髓再生和牙周再生的治疗潜力[11-12],去铁胺对牙髓、牙周血管再生和相应细胞牙源性分化的诱导使口腔复杂环境中的软、硬组织再生成为可能。而在糖尿病神经病变模型中,去铁胺对脂肪干细胞(adipose-derived stem cells,ADSCs)的干预能上调血管内皮生长因子表达的同时减少炎性因子的表达,其促进多种神经血管生成和抗炎细胞因子的协同作用是病变个体神经血管恢复所必需的。
值得注意的是,组织工程技术中植入体内的干细胞由于在体外是常氧环境下培养生长,植入体内时无法适应损伤组织处的低氧环境而发生凋亡。因此低氧处理剂如去铁胺对干细胞在体外培养的预处理能够有效提高干细胞移植后的存活率,并维持或增强其增殖迁移、分化潜能和免疫调节特性[13],这对于组织工程技术中的细胞移植具有重要意义。
2.1.2 低氧模拟剂 缺氧诱导因子1是由缺氧诱导因子1α和缺氧诱导因子1β两个亚单位组成的异源二聚体,其中缺氧诱导因子1β在细胞内稳定表达,起结构性组成作用;而作为活性亚基的缺氧诱导因子1α是一种细胞氧传感器,其降解与否决定了缺氧诱导因子1的活性及下游通路的激活。常氧环境下,缺氧诱导因子1α被脯氨酰羟化酶结构域蛋白(prolyl hydroxylase-domain protein,PHD)羟基化后经泛素-蛋白酶体途径分解,细胞中几乎检测不到其存在[22]。去铁胺对细胞的低氧模拟作用本质上是铁络合作用的衍生,即去铁胺能与PHD催化中心的铁离子螯合使PHD失活,间接导致缺氧诱导因子1α在细胞内的积累。而后缺氧诱导因子1α进入细胞核中与缺氧诱导因子1β结合形成异二聚体,缺氧诱导因子1与其辅助激活因子p300结合[22],导致缺氧诱导因子1α下游反应式的激活。缺氧诱导因子1α的表达触发了参与细胞增殖迁移、血管生成和组织再生的多个低氧反应基因的转录级联反应[23],此通路的激活对骨再生的促进具有重要意义。
2.1.3 抗氧化特性 去铁胺突出的抗氧化特性可保护细胞免受自由基的攻击,还能提高细胞内超氧化物歧化酶的活性以减轻细胞的氧化损伤。去铁胺的抗氧化特性也来源于铁沉积作用,体现在其对活性氧浓度的控制同样参与了铁稳态的维护。活性氧指代氧来源的自由基和非自由基,具有较高的化学反应活性,在机体内为细胞信号传递所必需并具有多种生理功能。过量的活性氧会破坏体内氧化和抗氧化系统之间的平衡状态,影响DNA、蛋白质和脂质的完整性、破坏细胞功能、导致炎症反应[24]。去铁胺能通过与活性氧反应生成去铁胺氮氧自由基(deferoxamine nitroxide radical,DfNO·)来调节细胞内的活性氧水平[25]。去铁胺的抗氧化能力最初被HARTLEY等[26]发现并证明,表现为当去铁胺浓度高于10 mmol/L时红细胞膜中的烷氧基和过氧基浓度随去铁胺浓度的升高而降低。至今为止,人们通过研究认识到去铁胺能够有效淬灭过氧基、烷氧基、羟基及超氧自由基,且当铁存在于反应体系中时可增强以上作用[26]。总的来说,去铁胺在细胞内触发的缺氧或低氧条件能减少自由基所造成的氧化损伤,而去铁胺除了通过抗氧化机制直接参与免疫调节外,还可通过调节干细胞之间的相互作用来发挥免疫调节功能[27]。
然而,关于去铁胺对活性氧的作用仍存在争议。多数研究及观点认同去铁胺对细胞内活性氧产生的降低作用,可避免细胞凋亡并管理铁稳态[12];与之相反的是,WANG等[28]和CHUNG等[19]在文章中报道去铁胺干预后细胞内活性氧水平增加。对于以上研究分歧的存在,不同团队间研究方法和侧重点存在差异,即不同的体外培养细胞条件、给予刺激及判断标准导致结论的不同。并且目前文章均缺乏对去铁胺作用于活性氧分子机制的具体研究,这对于明确其抗氧化特性的应用条件是必要的。
2.1.4 抗炎特性 作为激活氧化还原反应的敏感因子,活性氧是上调表达炎症基因信号通路的关键介质。病理条件下,氧化应激大量活性氧的产生、促炎细胞因子的表达及细菌感染等使创口持续处于炎性微环境。而非蛋白结合铁可诱导细胞的炎症反应,表现为黏附因子和白细胞介素6表达的增加。因此,铁络合剂如去铁胺对细胞内活性铁的清除可减少活性氧的产生及氧化应激反应,减轻细胞和组织的炎症反应及损伤[29]。去铁胺能通过激活或抑制相关通路来下调炎症基因的表达并抑制炎性因子的分泌,以此预防或减轻炎症。具体表现为激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinases,MAPK)和核转录因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)信号通路来显著抑制脂多糖诱导的肿瘤坏死因子α、铁调素、一氧化氮、前列腺素E2、白细胞介素2等的分泌[30];去铁胺还能下调参与炎症的基因表达,通过核转录因子红细胞系2-相关因子2/血红素氧合酶1(nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/ heme oxygenase-1,Nrf2/HO-1)信号通路减少核转录因子κB、活性氧和环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白/过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活物-1β(cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1β,CREB/PGC-1β)的信号转导来预防或减轻炎症[12]。另外,DING等[31]所制备的生物支架中去铁胺的加入可增强巨噬细胞的抗炎活性,具体表现为M2表型巨噬细胞的比例增高及抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的产生增加。目前研究已知铁中毒引起活性氧生成导致炎症反应后能继续诱导铁浓度的增加,继而进一步促进炎症并形成恶性循环[32],因此去铁胺的铁络合效应对于机体抗炎是一条有效途径。去铁胺可能具有的骨免疫调节潜能在于其在炎症环境下抗炎抗氧化特性的协同作用,其中对于活性氧水平的适当控制为关键,由此得出去铁胺剂量的优化对于其正确发挥抗炎抗氧化特性是必要的。
2.1.5 成血管特性 去铁胺作为缺氧诱导因子1α稳定剂,通过抑制PHDs的活性来激活缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路发挥其血管生成功能。简单来说即在去铁胺螯合铁的情况下,缺氧诱导因子1α得以累积并通过核转位与缺氧诱导因子1β结合后再与转录辅助激活因子p300结合形成缺氧诱导因子1/p300复合体,该复合体与缺氧元件结合启动下游级联反应,导致血管内皮生长因子、内皮型一氧化氮合成酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthases,eNOS)、基质细胞衍生因子1(stromal cell-derived factor-1,SDF-1)、血管生成素及其他下游血管生长因子的分泌,触发组织内的血管生成反应[33]。由于血管生成是一个多因素、多通路、多种活性因子共同协调的复杂过程,仅通过传递或提供其中的一两个生长因子或多肽(如组织工程支架中常携带血管内皮生长因子等)来促进组织的血管化具有局限性[34]。而缺氧诱导因子1α作为缺氧应激反应的关键上游转录因子,是血管生成的核心调节因子。去铁胺能通过缺氧诱导因子1α激活一系列成血管通路的信号转导,导致内皮细胞和其他祖细胞的募集及相关活性因子的表达以促进血管生成。事实证明,靶向缺氧诱导因子1α比单独应用任何血管生成因子更有效,去铁胺的血管化效应能增强组织工程技术中移植物-宿主组织之间的整合及组织修复[27],使未来复杂的多层组织移植在临床上存在可能性。另外,去铁胺还能有效促进老龄化、激素紊乱或放射个体中的血管形成,缓解或治疗其骨质疏松及骨丢失[8,35-37]。去铁胺是一种有效地诱导血管形成的小分子药物,具有较好的血管化及组织修复潜力。
有趣的是,研究发现去铁胺在组织创伤区域能促进H型血管的形成。H型血管是由KUSUMBE等[38]发现并命名的一种特殊血管亚型,特异性高表达CD31及Emcn(CD31hiEmcnhi)且骨祖细胞(Osterix+细胞)偏向于定植在其周围,具有偶联成血管和成骨的作用。不同类型骨组织修复的研究都证实,体内模型经去铁胺干预后在愈合早期能检测到H型血管的存在。对于软骨内成骨的长骨,ZENG等[39]通过研究发现去铁胺在修复股骨缺损的过程中促进了早期的H型血管形成。然而,多数负载去铁胺的组织工程支架体内研究选择长骨缺损模型,去铁胺应用于扁骨如颅骨的研究缺乏对H型血管存在的验证和观察,需要更多的检测和进一步的研究。同时,去铁胺诱导H型血管发生的分子机制尚未明确,这对于包括神经组织、皮肤组织、骨组织在内的修复是具有重要意义的。
2.1.6 成骨特性 去铁胺的成骨特性使其成为骨组织工程的研究热点之一,随着研究的深入,人们发现去铁胺主要通过以下几个方面来促进成骨,见图3。首先,去铁胺能激活成骨细胞中经典的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,调节靶基因Runt相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor 2,RUNX2)、骨形态发生蛋白2(bone morphogenetic protein-2,BMP-2)等的表达,刺激间充质干细胞(主要是骨髓间充质干细胞)分化为成骨细胞,并增强成骨细胞的活性(促进增殖、分化和矿化),以促进骨再生[40]。Wnt信号是骨重塑的关键调节因子,该通路有典型(β-catenin依赖)和非典型(β-catenin不依赖)两种类型,且二者主要通过促进成骨细胞分化和间接控制破骨细胞形成来调节骨转换,对骨量都有积极影响。当Wnt信号没有被激活时,细胞内的破坏性复合体与β-catenin结合,导致其被泛素化修饰后降解[41]。而在去铁胺激活该通路的情况下,Wnt与其受体及辅助受体结合,抑制破坏性复合体的形成从而使β-catenin在胞质内有所累积。之后β-catenin移位至细胞核内与转录因子结合,促进RUNX2等下游基因的表达,刺激骨祖细胞的成骨分化及活性因子的分泌。还有体外研究显示Wnt5a可能是去铁胺促进人间充质干细胞成骨分化作用的关键靶点基因[42]。然而,与此同时也存在去铁胺抑制成骨细胞中Wnt靶基因的实验结论[43]。由此得出Wnt信号作用的发挥强烈依赖于所处环境和细胞类型,在不同细胞类型中去铁胺对Wnt的作用可能会产生相反的表现。
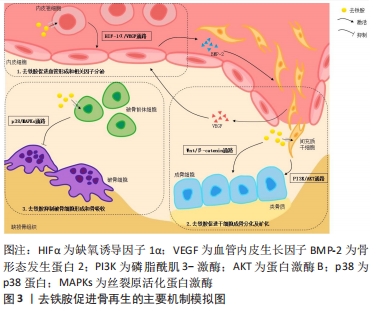
去铁胺模拟的低氧环境是否能直接调节间充质干细胞的成骨分化,不同的研究存在相互矛盾的结论。在YAO等[44]制备的双药物递送支架中,去铁胺与骨形态发生蛋白2能够协同促进人间充质干细胞的成骨活性,而单纯游离的去铁胺显著抑制细胞的成骨分化。另有ZHENG等[45]的实验表明,只负载去铁胺的明胶纳米纤维支架在体外对人间充质干细胞的成骨分化有抑制作用,但当在支架中引入纳米黏土时可解决这一问题。该团队的早前研究中去铁胺修饰的支架抑制了人间充质干细胞的早期成骨分化(碱性磷酸酶活性降低),而促进了成熟成骨标志物(骨钙素)的表达[44,46]。这些结论是否说明骨再生组织工程中应用去铁胺时仍需引入额外的成骨信号(包括生长因子、多肽或生物陶瓷材料等)以保证成骨效应,有待进一步严谨验证。
此外,充足的缺氧诱导因子1α信号对于骨再生是必不可少的。如前所述,去铁胺通过稳定缺氧诱导因子1α启动缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路,招募内皮祖细胞且促进细胞的增殖、迁移,激活下游血管生成因子的分泌,诱发血管生成。新生血管在提供营养、运输废物的同时,还为损伤区域运输驻留于血管壁内的干细胞及成骨前体细胞。体外共培养实验显示,内皮细胞可通过产生骨形态发生蛋白2刺激骨祖细胞分化,而骨祖细胞可分泌血管内皮生长因子刺激内皮细胞增殖,二者存在密切联系并在骨形成中共同发挥功能[47]。骨修复早期去铁胺调节H型血管的形成,该特殊血管亚型偶联血管生成与成骨促进骨再生,如H型血管能招募骨祖细胞分化为成骨细胞和骨细胞并积极参与骨的成熟与矿化[48]。此外,缺氧诱导因子1α信号的激活能同时促进骨髓间充质干细胞中线粒体的分裂和自噬来调节线粒体功能,对成骨也具有积极的调控作用[36]。
另一方面,去铁胺还能通过阻止骨丢失间接发挥成骨特性。铁过量会抑制成骨细胞的功能,而使用去铁胺对成骨细胞的成熟起积极作用[42]。铁超载下调Runt相关转录因子2及其靶基因碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素的表达,抑制间充质干细胞和骨祖细胞的成骨分化;对于成骨细胞,铁超载通过下调PI3K/AKT/FOX3α/DUSP14信号通路抑制其生长和矿化,并使细胞周期停滞于增殖G1期以抑制成骨细胞的增殖,破坏成骨细胞的代谢平衡、诱导细胞凋亡;过剩的铁还会促进活性氧的产生导致氧化应激反应,引起成骨细胞自噬和衰老。去铁胺能清除细胞内的铁离子和活性氧,以剂量依赖的形式缓解因成骨细胞增殖、分化受抑制导致的骨质疏松或骨丢失[49]。然而,有学者称去铁胺自身也可能剂量敏感地抑制成骨细胞的分化,防止骨丢失不能完全清除铁离子[50]。为了避免过度清除铁离子产生的副反应,去铁胺的使用剂量需要加以优化。
2.1.7 抗破骨特性 铁是破骨细胞分化所必须的微量元素,破骨细胞为了满足分化和骨吸收过程中的能量需求会增加铁的摄取和储存。破骨细胞摄取铁的主要途径为细胞膜上转铁蛋白受体介导的内吞作用。铁进入细胞后被运输到线粒体中,用于合成铁-硫团簇和血红素,参与电信号传递[51]。线粒体产生的活性氧对核转录因子κB受体激活剂配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)诱导骨髓单核巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化是必须的,即活性氧参与了对破骨细胞分化和吸收的调节。由于RANKL激活活性氧介导的MAPKs信号通路,其在成熟破骨细胞的激活和存活中充当关键角色[52]。而铁络合剂对破骨细胞的抑制作用是通过抑制电信号传递链和MAPKs信号通路来实现的[53],简言之就是去铁胺能显著降低转铁蛋白受体介导的细胞铁水平及破骨细胞生成,降低线粒体复合体的酶活性及亚单位的表达,并抑制MAPKs信号通路。另外,去铁胺对破骨细胞的抑制还可能由于对Nrf2和HO-1的激活[53]。在一项针对置换关节的研究中,去铁胺以剂量依赖的方式抑制破骨细胞的形成,从而抑制置换关节内特定颗粒诱导的骨溶解。从机制上看,去铁胺通过p38/MAPKs信号通路上调HO-1的表达,该因子的表达抑制破骨前体细胞的分化而抑制破骨细胞的形成[54]。
低氧环境被部分学者认为通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α来诱导破骨细胞的形成和骨吸收。有体外实验发现去铁胺对缺氧诱导因子1α的激活直接增加破骨细胞的数量和吸收活性;也有研究称该通路下游血管内皮生长因子的激活对破骨细胞的招募和活性具有积极作用[55]。而其他学者表达了相反观点,他们的结果显示去铁胺在体外抑制破骨细胞的形成和功能且同样是通过缺氧诱导因子1α途径[54,56]。因此文章推测,去铁胺对骨组织的联合作用可能是抑制破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和增加骨形成。尽管去铁胺在体外对破骨细胞形成和功能的影响仍具有争议性,但目前同样缺乏对去铁胺局部释放在体内影响破骨细胞介导骨吸收的验证及具体分子机制的探索,而研究对应细胞类型、动物模型、干预方式和药物剂量的选择对于探讨去铁胺作用于破骨细胞的整体特性具有重要意义。
2.2 去铁胺的优缺点 随着研究的深入,去铁胺的这些特性被用于骨再生研究中,让人们看到了去铁胺预防和治疗不同骨组织疾病的巨大潜力。并且,相较于传统骨再生研究中添加的生长因子或多肽,去铁胺作为小分子药物具有特有的优势:①与天然或重组生长因子相比,去铁胺诱导血管生成过程快、效率高且长期稳定[2]。②去铁胺通过缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路途径成血管。缺氧诱导因子1α作为缺氧应激反应的关键上游转录因子,可引发一系列生物信号的生成以招募用于血管生成及骨再生的祖细胞,而仅传递一两个生长因子来促进组织工程中的血管化作用是较为局限的[34]。③去铁胺的药理活性较生长因子的活性更好保存,长期使用几乎不会出现免疫反应,且更好合成、更加经济(生长因子价格昂贵)、载药过程简单。④负载生长因子的组织工程支架需要复杂的制造及消毒工艺,且生长因子较去铁胺更易降解而难以长期保存[41]。⑤由于具有成血管-成骨偶联作用,去铁胺在骨缺损研究中的成骨效果好,具体表现为除缺损外围有新生骨外往往缺损中心也有新生骨的存在,也在一定程度上加速了骨愈合,避免了骨组织工程支架在这方面的限制。⑥缺氧诱导因子1α通路的激活协同其他因素提供了一个有利于血管形成的局部环境趋势,最大限度减少炎症的不利影响,增加移植物或支架与宿主组织的结合程度,促进支架材料的吸收,并使移植复杂的多层组织应用于临床成为可能[57]。
然而,目前的研究显示去铁胺依然存在局限性。因此,总结以往研究并进一步完善其载药途径、优化药物剂量及确定应用时机是必要的。而骨组织工程支架也需要通过去铁胺的缓释来动态控制骨再生过程中的血管形成,优化骨再生支架的成血管能力,以实现支架的早期血管化及长期血管形成:①去铁胺的高细胞毒性、非靶点效应和较短半衰期极大限制了它的应用范围[58],因此给药需定点、定量,且载药支架需要控制缓释,在保持其药理活性的同时降低细胞毒性。②去铁胺在体内半衰期短,口服效果差(胃肠很难吸收)。由于其能被肾脏快速排泄导致血浆半衰期短(20-30 min)[39],需不断补充去铁胺溶液以维持有效的骨再生药物浓度,长期临床治疗成本高。③过量的去铁胺在体外可能导致细胞周期停滞和程序性死亡,而体内过量使用会导致去铁胺的剂量依赖性副反应[58]。尽管多数毒性反应为可逆的,腹痛、腹泻、恶心、呕吐和低血压等急性反应迫使患者遭受痛苦;长期的注射在给患者带来感染风险的同时也可能引起视觉和听觉神经毒性反应[4]。
2.3 去铁胺在骨再生研究中的应用
2.3.1 骨折 创伤可导致骨折并伴有血管破裂和骨髓通道开放,骨折愈合初期即为血肿的形成。血肿中主要含有免疫细胞、软骨细胞和骨祖细胞,而血肿的形成及促炎/抗炎过程的相互作用被认为是骨再生的起点。伴随血管的破裂和血肿的形成,炎症细胞和前体细胞被招募至损伤区域。新生血管是细胞和活性因子侵入骨折部位的通道,同时也通过维持成骨细胞的高代谢活动来促进成骨。有学者开发了一种由骨髓间充质干细胞通过间充质凝聚而得的无支架类骨结构,并在体外利用其与骨折血肿模型进行共培养[59]。其中,去铁胺的干预增加了骨折血肿模型对低氧的适应,能够抗炎并通过主动成骨的方式促进骨折处的愈合,还可预防缺血导致的骨不连。上述模型是对正常机体骨折时骨组织愈合的体外模拟,而临床骨折的治疗还可能存在机械卸载的不利情况。已有报道称缺氧诱导因子1α和几个关键血管生成因子在力学卸载的骨骼肌中表达减少,而机械卸载引起的抗血管生成可能导致了成骨潜能降低。MATSUMOT等[60]的研究旨在验证去铁胺增强血管生成是否能克服力学卸载期间骨修复的减少,来模拟由于卧床、活动不足引起的早期骨愈合减少情况。该研究大鼠胫骨缺损模型中,去铁胺干预后肢去负荷组结果显示血管生成的增强的确减轻了机械卸载对骨修复的不利影响,但却不能完全避免这种趋势。其中原因可能为机械刺激的减少会直接抑制成骨细胞的增殖和分化,还有运动不足使血压降低可能减少炎症细胞从血管间隙向缺损处的募集,从而延迟骨修复的过程。
2.3.2 骨坏死 缺氧被认为是骨坏死的主要病理特征,骨坏死机体一般同时存在血管疾病和骨退行性疾病。临床常见的骨坏死类型为激素性和放射性骨坏死。激素性骨坏死通常是由糖皮质激素治疗引起的并发症,多数为糖皮质激素诱导的股骨头坏死。血管内血栓闭塞和血管外骨髓脂质沉积损害血液供应是糖皮质激素诱导股骨头坏死的主要机制。糖皮质激素可直接损伤内皮细胞导致细胞凋亡、减少血管内皮生长因子的表达,抑制新生血管形成,最终减少血供;同时还能增加破骨细胞的活性导致骨吸收大于成骨。早在2014年就有学者发现局部注射去铁胺可促进兔早期股骨头坏死模型的血管生成和骨修复[61]。而相比于骨损伤局部注射的方式,去铁胺溶液腹腔注射或灌胃对于糖皮质激素性骨坏死同样有效。其中,去铁胺通过腹腔注射能上调缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子的表达,促进大鼠坏死骨组织中的血管生成和成骨;去铁胺还能部分恢复地塞米松诱导的缺氧诱导因子1α下调和血管生成抑制效应,并可通过调节线粒体功能促进细胞对低氧的适应[36]。SHENG等[62]利用去铁胺和阿仑膦酸盐联合灌胃,结果显示二者联合应用能有效调节骨吸收和骨再生以预防激素性股骨头坏死。
放射性骨坏死则是由于放疗引起的循环系统闭塞、细胞密度严重减弱导致骨组织微环境的改变,表现为骨骼机械强度降低和骨萎缩。由于其成血管特性,去铁胺能有效逆转放射引起的骨坏死。有研究利用大鼠下颌骨牵张模型证明了去铁胺靶向缺氧诱导因子1α通路而激活血管生成可对抗放疗导致的血管破坏效应[37]。另外,有学者首次报道了去铁胺在放疗患者牵张成骨术中的临床效应,观察显示局部注射去铁胺溶液无不良反应且可促进放射后的上颌骨牵张区域的骨形成[63]。然而,由于放疗是癌症的辅助治疗,去铁胺的给药途径及剂量是否会影响肿瘤复发仍有待研究。
2.3.3 牵张成骨 牵张成骨技术是一种内源性骨组织工程技术,依赖于张力对血管形成和骨祖细胞募集、增殖的刺激作用,且成骨过程是由血管生成驱动的,骨沉积的增加与新生血管的增加成正比。牵张成骨最初是用于长骨延长的骨科手术,如今已发展成为治疗骨骼畸形或病变缺损的常规重建方式。改善和促进牵张成骨术中的血供是扩大该技术适应证的一种有效方式,可能实现优化再生骨组织质量、减少治疗周期、增加牵张距离和再生骨体积等。该方面的研究目前主要集中于药物干预上,而具有成血管特性的小分子药物去铁胺就是其中一个选择。有研究指出在大鼠下颌骨牵张间隙内注射去铁胺后,显微CT扫描显示血管数量增加了40%且血管之间间隙变小[63]。而去铁胺的血管形成能力还能转化为骨再生中骨形成细胞数量的增加,体现在去铁胺治疗组的骨细胞明显增殖并形成了更致密的编织骨[64]。因此,去铁胺增加血管密度是一种加速骨再生甚至能改善再生骨质量或强度的有效方法[65]。上述研究的给药时机都集中于牵张期。LIU等[66]同样位于牵张间隙局部注射去铁胺,但改变了给药时机并观察成骨效果。结果显示固定期的去铁胺干预也能加速骨形成和骨改建,有利于骨再生。
值得注意的是,在生物力学条件不足的情况下只刺激血管生成可能不足以形成理想的骨再生。对于牵张成骨模型来说,去铁胺的应用是否能在一定程度上降低或替代骨修复过程中的生物力学要求仍需要进行体内外对比和验证。尽管牵张成骨术具有很多临床优势,但也存在牵张间隙中骨痂形成缓慢并需要较长时间矿化的局限性。总的来说,去铁胺能加速成骨及增加骨强度,实现骨愈合指标的改善,但去铁胺在牵张成骨技术中的应用时机、不同时期的剂量要求及相应临床效果仍具有很大研究价值。
2.3.4 骨移植/骨植入物 去铁胺局部治疗为骨移植或骨植入物初期稳定性及远期成功率的保证提供了新选择。植入物的稳定性及关节置换的长期成功不仅取决于良好的初始机械稳定性,还取决于植入后期的骨整合,即骨科植入物的成功很大程度上取决于其与周围骨的结合程度。通常植入部位为松质骨,其骨小梁稀疏、细小,对植体的机械支撑力不足,后期可能导致植体移位下沉甚至周围骨折。增加植入物周围骨量及骨强度是有效的预防措施。目前,除了改善植体表面性能和改进手术技术外,药物如去铁胺被引入研究用于加强植体周围的骨形成和增加骨整合,植体植入后通过药物使用来促进周围血管生成和增加骨量是可能实现的。去铁胺的局部应用能通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路增加骨内植入物周围成骨、促进骨整合,从而有效提高植体稳定性;去铁胺还能经RANKL/骨保护素(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand/osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor,OPG)通路抑制破骨细胞的分化和功能,减少骨量丢失[67-68]。其次,局部注射去铁胺可减少早期骨移植物的体积损失,增加移植物的融合与愈合(初级愈合),并限制皮质骨移植物的早期机械强度损失,更有利于骨形成及骨整合[69]。同时,植骨界面去铁胺对破骨细胞的抑制能抗骨吸收,利于骨移植物的存活。
2.3.5 口腔相关成骨 去铁胺在脱落牙模型中表现出了预防炎症和骨吸收的作用[12]。体外实验中,去铁胺的处理降低巨噬细胞内活性氧水平并抑制核转录因子κB信号的转导,使破骨细胞生成相关基因表达下降;体内大鼠磨牙再植模型中,经去铁胺溶液浸泡后再植的磨牙炎症和硬组织吸收减少。去铁胺具有作为撕脱牙根表面治疗选择的潜力,且相较于其他牙再植治疗方式,它具有成本、保存和可用性方面的优势。然而去铁胺的最佳疗效及安全剂量还有待后续研究的进一步评估,且该研究缺乏对牙再植模型的长期观察。
去铁胺也被用于引导骨再生(guided bone regeneration,GBR)的研究中,可作为优化牙周及口腔外科组织再生的方法。MU团队[18]证明,在体外去铁胺干预对成骨相关因子的上调有利于人牙周膜细胞增殖、迁移和成骨分化,且为其成骨和矿化提供了良好微环境。就分子机制而言,去铁胺作用于人牙周膜细胞具有与Nrf2通路相关的成骨分化特性。CHUNG等[19]学者发现去铁胺能以浓度依赖的方式促进人牙周膜细胞成骨分化,且去铁胺是通过MAPK、Nrf2/ARE通路诱导抗氧化酶以促进成骨。目前,去铁胺在体内对人牙周膜细胞形成牙周硬组织的影响及机制有待进一步明确。另外,在兔上颌窦底提升模型中,负载去铁胺的可注射水凝胶复合体具有血管化骨再生的作用,有望将去铁胺局部用于优化上颌窦底提升术的成骨效率[70]。口腔中复杂的成骨环境使组织工程中对生物活性因子的应用具有局限性且通常收效甚微,去铁胺的出现使口腔相关骨再生如牙周炎不可逆骨吸收的修复成为可能。
2.3.6 骨缺损 骨骼依靠血管和骨细胞之间的连接来维持完整性,是一种高度血管化的组织。骨再生是复杂多样及相互协调的过程,其中成血管与成骨的偶联起关键作用。血管网络向骨组织提供氧气和营养物质并运输代谢废物,招募细胞并传递或分泌活性因子,促进局部细胞的生长和分化、调节细胞之间的相互作用,维持骨组织的内部平衡。血管化骨再生即实现骨愈合过程中的成骨-成血管偶联,它对于保证骨愈合完全、加速骨修复过程、改善骨重建质量至关重要。动物实验中,支架植入后血管化主要从缺损外围开始发生且生长速度缓慢,由于营养物质和氧气的交换限制、细胞分布和迁移的不均匀以及细胞成骨分化的障碍,新生骨组织只能从外围向中心缓慢迁移。因此多数的研究结果,尤其大型节段性骨缺损模型中,仅有缺损外围形成再生骨组织而中央往往无愈合[56]。去铁胺的前述特性具有促进内源性骨再生、加速骨修复的巨大潜力,负载去铁胺的3D打印支架在体内诱导的新生骨组织不仅分布于支架周边,还与支架中心完全结合[56]。
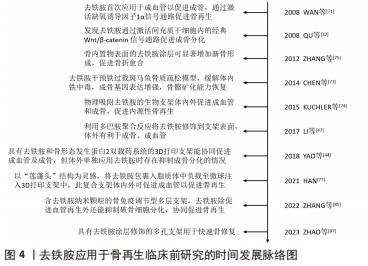
去铁胺研究最早以局部注射和灌胃等为应用方式,后续逐渐优化为支架载药的形式。WAN等[71]将去铁胺溶液体内注射到小鼠牵张间隙中时发现去铁胺通过缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路的激活增加血管生成以显著促进骨再生,由此开启了缺氧诱导因子激活剂作为促进骨愈合治疗方法的研究途径。与此同时,QU等[72]发现去铁胺通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号级联在间充质干细胞的成骨分化中发挥直接作用,且促进成骨细胞活性的同时抑制其凋亡。之后,去铁胺的全身干预对于斑马鱼骨质疏松模型具有缓解铁中毒并恢复骨骼矿化的能力[73]。以上研究发现扩展了去铁胺的应用潜力并为骨组织工程带来了新选择。学者们开始将去铁胺同骨组织工程支架结合,从一开始的物理吸附,到支架表面改性后用去铁胺修饰,再到利用各种方式优化载药性能及释药效率来达到血管化骨再生的目的[74-75]。同时,学者们通过体外研究对去铁胺偶联成骨和成血管进行了初步探索,结果显示去铁胺能促进成骨细胞前体细胞和内皮细胞的附着、增殖、迁移并能通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α通路上调成血管和成骨分化相关基因的表达[33,47]。然而,有研究提出了不同观点,认为去铁胺的剂量和释放效率从根本上决定了其成骨作用[44]。ZHENG等[45]则认为在去铁胺应用过程中需要额外的成骨信号来确保干细胞的成骨分化,以成功实现骨愈合。
由于水溶性小分子的特点,体内直接注射去铁胺容易使其失活且迅速降解。因此,骨组织工程将去铁胺负载或包裹到支架材料中,在保存药物活性、降低细胞毒性的同时实现控制释放、提高靶向性并延长半衰期。有数据显示若为单纯物理吸附至支架上,去铁胺在体内能于48 h内全部释放[74]。学者们利用各种方式将去铁胺负载到支架材料中,如YAO等[34]通过交联的方式使明胶纳米纤维支架中的去铁胺得以缓释并促进小鼠颅骨缺损的修复;CHENG等[17]则将去铁胺负载到水凝胶中以模拟天然骨的细胞外基质;更有甚者先用乙醇脂质体包裹去铁胺后再负载入水凝胶中进一步延缓去铁胺的释放[76]。在一项有趣的设计中,作者以“莲蓬头”为灵感,将去铁胺包裹到脂质体中后再通过浸泡吸附作用负载至甲基丙烯酸化水凝胶微球上注射到3D打印的β-磷酸三钙支架中,去铁胺在体外前6 h内的迅速释放有利于支架内早期血管网络的有效形成,而体内大鼠胫骨缺损模型也显示实验组骨愈合速度更快[77]。另有学者通过在支架表面涂覆电场诱导的定向纳米纤维层来调节去铁胺的释放,以实现对血管形成的动态控制[78]。还有学者将含有包裹去铁胺的明胶微球的温度敏感型水凝胶注射到大鼠股骨缺损区域时,观察到H型血管分布范围的扩大及表达时间的延长,这有利于骨组织再生[39]。
近年来,学者们也对去铁胺的有效剂量和最佳效果进行了研究。先前研究表示,当浓度超过5 μmol/L时去铁胺具有细胞毒性,而其在体内诱导血管生成的足够剂量需超过30 μmol/L。GENG等[79]将支架材料浸入梯度浓度去铁胺溶液中进行探索,去铁胺浓度< 25 μmol/L时只增加了细胞的增殖和迁移;当浓度≥50 μmol/L时可诱导血管生成。同一团队根据实验认为支架中去铁胺浓度为120 μmol在没有明显细胞毒性的同时显示出更好的血管生成能力[17,78]。CUI等[41]通过同轴电纺技术制备壳层携带去铁胺、核心层携带地塞米松的双载药电纺纤维膜,其中100 μmol/L组能兼顾良好细胞相容性与血管形成能力。而ZENG等[39]认为较高浓度(120 μmol/L)的去铁胺可导致H型血管生成减少,推测可能与组织或细胞内铁浓度不足有关。由于载药方式及实验模型的不同,不同研究得出了不同的最佳效果浓度,而去铁胺负载于不同材料的方式及不同支架的制备也存在差异[78-82],需要统一去铁胺浓度的认定标准方可得出有意义的结论。文章总结了去铁胺应用于骨缺损的浓度研究进展,见表2。
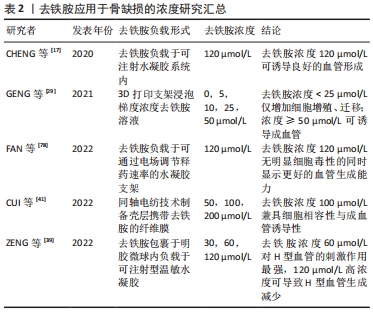
骨延迟愈合和骨不连主要由于血液供应不足所致。尽管骨组织具有良好的再生能力,但多数缺血骨缺损由于血供不足仍无法完全愈合导致骨不连,甚至出现骨丢失、骨畸形和持续感染等不良后果。值得注意的是,目前多数骨缺损模型多具有正常血供条件,其重点多在于支架成骨诱导能力的验证。然而在缺血骨缺损模型中,由于血供的缺乏,上述支架可能在缺损区域诱导纤维组织形成而导致骨修复的失败。因此,对于缺血条件下的骨缺损,结合成骨诱导及血管生成的支架引起的血管化骨再生是解决这一问题的有效策略。有研究就加载了黑磷纳米片和去铁胺的甲基丙烯酸化水凝胶对缺血胫骨缺损的修复作用进行了验证,结果显示在缺损区域产生了包括缺损中心在内的更多血管生成,该复合水凝胶具有促进血管生成和成骨、抑制纤维组织生长的作用[80],这提示去铁胺还具有更多的临床应用潜力,如对骨缺损合并动脉损伤、骨不连再生术或骨重建等的治疗。除此之外,还有学者将其他病理模型如骨质疏松、放疗后及炎症感染等作为对象纳入研究,该类模型血管生成率的降低也是导致骨修复不良的原因。负载去铁胺的聚乳酸乙醇酸支架能显著增加严重骨质疏松性股骨缺损区域的血管生成,为骨形成提供了有利条件,从而加速骨愈合[81]。另一被去铁胺/镁离子修饰的β-磷酸三钙支架在卵巢切除组大鼠体内能拮抗由于雌激素缺乏导致的血管生成抑制作而促进骨再生[82]。DONNEYS等[83]提出了一种负载去铁胺的透明质酸植入物,其体内结果显示去铁胺能显著改善放射性大鼠骨不连模型的骨愈合率,约为未治疗组的3.5倍。而载有抗菌、成骨和成血管3种功能纳米粒子的支架在大鼠开窗感染模型中,由于去铁胺对血管生成的促进及其抗氧化和抗炎作用减轻了感染和炎症对骨组织的破坏并协同另外两种因子促进成骨,给处在感染微环境中的骨再生提供了新策略[84]。去铁胺还能通过调节免疫系统和骨细胞之间的相互作用维持骨免疫平衡,使研究中的支架具有骨诱导、骨传导和骨整合的特性[85]。对病理模型骨缺损的研究是有意义的,临床的复杂情况及个体差异使此类临床前研究为去铁胺的临床应用拓展提供思路[85-88]。
文章最后总结了去铁胺支架在骨组织工程中的研究进展,见表3。
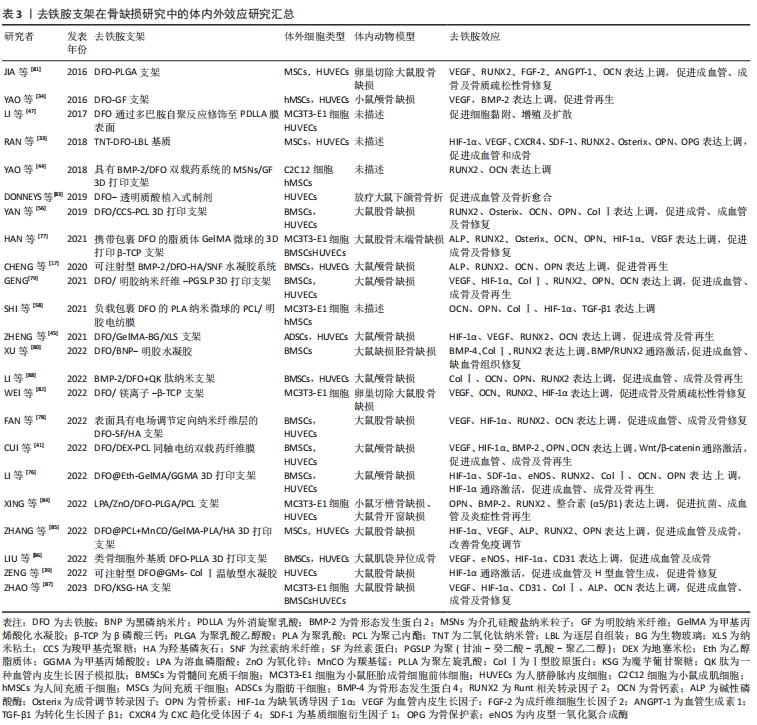
| [1] BAJBOUJ K, SHAFARIN J, HAMAD M. High-dose deferoxamine treatment disrupts intracellular iron homeostasis, reduces growth, and induces apoptosis in metastatic and nonmetastatic breast cancer cell lines. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2018;17:1533033818764470. [2] MOBARRA N, SHANAKI M, EHTERAM H, et al. A review on iron chelators in treatment of iron overload syndromes. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res 2016;10(4):239-247. [3] KEBERLE H. The Biochemistry of desferrioxamine and its relation to iron metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1964;119:758-768. [4] CUI HJ, HE HY, YANG AL, et al. Efficacy of deferoxamine in animal models of intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and stratified meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015;10(5):e0127256. [5] BEEGLE J, LAKATOS K, KALOMOIRIS S, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning of mesenchymal stromal cells induces metabolic changes, enhances survival, and promotes cell retention in vivo. Stem Cells 2015;33(6):1818-1828. [6] NOWAK-STEPNIOWSKA A, OSUCHOWSKA PN, FIEDOROWICZ H, et al. Insight in hypoxia-mimetic agents as potential tools for mesenchymal stem cell priming in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:8775591. [7] HWANG OK, NOH YW, HONG JT, et al. Hypoxia pretreatment promotes chondrocyte differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells via vascular endothelial growth factor. Tissue Eng Regen Med 2020;17(3):335-350. [8] WANG L, JIA P, SHAN Y, et al. Synergistic protection of bone vasculature and bone mass by desferrioxamine in osteoporotic mice. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):6642-6649. [9] LIU C, TSAI AL, LI PC, et al. Endothelial differentiation of bone marrow mesenchyme stem cells applicable to hypoxia and increased migration through Akt and NFkappaB signals. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):29. [10] NGUYEN VT, CANCIANI B, CIRILLO F, et al. Effect of chemically induced hypoxia on osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells in direct coculture. Cells. 2020;9(3):757. [11] JIANG L, PENG WW, LI LF, et al. Effects of deferoxamine on the repair ability of dental pulp cells in vitro. J Endod. 2014;40(8):1100-1104. [12] LEE KE, MO S, LEE HS, et al. Deferoxamine reduces inflammation and osteoclastogenesis in avulsed teeth. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8225. [13] MUSCARI C, GIORDANO E, BONAFE F, et al. Priming adult stem cells by hypoxic pretreatments for applications in regenerative medicine. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(1):63. [14] KHOSHLAHNI N, SAGHA M, MIRZAPOUR T, et al. Iron depletion with deferoxamine protects bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020;25(6):1059-1069. [15] PEYVANDI AA, ABBASZADEH HA, ROOZBAHANY NA, et al. Deferoxamine promotes mesenchymal stem cell homing in noise-induced injured cochlea through PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(2):e12434. [16] MATSUNAGA K, FUJISAWA K, TAKAMI T, et al. NUPR1 acts as a pro-survival factor in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and is induced by the hypoxia mimetic reagent deferoxamine. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2019;64(3):209-216. [17] CHENG W, DING Z, ZHENG X, et al. Injectable hydrogel systems with multiple biophysical and biochemical cues for bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(9): 2537-2548. [18] MU S, GUO S, WANG X, et al. Effects of deferoxamine on the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):9579-9586. [19] CHUNG JH, KIM YS, NOH K, et al. Deferoxamine promotes osteoblastic differentiation in human periodontal ligament cells via the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-mediated antioxidant signaling pathway. J Periodontal Res. 2014;49(5):563-573. [20] LIU GS, PESHAVARIYA HM, HIGUCHI M, et al. Pharmacological priming of adipose-derived stem cells for paracrine VEGF production with deferoxamine. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(3):E167-E176. [21] OSES C, OLIVARES B, EZQUER M, et al. Preconditioning of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells with deferoxamine increases the production of pro-angiogenic, neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory factors: potential application in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0178011. [22] CHEN H, JIA P, KANG H, et al. Upregulating hif-1alpha by hydrogel nanofibrous scaffolds for rapidly recruiting angiogenesis relative cells in diabetic wound. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(8):907-918. [23] CHOI JH, LEE YB, JUNG J, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha regulates the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via integrin alpha 4. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:7932185. [24] ARMSTRONG A, MANDALA A, MALHOTRA M, et al. Canonical wnt signaling in the pathology of iron overload-induced oxidative stress and age-related diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:7163326. [25] DAVIES MJ, DONKOR R, DUNSTER CA, et al. Desferrioxamine (Desferal) and superoxide free radicals. Formation of an enzyme-damaging nitroxide. Biochem J. 1987;246(3):725-729. [26] HARTLEY A, DAVIES M, RICE-EVANS C. Desferrioxamine as a lipid chain-breaking antioxidant in sickle erythrocyte membranes. FEBS Lett. 1990;264(1):145-148. [27] ZHU Y, CHANG B, PANG Y, et al. Advances in hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha stabilizer deferoxamine in tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023. doi:10.1089/ten.TEB.2022.0168. [28] WANG X, WU TT, JIANG L, et al. Deferoxamine-induced migration and odontoblast differentiation via ROS-dependent autophagy in dental pulp stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2535-2547. [29] DI PAOLA A, TORTORA C, ARGENZIANO M, et al. Emerging roles of the iron chelators in inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7977. [30] YAN HF, LIU ZY, GUAN ZA, et al. Deferoxamine ameliorates adipocyte dysfunction by modulating iron metabolism in ob/ob mice. Endocr Connect. 2018;7(4):604-616. [31] DING Z, ZHANG Y, GUO P, et al. Injectable desferrioxamine-laden silk nanofiber hydrogels for accelerating diabetic wound healing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(3):1147-1158. [32] ANDERSON GJ, FRAZER DM. Current understanding of iron homeostasis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;106(Suppl 6):1559S-1566S. [33] RAN Q, YU Y, CHEN W, et al. Deferoxamine loaded titania nanotubes substrates regulate osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation of MSCs via activation of HIF-1alpha signaling. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;91:44-54. [34] YAO Q, LIU Y, TAO J, et al. Hypoxia-mimicking nanofibrous scaffolds promote endogenous bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(47):32450-32459. [35] LI H, LIAO L, HU Y, et al. Identification of type H vessels in mice mandibular condyle. J Dent Res. 2021;100(9):983-992. [36] JING X, DU T, YANG X, et al. Desferoxamine protects against glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via activating HIF-1alpha expression. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(12):9864-9875. [37] FARBERG AS, JING XL, MONSON LA, et al. Deferoxamine reverses radiation induced hypovascularity during bone regeneration and repair in the murine mandible. Bone. 2012;50(5):1184-1187. [38] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328. [39] ZENG Y, HUANG C, DUAN D, et al. Injectable temperature-sensitive hydrogel system incorporating deferoxamine-loaded microspheres promotes H-type blood vessel-related bone repair of a critical size femoral defect. Acta Biomater. 2022;153:108-123. [40] XING W, POURTEYMOOR S, MOHAN S. Ascorbic acid regulates osterix expression in osteoblasts by activation of prolyl hydroxylase and ubiquitination-mediated proteosomal degradation pathway. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(12):749-757. [41] CUI J, YU X, YU B, et al. Coaxially fabricated dual-drug loading electrospinning fibrous mat with programmed releasing behavior to boost vascularized bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(16):e2200571. [42] BASCHANT U, RAUNER M, BALAIAN E, et al. Wnt5a is a key target for the pro-osteogenic effects of iron chelation on osteoblast progenitors. Haematologica. 2016;101(12):1499-1507. [43] CHEN D, LI Y, ZHOU Z, et al. Synergistic inhibition of Wnt pathway by HIF-1alpha and osteoblast-specific transcription factor osterix (Osx) in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52948. [44] YAO Q, LIU Y, SELVARATNAM B, et al. Mesoporous silicate nanoparticles/3D nanofibrous scaffold-mediated dual-drug delivery for bone tissue engineering. J Control Release. 2018;279:69-78. [45] ZHENG X, ZHANG X, WANG Y, et al. Hypoxia-mimicking 3D bioglass-nanoclay scaffolds promote endogenous bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3485-3495. [46] HOSSEINPOUR S, FEKRAZAD R, ARANY PR, et al. Molecular impacts of photobiomodulation on bone regeneration: a systematic review. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019;149:147-159. [47] LI H, LUO B, WEN W, et al. Deferoxamine immobilized poly(D,L-lactide) membrane via polydopamine adhesive coating: The influence on mouse embryo osteoblast precursor cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 1):701-709. [48] LIU Q, LI M, WANG S, et al. Recent advances of osterix transcription factor in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:601224. [49] LUO C, XU W, TANG X, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling works downstream of iron overload to prevent ferroptosis from damaging osteoblast differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;188:337-350. [50] BORRIELLO A, CALDARELLI I, SPERANZA MC, et al. Iron overload enhances human mesenchymal stromal cell growth and hampers matrix calcification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1860(6):1211-1223. [51] GATTERMANN N. Iron rusting in the mitochondria? Blood. 2016;128(15):1907-1908. [52] CALLAWAY DA, JIANG JX. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in osteoclastogenesis, skeletal aging and bone diseases. J Bone Miner Metab. 2015;33(4):359-370. [53] ZHANG J, HU W, DING C, et al. Deferoxamine inhibits iron-uptake stimulated osteoclast differentiation by suppressing electron transport chain and MAPKs signaling. Toxicol Lett. 2019;313:50-59. [54] KANG H, YAN Y, JIA P, et al. Desferrioxamine reduces ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene-induced osteolysis by restraining inflammatory osteoclastogenesis via heme oxygenase-1. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(10):e2435. [55] KNOWLES HJ, CLETON-JANSEN AM, KORSCHING E, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates osteoclast-mediated bone resorption: role of angiopoietin-like 4. FASEB J. 2010;24(12):4648-4659. [56] YAN Y, CHEN H, ZHANG H, et al. Vascularized 3D printed scaffolds for promoting bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;190-191:97-110. [57] HOLDEN P, NAIR LS. Deferoxamine: an angiogenic and antioxidant molecule for tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(6):461-470. [58] SHI R, ZHANG J, NIU K, et al. Electrospun artificial periosteum loaded with DFO contributes to osteogenesis via the TGF-beta1/Smad2 pathway. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(6):2090-2102. [59] PFEIFFENBERGER M, DAMERAU A, PONOMAREV I, et al. Functional scaffold-free bone equivalents induce osteogenic and angiogenic processes in a human in vitro fracture hematoma model. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(6):1189-1201. [60] MATSUMOTO T, SATO S. Stimulating angiogenesis mitigates the unloading-induced reduction in osteogenesis in early-stage bone repair in rats. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(3):e12335. [61] LI J, FAN L, YU Z, et al. The effect of deferoxamine on angiogenesis and bone repair in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of rabbit femoral heads. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(2):273-280. [62] SHENG H, LAO Y, ZHANG S, et al. Combined pharmacotherapy with alendronate and desferoxamine regulate the bone resorption and bone regeneration for preventing glucocorticoids-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:3120458. [63] MOMENI A, RAPP S, DONNEYS A, et al. Clinical use of deferoxamine in distraction osteogenesis of irradiated bone. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(4):880-882. [64] FARBERG AS, SARHADDI D, DONNEYS A, et al. Deferoxamine enhances bone regeneration in mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 133(3):666-671. [65] KALAY E, ERMUTLU C, YENIGUL AE, et al. Effect of bone morphogenic protein-2 and desferoxamine on distraction osteogenesis. Injury. 2022;53(6):1854-1857. [66] LIU Y, LIU J, CAI F, et al. Hypoxia during the consolidation phase of distraction osteogenesis promotes bone regeneration. Front Physiol. 2022;13:804469. [67] LIU J, KANG H, LU J, et al. Experimental study of the effects of hypoxia simulator on osteointegration of titanium prosthesis in osteoporotic rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):944. [68] YU Y, RAN Q, SHEN X, et al. Enzyme responsive titanium substrates with antibacterial property and osteo/angio-genic differentiation potentials. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;185:110592. [69] GUZEY S, AYKAN A, OZTURK S, et al. The effects of desferroxamine on bone and bone graft healing in critical-size bone defects. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;77(5):560-568. [70] XUN X, QIU J, ZHANG J, et al. Triple-functional injectable liposome-hydrogel composite enhances bacteriostasis and osteo/angio-genesis for advanced maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;217:112706. [71] WAN C, GILBERT SR, WANG Y, et al. Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway accelerates bone regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(2):686-691. [72] QU ZH, ZHANG XL, TANG TT, et al. Promotion of osteogenesis through beta-catenin signaling by desferrioxamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;370(2):332-337. [73] CHEN B, YAN YL, LIU C, et al. Therapeutic effect of deferoxamine on iron overload-induced inhibition of osteogenesis in a zebrafish model. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014; 94(3):353-360. [74] KUCHLER U, KEIBL C, FUGL A, et al. Dimethyloxalylglycine lyophilized onto bone substitutes increase vessel area in rat calvarial defects. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(5):485-491. [75] ZHANG W, LI G, DENG R, et al. New bone formation in a true bone ceramic scaffold loaded with desferrioxamine in the treatment of segmental bone defect: a preliminary study. J Orthop Sci. 2012;17(3):289-298. [76] LI Z, LI S, YANG J, et al. 3D bioprinted gelatin/gellan gum-based scaffold with double-crosslinking network for vascularized bone regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;290:119469. [77] HAN X, SUN M, CHEN B, et al. Lotus seedpod-inspired internal vascularized 3D printed scaffold for bone tissue repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(6):1639-1652. [78] FAN Z, LIU H, SHI S, et al. Anisotropic silk nanofiber layers as regulators of angiogenesis for optimized bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;15:100283. [79] GENG M, ZHANG Q, GU J, et al. Construction of a nanofiber network within 3D printed scaffolds for vascularized bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(7):2631-2646. [80] XU D, GAN K, WANG Y, et al. A composite deferoxamine/black phosphorus nanosheet/gelatin hydrogel scaffold for ischemic tibial bone repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1015-1030. [81] JIA P, CHEN H, KANG H, et al. Deferoxamine released from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) promotes healing of osteoporotic bone defect via enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(10):2515-2527. [82] WEI S, ZHANG RG, WANG ZY. Deferoxamine/magnesium modified beta-tricalcium phosphate promotes the bone regeneration in osteoporotic rats. J Biomater Appl. 2022;37(5):838-849. [83] DONNEYS A, YANG Q, FORREST ML, et al. Implantable hyaluronic acid-deferoxamine conjugate prevents nonunions through stimulation of neovascularization. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:11. [84] XING D, ZUO W, CHEN J, et al. Spatial delivery of triple functional nanoparticles via an extracellular matrix-mimicking coaxial scaffold synergistically enhancing bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(33):37380-37395. [85] ZHANG J, TONG D, SONG H, et al. Osteoimmunity-regulating biomimetically hierarchical scaffold for augmented bone regeneration. Adv Mater. 2022;34(36):e2202044. [86] LIU K, LI L, CHEN J, et al. Bone ECM-like 3D printing scaffold with liquid crystalline and viscoelastic microenvironment for bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2022;16(12):21020-21035. [87] ZHAO Y, CHEN H, RAN K, et al. Porous hydroxyapatite scaffold orchestrated with bioactive coatings for rapid bone repair. Biomater Adv. 2023;144:213202. [88] LI Z, CHENG S, LI A, et al. Fabrication of BMP-2-peptide-Deferoxamine- and QK-peptide-functionalized nanoscaffolds and their application for bone defect treatment. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;16(12):1223-1237. |
| [1] | 杨玉芳, 杨芷姗, 段棉棉, 刘毅恒, 唐正龙, 王 宇. 促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | 王姗姗, 舒 晴, 田 峻. 物理因子促进干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [3] | 尹 彤, 杨吉垒, 李友瑞, 刘卓冉, 姜 明. 核壳结构纳米纤维在口腔组织再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [4] | 王业元, 杜易朗, 于德浩, 宁凤婷, 白 冰. 微弧氧化处理对医用金属生物活性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 771-776. |
| [5] | 王嘉旎, 陈俊宇. 金属离子促血管生成机制及在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [6] | 张 娅, 牟秋菊, 王自林, 刘宏杰, 祝丽丽. 负载富血小板血浆的水凝胶促进糖尿病大鼠创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [7] | 朱礼威, 王江玥, 白 丁. 纳米复合甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶在不同骨缺损环境中应用的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [8] | 杨雨晴, 陈志宇. 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [9] | 高雪钰, 张文涛, 孙天泽, 张 警, 李忠海. 金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [10] | 陈品叡, 裴锡波, 薛轶元. 磁响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中的作用与优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [11] | 龙智睿, 黄 雷, 肖 放, 王 琳, 王晓蓓. 骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [12] | 徐 静, 吕慧欣, 鲍 鑫, 张 逸, 王一涵, 周延民. 近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [13] | 董心雨, 董馨月, 王婉婷, 范海霞, 程焕芝. 中药有效成分结合支架材料促进骨组织再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(20): 3240-3245. |
| [14] | 田 艾, 李 丽, 肖天骄, 康佳兵, 湛济帆, 韦 艳, 陈河林. 甲磺酸去铁胺促进去势骨质疏松大鼠颌骨缺损的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(20): 3143-3149. |
| [15] | 潘成镇, 陈 锋, 林宗汉, 莫 坚, 张 驰, 韦沅汛, 韦宗波. 萜类中药单体调控核转录因子κB信号通路防治骨质疏松症的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(14): 2234-2241. |
铁是人体内对细胞生长存活和新陈代谢具有重要意义的微量元素。人体内存在复杂的机制严格调控铁的吸收和释放以维持铁的动态平衡,即“铁稳态”;而铁稳态的破坏将引起细胞内稳态的破坏并导致心血管并发症、神经系统疾病、感染或癌症等多种疾病的发生[1]。去铁胺是由多毛链霉菌的代谢产物经化学处理将其中含铁胺类物质的铁去除后制得[2],于1968年获得美国食品和药物管理局批准作为一种有效的铁络合剂,临床用于铁负荷过高疾病的长期治疗。去铁胺对铁具有最高亲和力,该分子的六齿结构使之能与铁以1∶1的比例匹配结合,即去铁胺在接触铁离子时能扭曲自身的直链结构并通过3个异羟肟酸基团与其结合[3]。除此之外,去铁胺沉积铁的主要机制还有以下几种:①陈旧红细胞的储存铁被网状内皮系统巨噬细胞释放后能被去铁胺螯合并通过尿液快速排出;②未结合铁的游离去铁胺可被肝实质细胞内化,并附着在多余的肝铁上后通过胆汁排泄;③去铁胺可直接吸收心肌细胞中积聚的铁[2-4]。去铁胺的骨再生效应本质上是其铁络合作用的衍生,它在组织工程研究中所表现出的其他有趣特性如干细胞调节、抗炎抗氧化及成骨成血管等使去铁胺具有促进内源性骨再生、加速骨修复的巨大潜力。骨再生研究中,无论单纯溶液注射或载药支架植入,去铁胺的引入都能通过有效改善损伤区域的成骨微环境来促进骨修复。然而,去铁胺促进骨再生的相关特性及具体机制尚未完全阐明。
文章按照干细胞调节、低氧模拟、抗炎抗氧化、成血管、成骨及抗破骨等模块对去铁胺发挥骨再生效应的相关特性进行描述及总结,并对研究中涉及的分子机制及信号通路进行系统阐述,以将去铁胺发挥作用的整体效应进行串联,为后续去铁胺促进骨再生机制的研究提供方向。目前已有的文章主要集中于对去铁胺成骨成血管特性的讨论和研究,而该文中创新性地综述了去铁胺对骨髓间充质干细胞及破骨细胞的作用,由于二者仍具有争议性,文章对矛盾点的思考与总结能为未来去铁胺在骨再生中的应用提供新思路。同时,该文将去铁胺在骨再生研究中的应用通过骨损伤的分类进行综述。不同损伤类型修复时所侧重的成骨特性存在差异,而去铁胺在不同类型中也通过上述不同特性促进骨修复,对于后续研究中模型的选择具有参考意义。另外,文章对去铁胺在骨缺损研究中的应用进行了重点叙述,创新性地总结了去铁胺在生物支架中的负载方式、安全剂量及最佳浓度,并提及缺血骨缺损模型的研究必要及临床意义,为未来去铁胺的骨再生应用提供新策略及建议。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2023年3月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间为2018年3月至2023年3月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“deferoxamine OR desferrioxamine OR desferal OR DFO”“bone tissue engineering OR bone regeneration OR bone remodelingOR bone repair OR bone healing OR osteogenesis”“angiogenesis OR vascularized bone regeneration OR angiogenic-osteogenic coupling”为英文关键词;以“去铁胺”“骨组织工程,骨再生,骨重建,骨修复,骨愈合”“成血管,血管化成骨,成骨-成血管偶联”为中文关键词。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著及综述。
1.1.6 人工检索 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 见图1。
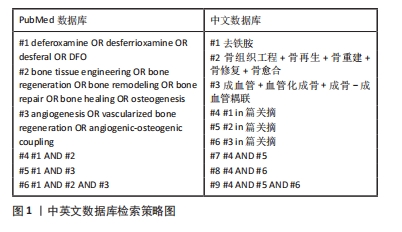
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与去铁胺应用于骨再生相关的文献;②与去铁胺促进成骨机制有关的文献;③文章中存在对去铁胺成骨效应的体内外验证内容;④选择5年内该领域内高质量的中英文文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与研究内容不符的文献;②去铁胺应用方式及验证内容过于相似的文献;③实验设计不严谨且验证不完善的文献;④重复发表文章。
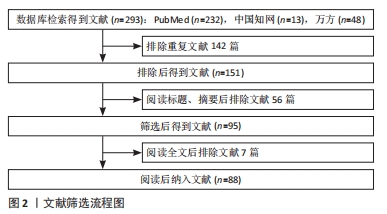
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 通过中英文数据库检索共获取293篇文献,包括英文文献232篇及中文文献61篇。去除不同数据库中重复文献,阅读文献题目和摘要后去除内容不符文献,阅读全文排除研究不严谨文献,最终纳入文献88篇。文献筛选流程见图2。
 由于去铁胺良好的成血管特性,学者们利用不同方式将去铁胺负载于支架材料中植入至损伤区域以研究其骨再生效应、相关特性及分子机制。在骨损伤区域,去铁胺能招募并调节干细胞功能,激活相关信号通路提高细胞的低氧适应能力,发挥抗炎抗氧化特性改善局部炎性环境,并通过偶联成骨-成血管及抑制骨吸收来促进骨组织愈合。同时,由于自身效应的多面性,去铁胺对于各类型骨损伤都具有治疗潜力。然而,目前的研究仍欠缺对以下问题的论证:①去铁胺对活性氧的影响是否存在造成相反作用的临界值,这也要求通过剂量优化使去铁胺对活性氧水平的控制具有合适范围;②单独的去铁胺应用对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用是否需要额外成骨因子的协同存在争议性;③去铁胺在扁骨及不规则骨中对H型血管的促进作用需要观察及论证,由于成骨方式的不同可能与长骨的观察结果存在一定差异;④骨组织工程支架中去铁胺的负载方式及剂量有待优化,因支架对缺损区域的支撑要求材料降解与组织再生速度相匹配,以实现药物缓释与材料降解的平衡。
由于去铁胺良好的成血管特性,学者们利用不同方式将去铁胺负载于支架材料中植入至损伤区域以研究其骨再生效应、相关特性及分子机制。在骨损伤区域,去铁胺能招募并调节干细胞功能,激活相关信号通路提高细胞的低氧适应能力,发挥抗炎抗氧化特性改善局部炎性环境,并通过偶联成骨-成血管及抑制骨吸收来促进骨组织愈合。同时,由于自身效应的多面性,去铁胺对于各类型骨损伤都具有治疗潜力。然而,目前的研究仍欠缺对以下问题的论证:①去铁胺对活性氧的影响是否存在造成相反作用的临界值,这也要求通过剂量优化使去铁胺对活性氧水平的控制具有合适范围;②单独的去铁胺应用对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用是否需要额外成骨因子的协同存在争议性;③去铁胺在扁骨及不规则骨中对H型血管的促进作用需要观察及论证,由于成骨方式的不同可能与长骨的观察结果存在一定差异;④骨组织工程支架中去铁胺的负载方式及剂量有待优化,因支架对缺损区域的支撑要求材料降解与组织再生速度相匹配,以实现药物缓释与材料降解的平衡。3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章不仅系统综述了去铁胺发挥骨再生效应的相关特性,还在每一部分阐述了目前研究所证明的分子机制,这对文章后部去铁胺促进不同骨损伤修复的理解和思考具有意义,也为后续通路的发现、验证及串联指明新方向。对于去铁胺最重要的成骨-成血管特性,文章通过模拟图将细胞及分子机制间的关系和相互作用也进行了总结。对于去铁胺在骨再生研究中的应用,由于去铁胺发挥骨再生效应侧重点的不同,对不同骨损伤的分类叙述是必要的。而笔者对去铁胺不同应用过程中的优缺点总结具有很大参考意义。另外,文章通过表格对负载去铁胺的骨组织工程支架作一总结,关注去铁胺与不同材料的结合方式及体内外效应,为未来进一步的优化和探究提供参考。
3.3 综述的局限性 该文章筛选5年内的相关领域文献进行综述,存在可能遗漏早期重要研究的问题。另外,文章重点在于对骨组织工程中去铁胺的应用进行归纳,对其他类型骨损伤的应用方法的总结和思考存在一定局限性。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章对去铁胺的骨再生相关特性及分子机制进行归纳和阐述,并对去铁胺应用于不同类型骨损伤的进展和争议性结论提供总结和思考,其中重点叙述研究中去铁胺在生物支架中的负载方式、安全剂量及最佳浓度,同时强调缺血及其他病理性骨缺损模型的研究必要及临床意义,为去铁胺后续的骨再生临床应用提供有价值的方向和建议。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 首先,目前对去铁胺特性的开发和利用已较为充分,而对分子机制的研究相对不全面,且去铁胺对活性氧、间充质干细胞的作用仍存在争议,可从此角度出发进行分子级别的深入研究。其次,具有更好保存去铁胺活性及更加“智能”、缓释更好的负载方式需要进行尝试和验证。另外,对于不同负载方式释放效率及再生效果的研究应予以对照和比较,也同样存在尝试不同浓度及不同模型的必要。总之,去铁胺作为优化骨再生治疗的药物,应充分利用其研究价值和应用潜力。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
去铁胺:是一种被美国食品和药物管理局批准的铁络合剂,属羟肟酸络合剂。在体内,去铁胺的羟肟酸基团对三价铁离子具有高亲和力并形成水溶性铁胺复合物后主要由尿排出,常用于铁超载或铁中毒的临床治疗。骨组织再生:此过程通常将生物活性物质或药物局部注射,或利用生物材料、生物活性物质及药物制备组织工程支架植入骨缺损部位,改善损伤区域局部微环境以促进相关细胞归巢及生物活性因子表达形成新生骨,加速病变或缺损骨组织的再生及功能恢复。
去铁胺作为一种铁络合剂被熟知,学者们利用其模拟低氧及稳定缺氧诱导因子1α的特性、通过单纯溶液注射或载药生物支架植入的方式将去铁胺应用于骨组织工程中研究其骨再生效应。研究显示,去铁胺还具有干细胞调节、抗炎抗氧化、成血管、成骨、抗破骨等骨再生相关特性,这些特性使去铁胺在骨折、骨坏死、牵张成骨、骨移植、口腔相关成骨及骨缺损中表现出巨大潜力的同时也存在优缺点,其应用方式和剂量应优化以实现更有效的骨再生。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||