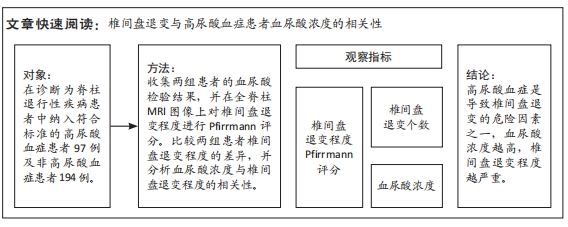
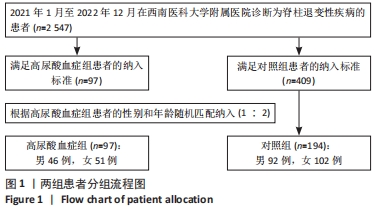
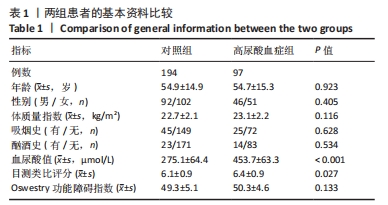
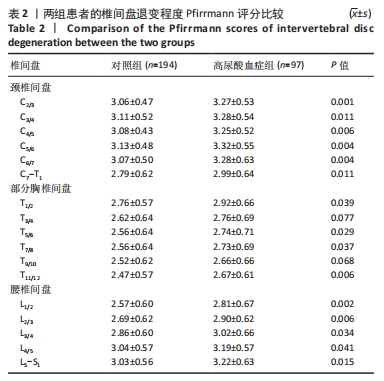
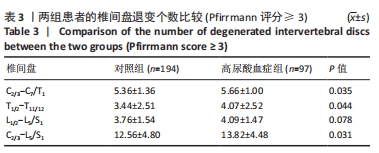
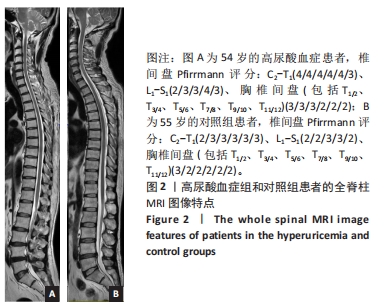
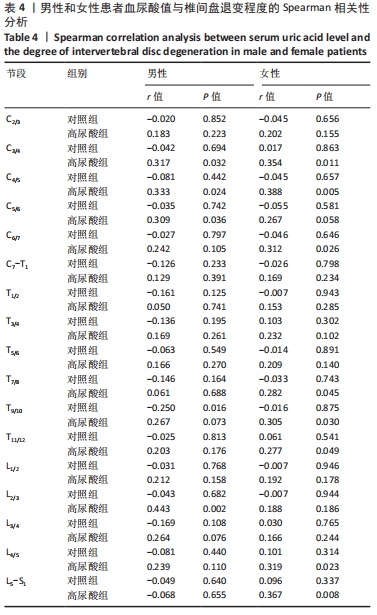
[1] ASHINSKY BG, BONNEVIE ED, MANDALAPU SA, et al. Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Is Associated With Aberrant Endplate Remodeling and Reduced Small Molecule Transport. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(8): 1572-1581.
[2] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60.
[3] HUANG YC, URBAN JP, LUK KD. Intervertebral disc regeneration: do nutrients lead the way? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(9):561-566.
[4] SAKAI D, GRAD S. Advancing the cellular and molecular therapy for intervertebral disc disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84:159-171.
[5] KNEZEVIC NN, CANDIDO KD, VLAEYEN JWS, et al. Low back pain. Lancet. 2021;398(10294):78-92.
[6] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[7] HUET T, COHEN-SOLAL M, LAREDO JD, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis and disc alterations affect the upper lumbar spine in adults with achondroplasia. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):4699.
[8] ZHANG Y, SI M, LI C, et al. Effect of hyperlipidaemia to accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration in the injured rat caudal disc model. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):42-49.
[9] JIANG Z, JIANG C, JIN L, et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus on nucleus pulposus cell senescence. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(10):2350-2361.
[10] SHENG B, FENG C, ZHANG D, et al. Associations between Obesity and Spinal Diseases: A Medical Expenditure Panel Study Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(2):183.
[11] SINGH G, LINGALA B, MITHAL A. Gout and hyperuricaemia in the USA: prevalence and trends. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(12):2177-2180.
[12] SHIRASAWA T, OCHIAI H, YOSHIMOTO T, et al. Cross-sectional study of associations between normal body weight with central obesity and hyperuricemia in Japan. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020;20(1):2.
[13] BURSILL D, TAYLOR WJ, TERKELTAUB R, et al. Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal-Associated Disease Network Consensus Statement Regarding Labels and Definitions for Disease Elements in Gout. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71(3):427-434.
[14] DAS DE S. Intervertebral disc involvement in gout: brief report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70(4):671.
[15] SNIJDERS GF, SCHIPPER LG, MASTELING-SLAATS MG, et al. Spondylodiscitis als zeldzame manifestatie van jicht [Spondylodiscitis as a rare manifestation of gout. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2017;161:D1898.
[16] KARAM I, AHMAD A, BAKER DL. A Man With Intractable Back Pain, Spondylodiscitis: A Case Report of Uncommon Site of Spinal Gout. Cureus. 2021;13(7):e16480.
[17] ZHOU S, XIAO Y, LIU X, et al. Gout involved the cervical disc and adjacent vertebral endplates misdiagnosed infectious spondylodiscitis on imaging: case report and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):425.
[18] DUPREZ TP, MALGHEM J, VANDE BERG BC, et al. Gout in the cervical spine: MR pattern mimicking diskovertebral infection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996;17(1):151-153.
[19] YEN HL, CHENG CH, LIN JW. Cervical myelopathy due to gouty tophi in the intervertebral disc space. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2002;144(2):205-207.
[20] SUK KS, KIM KT, LEE SH, et al. Tophaceous gout of the lumbar spine mimicking pyogenic discitis. Spine J. 2007;7(1):94-99.
[21] WILLNER N, MONORANU CM, STETTER C, et al. Gout tophus on an intradural fascicle: a case description. Eur Spine J. 2016;25 Suppl 1: 162-166.
[22] BOODY BS, TARAZONA DA, VACCARO AR. Evaluation and Management of Pyogenic and Tubercular Spine Infections. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(4):643-652.
[23] CHAN SC, FERGUSON SJ, GANTENBEIN-RITTER B. The effects of dynamic loading on the intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(11):1796-1812.
[24] RAJASEKARAN S, TANGAVEL C, AIYER SN, et al. ISSLS PRIZE IN CLINICAL SCIENCE 2017: Is infection the possible initiator of disc disease? An insight from proteomic analysis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(5):1384-1400.
[25] KRUPKOVA O, SADOWSKA A, KAMEDA T, et al. p38 MAPK Facilitates Crosstalk Between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and IL-6 Release in the Intervertebral Disc. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1706.
[26] ZHANG XB, HU YC, CHENG P, et al. Targeted therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration: inhibiting apoptosis is a promising treatment strategy. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(13):2799-2813.
[27] ZHU L, XIE ZY, JIANG ZL, et al. Unfolded protein response alleviates acid-induced premature senescence by promoting autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46(4):568-578.
[28] SKOCZYŃSKA M, CHOWANIEC M, SZYMCZAK A, et al. Pathophysiology of hyperuricemia and its clinical significance - a narrative review. Reumatologia. 2020;58(5):312-323.
[29] LIU N, XU H, SUN Q, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Hyperuricemia and Xanthine Oxidoreductase (XOR) Inhibitors. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1470380.
[30] GHERGHINA ME, PERIDE I, TIGLIS M, et al. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3188.
[31] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021; 397(10287):1843-1855.
[32] YANAI H, ADACHI H, HAKOSHIMA M, et al. Molecular Biological and Clinical Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Treatments of Hyperuricemia and Its Association with Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Diseases and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9221.
[33] ALLEGRINI S, GARCIA-GIL M, PESI R, et al. The Good, the Bad and the New about Uric Acid in Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4959.
[34] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448.
[35] CHENG X, LIN J, CHEN Z, et al. CB2-mediated attenuation of nucleus pulposus degeneration via the amelioration of inflammation and oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):92.
[36] LIN J, DU J, WU X, et al. SIRT3 mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by delaying oxidative stress-induced senescence of nucleus pulposus cells. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(9):6441-6456.
[37] YANG Y, ZHOU Y, CHENG S, et al. Effect of uric acid on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Genet Mol Res. 2016; 15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15028644.
[38] KIMURA Y, TSUKUI D, KONO H. Uric Acid in Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12394.
[39] 秦思宇,兰榕榆,曾佳,等.高浓度尿酸对一氧化氮的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2023,45(4):666-671.
[40] HE B, NIE Q, WANG F, et al. Hyperuricemia promotes the progression of atherosclerosis by activating endothelial cell pyroptosis via the ROS/NLRP3 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2023;238(8):1808-1822.
[41] HOCHBERG MC. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism moves to online-only publication. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;52:151960.
[42] ZHONG CS, ZENG B, QIU JH, et al. Gout-associated monosodium urate crystal-induced necrosis is independent of NLRP3 activity but can be suppressed by combined inhibitors for multiple signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(5):1324-1336.
[43] SUBRATI N, WERNDLE MC, TOLIAS CM. Spinal tophaceous gout encasing the thoracic spinal cord. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016214869.
[44] ROUSSOULY P, PINHEIRO-FRANCO JL. Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):609-618. |