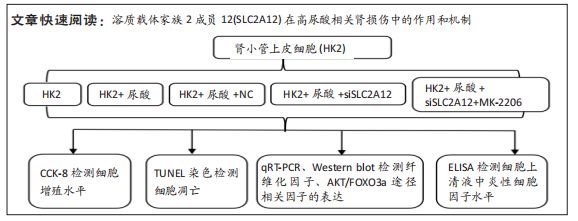
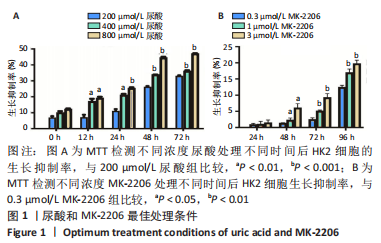
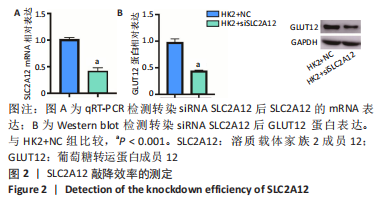
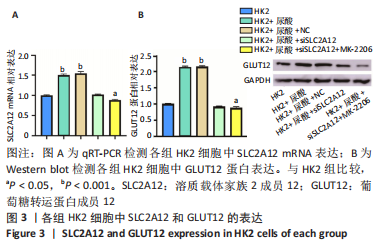
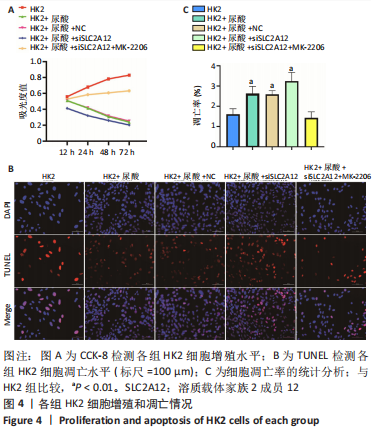
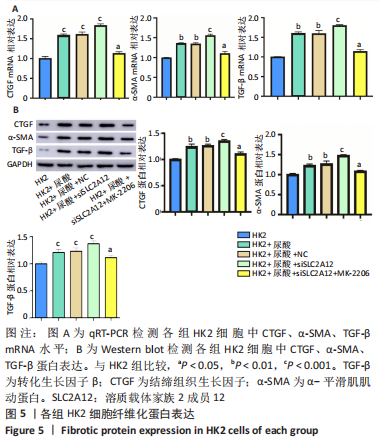
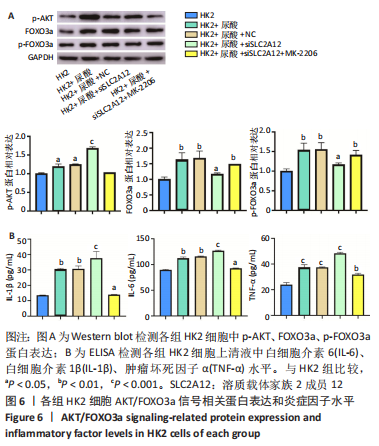
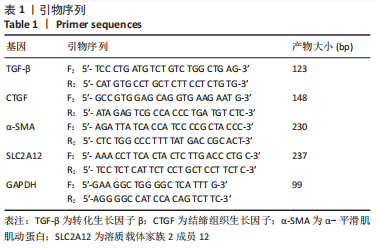
[1] YU X, ZHANG L, ZHANG P, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect mice from hyperuricaemia through promoting kidney excretion of uric acid and inhibiting liver xanthine oxidase. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):944-949.
[2] SU HY, YANG C, LIANG D, et al. Research Advances in the Mechanisms of Hyperuricemia-Induced Renal Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:5817348.
[3] WANG Y, XU F, ZHANG X, et al. Cross-sectional association between gamma-glutamyl transferase and hyperuricaemia: the China Multi-Ethinic Cohort (CMEC) study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(5):e058793.
[4] LUO Q, DING R, CHEN L, et al. The Association Between Spicy Food Intake and Risk of Hyperuricemia Among Chinese Adults. Front Public Health. 2022;10:919347.
[5] SANG S, WANG L, LIANG T, et al. Potential role of tea drinking in preventing hyperuricaemia in rats: biochemical and molecular evidence. Chin Med. 2022;17(1):108.
[6] WU X, YOU C. The biomarkers discovery of hyperuricemia and gout: proteomics and metabolomics. PeerJ. 2023;11:e14554.
[7] TSAI CW, LIN SY, KUO CC, et al. Serum Uric Acid and Progression of Kidney Disease: A Longitudinal Analysis and Mini-Review. PLoS One. 2017;12(1): e0170393.
[8] YANG B, XIN M, LIANG S, et al. New insight into the management of renal excretion and hyperuricemia: Potential therapeutic strategies with natural bioactive compounds. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1026246.
[9] QIN Y, ZHANG X, TAO H, et al. Ameliorative effect and mechanism of Yi-Suan-Cha against hyperuricemia in rats. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(8):e23859.
[10] TOYODA Y, TAKADA T, MIYATA H, et al. Identification of GLUT12/SLC2A12 as a urate transporter that regulates the blood urate level in hyperuricemia model mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(31):18175-18177.
[11] NIAN YL, YOU CG. Susceptibility genes of hyperuricemia and gout. Hereditas. 2022;159(1):30.
[12] WAHEED Y, YANG F, SUN D. Role of asymptomatic hyperuricemia in the progression of chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Korean J Intern Med. 2021;36(6):1281-1293.
[13] BOHATA J, HORVATHOVA V, PAVLIKOVA M, et al. Circulating microRNA alternations in primary hyperuricemia and gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021; 23(1):186.
[14] DOBSON M, RAMAKRISHNAN G, MA S, et al. Bimodal regulation of FoxO3 by AKT and 14-3-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(8):1453-1464.
[15] LIU L, ZHAO T, SHAN L, et al. Estradiol regulates intestinal ABCG2 to promote urate excretion via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021;18(1):63.
[16] LEE TH, CHEN JJ, WU CY, et al. Hyperuricemia and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review from Physiology and Pathogenesis to the Role of Urate-Lowering Therapy. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(9):1674.
[17] LIU N, XU H, SUN Q, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Hyperuricemia and Xanthine Oxidoreductase (XOR) Inhibitors. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:1470380.
[18] MAIUOLO J, OPPEDISANO F, GRATTERI S, et al. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int J Cardiol. 2016;213: 8-14.
[19] BRODERICK L, HOFFMAN HM. IL-1 and autoinflammatory disease: biology, pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(8): 448-463.
[20] STANIROWSKI PJ, SZUKIEWICZ D, MAJEWSKA A, et al. Differential Expression of Glucose Transporter Proteins GLUT-1, GLUT-3, GLUT-8 and GLUT-12 in the Placenta of Macrosomic, Small-for-Gestational-Age and Growth-Restricted Foetuses. J Clin Med. 2021;10(24):5 833.
[21] CHIBA Y, MURAKAMI R, MATSUMOTO K, et al. Glucose, Fructose, and Urate Transporters in the Choroid Plexus Epithelium. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19): 7230.
[22] NIE S, QIAN X, SHI M, et al. ALDH1A3 Accelerates Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis by Promoting Glucose Metabolism. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 915.
[23] DAY RO, KAMEL B, KANNANGARA DR, et al. Xanthine oxidoreductase and its inhibitors: relevance for gout. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(23):2167-2180.
[24] NISHINO M, EGAMI Y, KAWANAMI S, et al. Lowering Uric Acid May Improve Prognosis in Patients With Hyperuricemia and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;11(19):e026301.
[25] RIAZ M, AL KURY LT, ATZAZ N, et al. Carvacrol Alleviates Hyperuricemia-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Modulating the NLRP3/NF-κB Pathwayt. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:1159-1170.
[26] CHEN Y, YANG Y, ZHONG Y, et al. Genetic risk of hyperuricemia in hypertensive patients associated with antihypertensive drug therapy: A longitudinal study. Clin Genet. 2022;101(4):411-420.
[27] LUO Q, XIA X, LI B, et al. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019; 20(1): 18.
[28] GHERGHINA ME, PERIDE I, TIGLIS M, et al. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3188.
[29] MARINKOVIC D, ZHANG X, YALCIN S, et al. Foxo3 is required for the regulation of oxidative stress in erythropoiesis. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(8): 2133-2144.
[30] GOMEZ-CABRERA MC, ARC-CHAGNAUD C, SALVADOR-PASCUAL A, et al. Redox modulation of muscle mass and function. Redox Biol. 2020; 35: 101531.
[31] MA WG, WANG J, BU XW, et al. Effects of Polygonum cuspidatum on AMPK-FOXO3α Signaling Pathway in Rat Model of Uric Acid-Induced Renal Damage. Chin J Integr Med. 2019;25(3):182-189.
[32] ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, HU L, et al. lncRNA TUG1 regulates hyperuricemia-induced renal fibrosis in a rat model. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;54(9):1365-1375.
[33] SHI Y, XU L, TAO M, et al. Blockade of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 alleviates renal injury associated with hyperuricemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;316(3):F488-F505.
[34] XU L, LU LL, GAO JD. Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine Plays a Role in the Liver, Kidney, and Intestine to Ameliorate Hyperuricemia according to Experimental Studies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021: 4618352.
[35] CRIȘAN TO, CLEOPHAS MC, OOSTING M, et al. Soluble uric acid primes TLR-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by human primary cells via inhibition of IL-1Ra. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(4):755-762.
[36] SHEN L, DONG Y, LI M, et al. The relationship between leukocyte level and hypertension in elderly patients with hyperuricemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(51):e32327.
[37] BAINBRIDGE SA, ROBERTS JM. Uric acid as a pathogenic factor in preeclampsia. Placenta. 2008;29 Suppl A(Suppl A):S67-72.
[38] NATSUKO PD, LAURA SC, DENISE CC, et al. Differential gene expression of ABCG2, SLC22A12, IL-1β, and ALPK1 in peripheral blood leukocytes of primary gout patients with hyperuricemia and their comorbidities: a case-control study. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):62.
[39] WANG CC, LI YL, CHIU PY, et al. Protective effects of corni fructus extract in mice with potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia. J Vet Med Sci. 2022; 84(8):1134-1141.
[40] SCANU A, LUISETTO R, RAMONDA R, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Hypouricemic Effect of Bioactive Compounds: Molecular Evidence and Potential Application in the Management of Gout. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022;44(11):5173-5190.
|