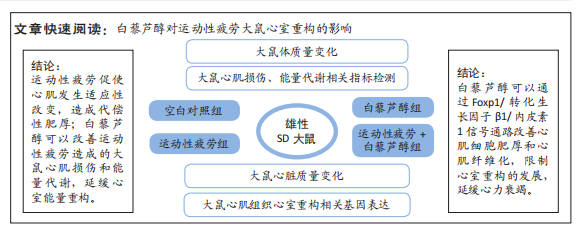
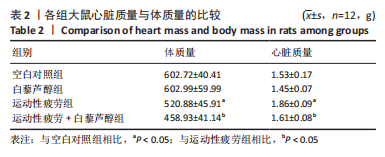
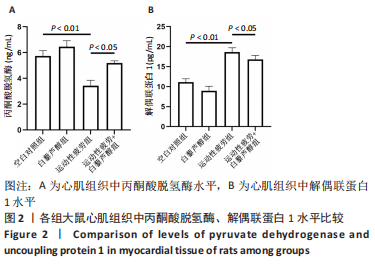
[1] 张治方,梁玉磊,吕天元,等.艾灸神阙穴对运动性疲劳大鼠心肌重构及心肌功能的影响[J].针灸推拿医学(英文版),2021,19(4):9.
[2] 张研.Zacopride抑制血管紧张素Ⅱ诱发的心室重构作用的研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2018.
[3] 宋媛媛,史朋晓,闫洪娟.丹参酮ⅡA对心力衰竭大鼠心室重构和PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022, 20(4):638-642.
[4] BEHROOZAGHDAM M, DEHGHANI M, ZABOLIAN A, et al. Resveratrol in breast cancer treatment: from cellular effects to molecular mechanisms of action. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(11):539.
[5] QIN L, LU T, QIN Y, et al. In Vivo Effect of Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Relieve Physical Fatigue for Sports Nutrition Supplements. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;25(22):5302.
[6] KAZEMIRAD H, KAZERANI HR. Cardioprotective effects of resveratrol following myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Mol Biol Rep. 2020; 47(8):5843-5850.
[7] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, WANG T, et al. Resveratrol, a natural ingredient of grape skin: antiarrhythmic efficacy and ionic mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340(4):1192-1199.
[8] DONG Q, WU Z, LI X, et al. Resveratrol ameliorates cardiac dysfunction induced by pressure overload in rats via structural protection and modulation of Ca(2+) cycling proteins. J Transl Med. 2014;12:323.
[9] KANAMORI H, TAKEMURA G, GOTO K, et al. Resveratrol reverses remodeling in hearts with large, old myocardial infarctions through enhanced autophagy-activating AMP kinase pathway. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(3):701-713.
[10] CSISZAR A. Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol: possible role in prevention of age-related cardiovascular disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1215:117-122.
[11] FERNANDES T, HASHIMOTO NY, MAGALHÃES FC, et al. Aerobic exercise training-induced left ventricular hypertrophy involves regulatory MicroRNAs, decreased angiotensin-converting enzyme-angiotensin ii, and synergistic regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-angiotensin (1-7). Hypertension. 2011;58(2):182-189.
[12] 上官若男,苏全生,尚画雨,等.运动负荷强度与运动疲劳程度量化分级研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(2):188-192.
[13] 李方,曹建民,王传军,等.白藜芦醇通过调节SIRT1/NF-κB通路减轻力竭训练致大鼠肾的炎症反应[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2019,35(7):773-779.
[14] ALWAY SE, MCCRORY JL, KEARCHER K, et al. Resveratrol Enhances Exercise-Induced Cellular and Functional Adaptations of Skeletal Muscle in Older Men and Women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(12): 1595-1606.
[15] ADMINISTRATION FAD. Guidance for industry: estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. CDER. 2005;7(0.001):1-27.
[16] OPIE LH, COMMERFORD PJ, GERSH BJ, et al. Controversies in ventricular remodelling. Lancet (London, England). 2006;367(9507):356-367.
[17] LI Q, XU Y, LI X, et al. Inhibition of Rho-kinase ameliorates myocardial remodeling and fibrosis in pressure overload and myocardial infarction: role of TGF-β1-TAK1. Toxicol Lett. 2012;211(2):91-97.
[18] QIN N, GONG Q, WEI L, et al. Total ginsenosides inhibit the right ventricular hypertrophy induced by monocrotaline in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31(8):1530-1535.
[19] 关鹏.慢性间歇性低氧引起大鼠心脏损伤的机制及白藜芦醇的干预研究[D].石家庄:河北中医学院,2020.
[20] 陆艳,郭萱.白藜芦醇抑制血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导大鼠心脏成纤维细胞胶原合成的实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2016,45(6):658-661+676.
[21] 李泽聪,马中富.白藜芦醇通过改变肠道菌群谱改善压力超负荷大鼠心室功能[J].热带医学杂志,2021,21(10):1242-1247+1375.
[22] LIU Z, SONG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of trans-resveratrol on hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy using the partially nephrectomized rat model. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005;32(12): 1049-1054.
[23] 杨振华.中华医学会检验学会文件心肌损伤标志物的应用准则[J].中华检验医学杂志,2002,25(3):56-60.
[24] 郭新苇,王传军,吉喆,等.白藜芦醇对长期大负荷运动大鼠心肌肌钙蛋白T的影响: 第十二届全国体育科学大会[C].中国山东日照,2022.
[25] 吴宏江,高晖,王毕妮.白藜芦醇对大强度运动大鼠心肌组织脂质过氧化损伤保护作用的研究[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,43(4):595-598.
[26] 张鹏,艾力曼·马合木提,孙娟.心肌能量代谢与慢性心力衰竭心室重构关系及心肌能量代谢药物应用的研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2018,32(1):94-97.
[27] LOPASCHUK GD. Metabolic Modulators in Heart Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Can J Cardiol. 2017;33(7):838-849.
[28] 娄旭佳,阮蓉,金其贯,等.白藜芦醇干预运动性疲劳模型大鼠线粒体动力学的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(17):2625-2630.
[29] ZHANG L, CHEN J, YAN L, et al. Resveratrol Ameliorates Cardiac Remodeling in a Murine Model of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:646240.
[30] LIU X, DU S, MIAO R, et al. Targeting the forkhead box protein P1 pathway as a novel therapeutic approach for cardiovascular diseases. Heart Fail Rev. 2022;27(1):345-355.
[31] WANG B, WEIDENFELD J, LU MM, et al. Foxp1 regulates cardiac outflow tract, endocardial cushion morphogenesis and myocyte proliferation and maturation. Development(Cambridge,England). 2004;131(18): 4477-4487.
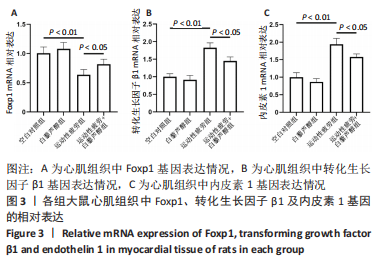
[32] 蓝林辉,王志维.转录调控因子Foxp1与心血管疾病的研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(8):1491-1496.
[33] CHANG SW, MISLANKAR M, MISRA C, et al. Genetic abnormalities in FOXP1 are associated with congenital heart defects. Hum Mutat. 2013;34(9):1226-1230.
[34] LIU J, ZHUANG T, PI J, et al. Endothelial Forkhead Box Transcription Factor P1 Regulates Pathological Cardiac Remodeling Through Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Endothelin-1 Signal Pathway. Circulation. 2019;140(8):665-680.
[35] 陈玲,胡建新,程晓曙,等.血小板反应蛋白1在转化生长因子β1诱导的大鼠心肌成纤维细胞中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2009,25(1):69-72.
[36] KUWAHARA F, KAI H, TOKUDA K, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta function blocking prevents myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction in pressure-overloaded rats. Circulation. 2002;106(1):130-135.
[37] ZHANG J, WANG Q, ZHAO S, et al. Astaxanthin attenuated pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis: Partially by activating SIRT1. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(7): 1715-1728.
[38] HUANG X, WEN D, ZHANG M, et al. Sirt1 activation ameliorates renal fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2014; 115(5):996-1005.
[39] LI H, WANG Y, LIU J, et al. Endothelial Klf2-Foxp1-TGFβ signal mediates the inhibitory effects of simvastatin on maladaptive cardiac remodeling. Theranostics. 2021;11(4):1609-1625.
[40] CHEN Y, HE T, ZHANG Z, et al. Activation of SIRT1 by Resveratrol Alleviates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy via Suppression of TGF-β1 Signaling. Pharmacology. 2021;106(11-12): 667-681.
[41] WANG X, YOU W, WU Z, et al. Apnea Hypopnea Index is an Independent Predictor of Coronary Microcirculatory Dysfunction in Stable Angina Pectoris Patients with a Single Borderline Lesion. Acta Cardiologica Sinica. 2020;36(3):207-215.
[42] KAMO T, AKAZAWA H, KOMURO I. Cardiac nonmyocytes in the hub of cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 2015;117(1):89-98.
[43] LEASK A. Getting to the heart of the matter: new insights into cardiac fibrosis. Circ Res. 2015;116(7):1269-7276.
[44] NICHOLSON SK, TUCKER GA, BRAMELD JM. Effects of dietary polyphenols on gene expression in human vascular endothelial cells. Proc Nutr Soc. 2008;67(1):42-47. |