中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3184-3189.doi: 10.12307/2022.618
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
沉默信息调节因子1基因对绝经后模型小鼠慢性心力衰竭的作用及机制
张海洋1,毕胜利2,冯静茹1,李 凡1,王 静1,赵 娜1,李新军1
- 河北北方学院附属第二医院,1心内科,2妇科,河北省张家口市 075100
Effects of silent information regulator 1 on chronic heart failure in a postmenopausal mouse model and its mechanism
Zhang Haiyang1, Bi Shengli2, Feng Jingru1, Li Fan1, Wang Jing1, Zhao Na1, Li Xinjun1
- 1Department of Cardiology, 2Department of Gynecology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075100, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
沉默信息调节因子1:一种进化上高度保守的组蛋白去乙酰化酶,通过催化去乙酰化过程起到抗炎、抗氧化、抗凋亡作用,参与慢性心力衰竭、心肌梗死、动脉粥样硬化等多种疾病的发生发展。
卵巢切除模型:通过切除实验动物双侧卵巢的方法造成雌激素缺乏,以此模拟绝经后状态,该模型在心血管疾病研究中应用广泛。因为绝经是心肌梗死、心力衰竭等心血管疾病的独立危险因素,卵巢切除模型的建立为研究绝经后心血管疾病的发病机制提供了良好的工具。
背景:绝经后冠心病妇女血清雌二醇降低与心功能减退、心室重构加重有关,绝经对慢性心力衰竭病情的影响及机制尚不十分清楚。沉默信息调节因子1在心血管系统中发挥保护作用。
目的:研究沉默信息调节因子1在卵巢切除加重小鼠慢性心力衰竭中的作用及机制。
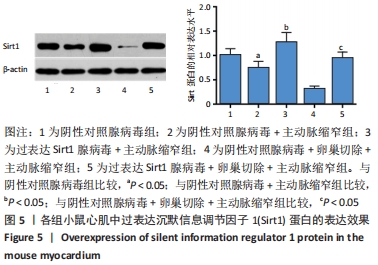
方法:选择野生型雌性C57BL/6J小鼠及沉默信息调节因子1基因敲除的雌性C57BL/6J小鼠进行实验。①将野生型小鼠随机分为:假手术组、主动脉缩窄组、卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄组、卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄+雌二醇组。术后第1天开始,卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄+雌二醇组大鼠按照0.2 mg/(kg·d)的剂量给予苯甲酸雌二醇皮下注射,其余各组大鼠给予等剂量生理盐水皮下注射,共8周。②将沉默信息调节因子1基因敲除小鼠随机分为:沉默信息调节因子1基因敲除+假手术组、沉默信息调节因子1基因敲除+主动脉缩窄组。③实验分为5组:阴性对照腺病毒组、阴性对照腺病毒+主动脉缩窄组、过表达沉默信息调节因子1腺病毒+主动脉缩窄组、阴性对照腺病毒+卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄组、过表达沉默信息调节因子1腺病毒+卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄组。通过多点注射阴性对照腺病毒或过表达沉默信息调节因子1的腺病毒实现沉默信息调节因子1的过表达。④造模后8周,检测左心室收缩末内径、左心室舒张末内径、左心室射血分数、血清雌二醇、脑钠肽水平、子宫质量、心肌病理改变及沉默信息调节因子1表达水平。
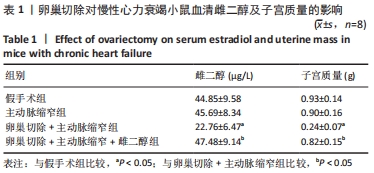
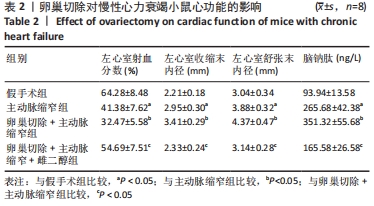
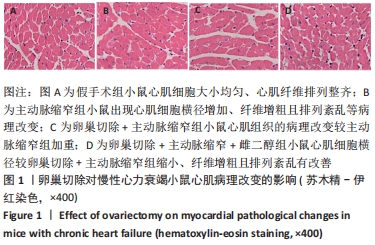
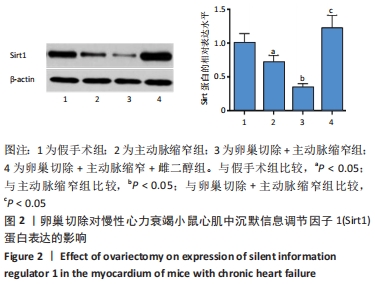
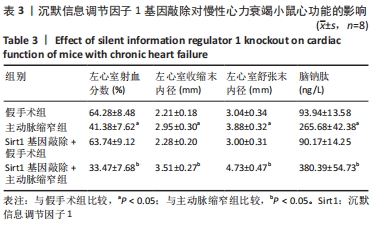
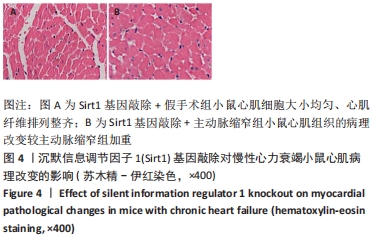
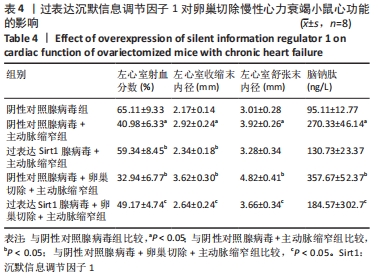
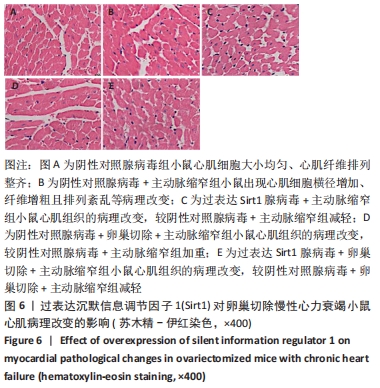
结果与结论:①与假手术组比较,主动脉缩窄组小鼠左心室收缩末内径、左心室舒张末内径、血清脑钠肽水平显著增加,左心室射血分数、心肌沉默信息调节因子1表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与主动脉缩窄组比较,卵巢切除 +主动脉缩窄组小鼠左心室收缩末内径、左心室舒张末内径、血清脑钠肽水平显著增加,左心室射血分数、血清雌二醇水平、心肌沉默信息调节因子1表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);沉默信息调节因子1基因敲除+主动脉缩窄组小鼠不表达沉默信息调节因子1,左心室收缩末内径、左心室舒张末内径、血清脑钠肽水平显著增加,左心室射血分数显著降低(P < 0.05);与阴性对照腺病毒+卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄组比较,过表达沉默信息调节因子1腺病毒+卵巢切除+主动脉缩窄组小鼠左心室收缩末内径、左心室舒张末内径、血清脑钠肽水平显著降低,左心室射血分数、心肌沉默信息调节因子1表达水平显著增加(P < 0.05);②结果说明,卵巢切除起到加重小鼠慢性心力衰竭病情的作用,抑制心肌中沉默信息调节因子1表达是与该作用相关的分子机制。
缩略语:沉默信息调节因子1:silent information regulator 1,Sirt1
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6689-9827 (张海洋)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: