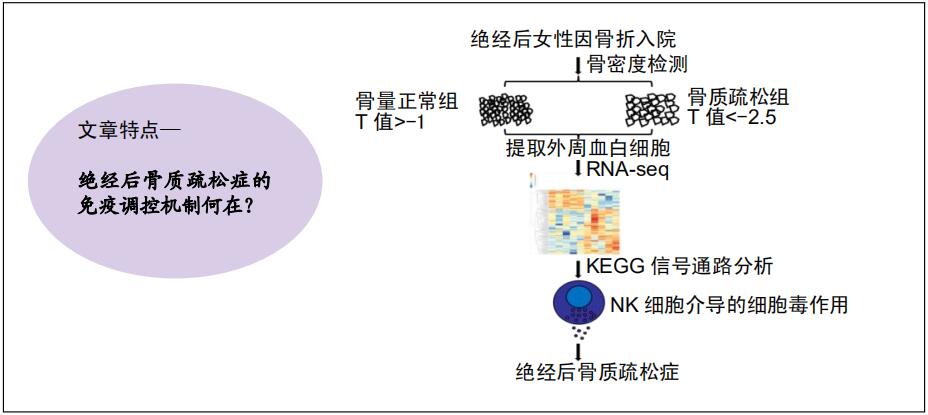
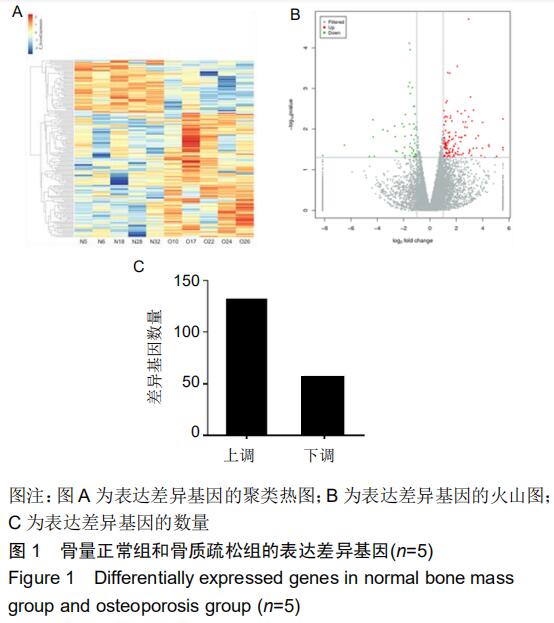
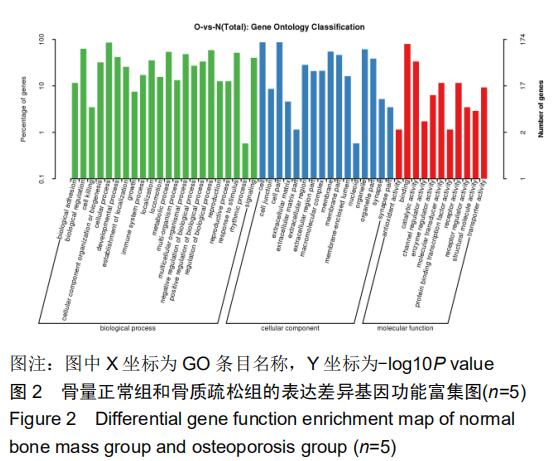
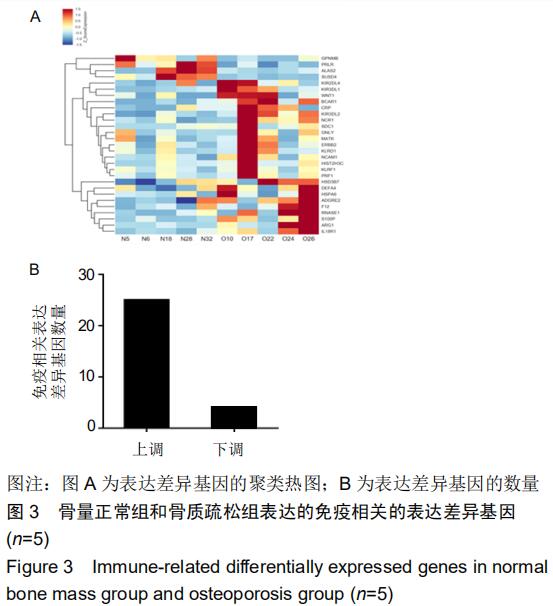
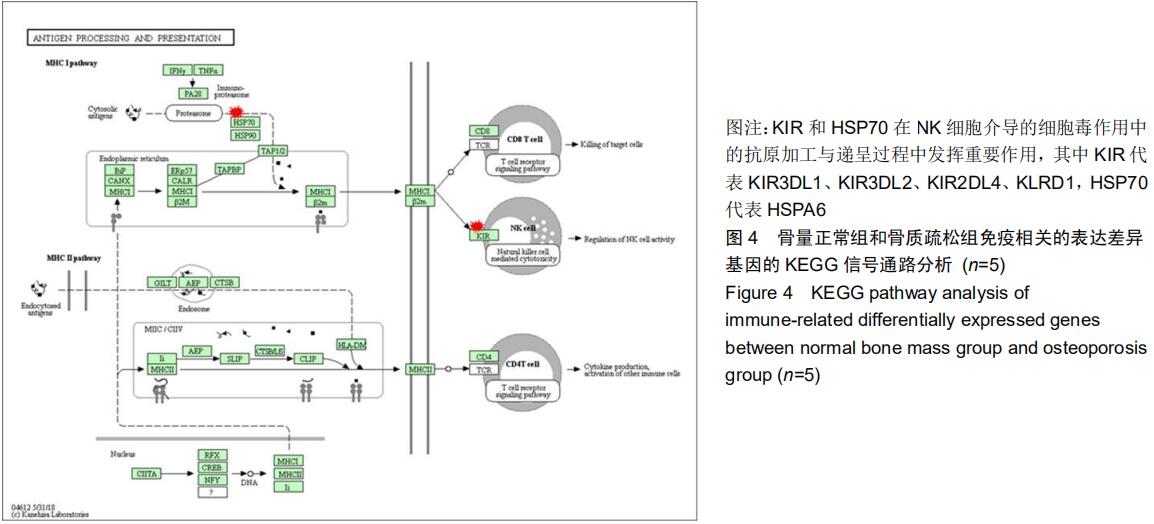
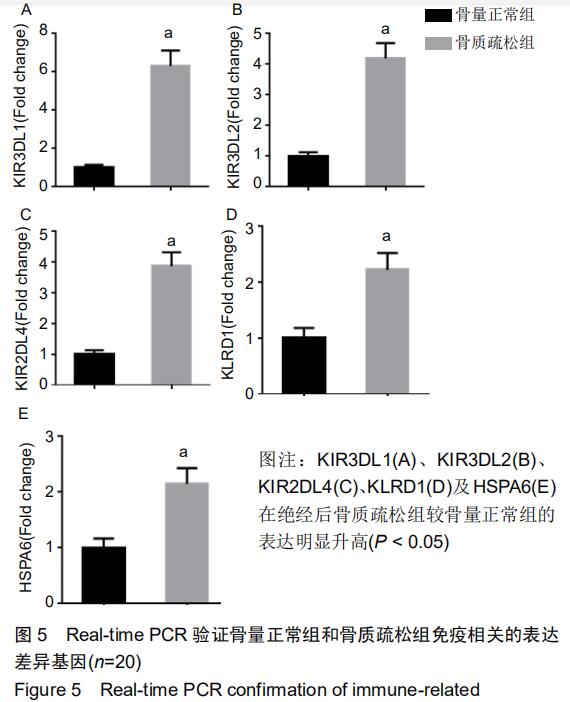
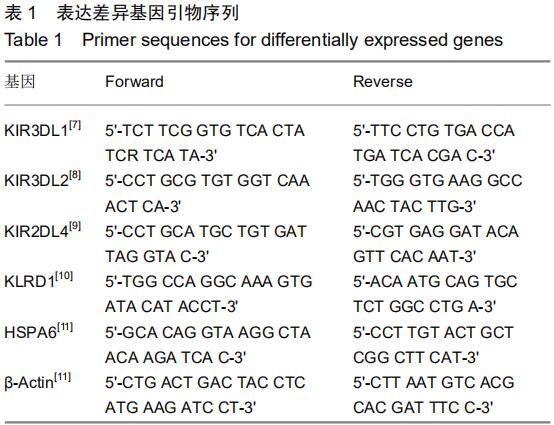
|
[1] COSMAN F.Long-term treatment strategies for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018; 30(4):420-426.
[2] WATTS NB. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Clinical Review. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2018;27(9):1093-1096.
[3] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408(6812):535-536.
[4] TAKAYANAGI H, OGASAWARA K, HIDA S, et al. T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature. 2000; 408(6812):600-605.
[5] MORI G,D'AMELIO P,FACCIO R, et al. Bone-immune cell crosstalk: bone diseases.J Immunol Res. 2015; 2015:108451.
[6] ANDERS S, HUBER W. Differential expression of RNA-Seq data at the gene level–the DESeq package. Heidelberg, Germany: European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). 2012.
[7] ZVYAGIN IV, MAMEDOV IZ, BRITANOVA OV, et al. Contribution of functional KIR3DL1 to ankylosing spondylitis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7(6):471-476.
[8] BATTISTELLA M, JANIN A, JEAN-LOUIS F, et al. KIR3DL2 (CD158k) is a potential therapeutic target in primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175(2):325-333.
[9] NOWAK I,MAJORCZYK E,PŁOSKI R,et al.Lack of KIR2DL4 gene in a fertile Caucasian woman.Tissue Antigens. 2011; 78(2):115-119.
[10] SHIN DL, PANDEY AK, ZIEBARTH JD, et al. Segregation of a spontaneous Klrd1 (CD94) mutation in DBA/2 mouse substrains. G3 (Bethesda). 2014;5(2):235-239.
[11] REGELING A, IMHANN F, VOLDERS HH, et al. HSPA6 is an ulcerative colitis susceptibility factor that is induced by cigarette smoke and protects intestinal epithelial cells by stabilizing anti-apoptotic Bcl-XL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1862(4):788-796.
[12] NILSSON S, KOEHLER KF, GUSTAFSSON JÅ. Development of subtype-selective oestrogen receptor-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10(10):778-792.
[13] MIYAUCHI Y, SATO Y, KOBAYASHI T, et al. HIF1α is required for osteoclast activation by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(41):16568-16573.
[14] STREICHER C, HEYNY A, ANDRUKHOVA O, et al. Estrogen Regulates Bone Turnover by Targeting RANKL Expression in Bone Lining Cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6460.
[15] RIZZOLI R.Postmenopausal osteoporosis: Assessment and management. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 32(5):739-757.
[16] SRIVASTAVA RK, DAR HY, MISHRA PK. Immunoporosis: Immunology of Osteoporosis-Role of T Cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:657.
[17] TILKERIDIS K, KIZIRIDIS G, VERVERIDIS A, et al. Immunoporosis: A New Role for Invariant Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells Through Overexpression of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Ligand (RANKL). Med Sci Monit. 2019;25: 2151-2158.
[18] LISOVSKY I, KANT S, TREMBLAY-MCLEAN A, et al. Differential contribution of education through KIR2DL1, KIR2DL3, and KIR3DL1 to antibody-dependent (AD) NK cell activation and ADCC. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;105(3):551-563.
[19] CHENG H, SCHWELL V, CURTIS BR, et al. Conformational Changes in the Cytoplasmic Region of KIR3DL1 upon Interaction with SHP-2. Structure. 2019;27(4):639-650 e2.
[20] URESHINO H, SHINDO T, KOJIMA H, et al. Allelic Polymorphisms of KIRs and HLAs Predict Favorable Responses to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in CML. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018;6(6):745-754.
[21] KAMIYA T, SEOW SV, WONG D, et al. Blocking expression of inhibitory receptor NKG2A overcomes tumor resistance to NK cells. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(5):2094-2106.
[22] KORDELAS L, STECKEL NK, HORN PA, et al. The Activating NKG2C Receptor Is Significantly Reduced in NK Cells after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Severe Graft-versus-Host Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 27;17(11). pii: E1797.
[23] HUANG H, PATEL DD, MANTON KG. The immune system in aging: roles of cytokines, T cells and NK cells. Front Biosci. 2005;10: 192-215.
[24] LI L, WANG Y, ZHANG N,et al. Heterozygous deletion of LRP5 gene in mice alters profile of immune cells and modulates differentiation of osteoblasts. Bioscience trends. 2018;12(3): 266-274.
[25] SCHILLING D, TETZLAFF F, KONRAD S, et al. A hypoxia-induced decrease of either MICA/B or Hsp70 on the membrane of tumor cells mediates immune escape from NK cells. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015;20(1):139-147.
|