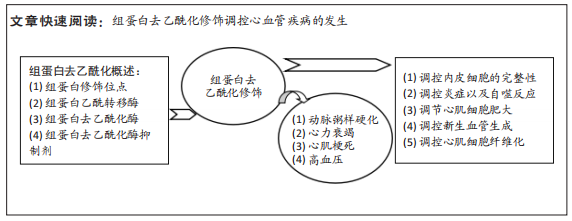
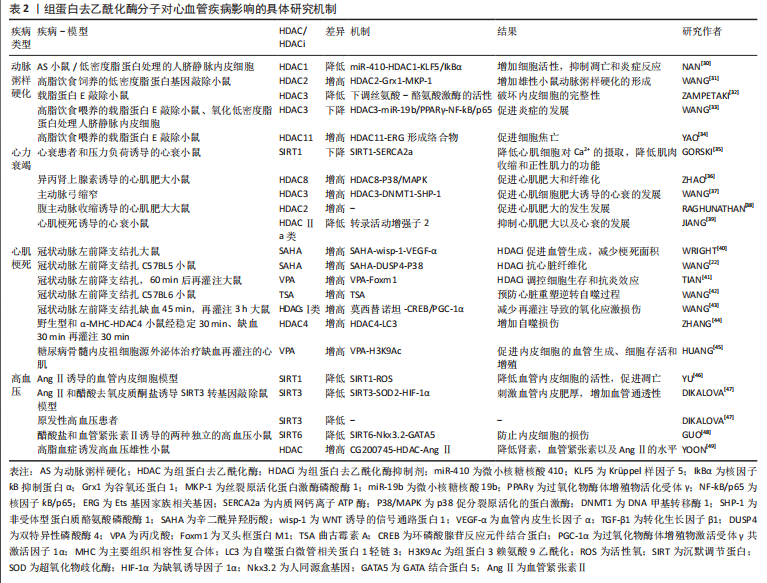
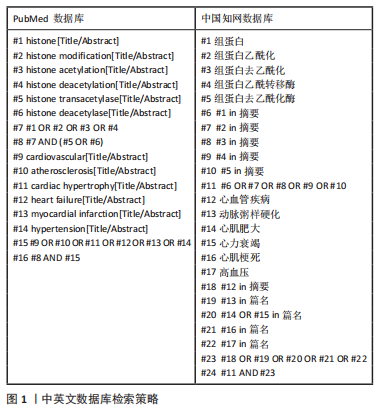
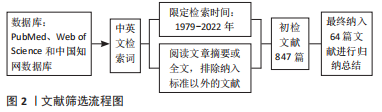
[1] 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告》编写组.《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020》要点解读[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2021,26(3):209-218.
[2] ZHAO D, LIU J, WANG M, et al. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: current features and implications. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(4):203-212.
[3] PRASHER D, GREENWAY SC, SINGH RB. The impact of epigenetics on cardiovascular disease. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98(1):12-22.
[4] LACAGNINA S. Epigenetics. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2019;13(2):165-169.
[5] CAVALLI G, HEARD E. Advances in epigenetics link genetics to the environment and disease. Nature. 2019;571(7766):489-499.
[6] LEE HT, OH S, RO DH, et al. The Key Role of DNA Methylation and Histone Acetylation in Epigenetics of Atherosclerosis. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2020;9(3): 419-434.
[7] CHELLADURAI P, BOUCHERAT O, STENMARK K, et al. Targeting histone acetylation in pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(1):54-71.
[8] FUNAMOTO M, SUNAGAWA Y, KATANASAKA Y, et al. Histone Acetylation Domains Are Differentially Induced during Development of Heart Failure in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1771.
[9] LEI I, TIAN S, GAO W, et al. Acetyl-CoA production by specific metabolites promotes cardiac repair after myocardial infarction via histone acetylation. Elife. 2021;10:e60311.
[10] SUDA M, IWAI K. Identification of suberimidate cross-linking sites of four histone sequences in H1-depleted chromatin. Histone arrangement in nucleosome core. J Biochem. 1979;86(6):1659-1670.
[11] LIU Y, MIN J. Structure and function of histone methylation-binding proteins in plants. Biochem J. 2016;473(12):1663-1680.
[12] TSE C, HANSEN JC. Hybrid trypsinized nucleosomal arrays: identification of multiple functional roles of the H2A/H2B and H3/H4 N-termini in chromatin fiber compaction. Biochemistry. 1997;36(38):11381-11388.
[13] XU H, YE M, XIA A, et al. The Fng3 ING protein regulates H3 acetylation and H4 deacetylation by interacting with two distinct histone-modifying complexes. New Phytol. 2022;235(6):2350-2364.
[14] KOUZARIDES T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128(4): 693-705.
[15] BHAUMIK S R, SMITH E, SHILATIFARD A. Covalent modifications of histones during development and disease pathogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007;14(11): 1008-1016.
[16] ROPERO S, ESTELLER M. The role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol Oncol. 2007;1(1):19-25.
[17] SANCHEZ-FERNANDEZ C, LORDA-DIEZ C I, DUARTE-OLIVENZA C, et al. Histone Epigenetic Signatures in Embryonic Limb Interdigital Cells Fated to Die. Cells. 2021;10(4):911.
[18] SCHLüTER A, AKSAN B, FIORAVANTI R, et al. Histone Deacetylases Contribute to Excitotoxicity-Triggered Degeneration of Retinal Ganglion Cells In Vivo. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(12):8018-8034.
[19] HE Q, CHEN K, YE R, et al. Associations of sirtuins with clinicopathological variables and prognosis in human ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 2020;19(4):3278-3288.
[20] NúñEZ-ÁLVAREZ Y, SUELVES M. HDAC11: a multifaceted histone deacetylase with proficient fatty deacylase activity and its roles in physiological processes. FEBS J. 2022;289(10):2771-2792.
[21] KONG Y, REN W, FANG H, et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) Promote KLF5 Ubiquitination and Degradation in Basal-like Breast Cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(5):2104-2115.
[22] WANG K, TANG R, WANG S, et al. SAHA could inhibit TGF-β1/p38 pathway in MI-induced cardiac fibrosis through DUSP4 overexpression. Heart Vessels. 2022; 37(1):152-160.
[23] RUESS DA, PROBST M, MARJANOVIC G, et al. HDACi Valproic Acid (VPA) and Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA) Delay but Fail to Protect against Warm Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0161233.
[24] LIU Z, CHEN T, HAN Q, et al. HDAC inhibitor LMK‑235 promotes the odontoblast differentiation of dental pulp cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):1445-1452.
[25] BALPARDA M, ELSäSSER M, BADIA M B, et al. Acetylation of conserved lysines fine-tunes mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase activity in land plants. Plant J. 2022;109(1):92-111.
[26] SARAIVA N Z, OLIVEIRA C S, ALMEIDA N, et al. Epigenetic modifiers during in vitro maturation as a strategy to increase oocyte competence in bovine. Theriogenology. 2022;187:95-101.
[27] TAO L, YU H V, LLAMAS J, et al. Enhancer decommissioning imposes an epigenetic barrier to sensory hair cell regeneration. Dev Cell. 2021;56(17):2471-2485.e5.
[28] WANG D, LIU C, LI Z, et al. Regulation of Histone Acetylation on Expression Profiles of Potassium Channels During Cardiomyocyte Differentiation From Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(12):4460-4467.
[29] PONS D, DE VRIES FR, VAN DEN ELSEN PJ, et al. Epigenetic histone acetylation modifiers in vascular remodelling: new targets for therapy in cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2009;30(3):266-277.
[30] NAN S, WANG Y, XU C, et al. Interfering microRNA-410 attenuates atherosclerosis via the HDAC1/KLF5/IKBα/NF-κB axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:646-657.
[31] WANG L, AHN Y J, ASMIS R. Inhibition of myeloid HDAC2 upregulates glutaredoxin 1 expression, improves protein thiol redox state and protects against high-calorie diet-induced monocyte dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2021;328:23-32.
[32] ZAMPETAKI A, ZENG L, MARGARITI A, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 is critical in endothelial survival and atherosclerosis development in response to disturbed flow. Circulation. 2010;121(1):132-142.
[33] WANG J, XU X, LI P, et al. HDAC3 protects against atherosclerosis through inhibition of inflammation via the microRNA-19b/PPARγ/NF-κB axis. Atherosclerosis. 2021;323:1-12.
[34] YAO F, JIN Z, ZHENG Z, et al. HDAC11 promotes both NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD
and caspase-3/GSDME pathways causing pyroptosis via ERG in vascular endothelial cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):112.
[35] GORSKI PA, JANG SP, JEONG D, et al. Role of SIRT1 in Modulating Acetylation of the Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase in Heart Failure. Circ Res. 2019;124(9):e63-e80.
[36] ZHAO T, KEE H J, BAI L, et al. Selective HDAC8 Inhibition Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis via p38 MAPK Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:677757.
[37] WANG YY, GAO B, YANG Y, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 suppresses the expression of SHP-1 via deacetylation of DNMT1 to promote heart failure. Life Sci. 2022;292: 119552.
[38] RAGHUNATHAN S, GOYAL RK, PATEL BM. Selective inhibition of HDAC2 by magnesium valproate attenuates cardiac hypertrophy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;95(3):260-267.
[39] JIANG H, JIA D, ZHANG B, et al. Exercise improves cardiac function and glucose metabolism in mice with experimental myocardial infarction through inhibiting HDAC4 and upregulating GLUT1 expression. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020;115(3):28.
[40] WRIGHT LH, HERR DJ, BROWN SS, et al. Angiokine Wisp-1 is increased in myocardial infarction and regulates cardiac endothelial signaling. JCI Insight. 2018;3(4):e95824.
[41] TIAN S, LEI I, GAO W, et al. HDAC inhibitor valproic acid protects heart function through Foxm1 pathway after acute myocardial infarction. EBioMedicine. 2019; 39:83-94.
[42] WANG Y, CHEN P, WANG L, et al. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases Prevents Cardiac Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction by Restoring Autophagosome Processing in Cardiac Fibroblasts. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(5):1999-2011.
[43] WANG K, TANG R, WANG S, et al. Isoform-Selective HDAC Inhibitor Mocetinostat (MGCD0103) Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Via Mitochondrial Protection Through the HDACs/CREB/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022;79(2):217-228.
[44] ZHANG L, WANG H, ZHAO Y, et al. Myocyte-specific overexpressing HDAC4 promotes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med. 2018;24(1):37.
[45] HUANG G, CHENG Z, HILDEBRAND A, et al. Diabetes impairs cardioprotective function of endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles via H3K9Ac inhibition. Theranostics. 2022;12(9):4415-4430.
[46] YU Q, ZHAO J, LIU B. Bazedoxifene activates the angiotensin II-induced HUVEC hypertension model by targeting SIRT1. Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(2):120.
[47] DIKALOVA A E, PANDEY A, XIAO L, et al. Mitochondrial Deacetylase Sirt3 Reduces Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension While Sirt3 Depletion in Essential Hypertension Is Linked to Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Circ Res. 2020;126(4):439-452.
[48] GUO J, WANG Z, WU J, et al. Endothelial SIRT6 Is Vital to Prevent Hypertension and Associated Cardiorenal Injury Through Targeting Nkx3.2-GATA5 Signaling. Circ Res. 2019;124(10):1448-1461.
[49] YOON GE, JUNG JK, LEE YH, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor CG200745 ameliorates high-fat diet-induced hypertension via inhibition of angiotensin II production. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(3):491-500.
[50] DHAGIA V, KITAGAWA A, JACOB C, et al. G6PD activity contributes to the regulation of histone acetylation and gene expression in smooth muscle cells and to the pathogenesis of vascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021;320(3):H999-H1016.
[51] GROOTAERT M, FINIGAN A, FIGG N L, et al. SIRT6 Protects Smooth Muscle Cells From Senescence and Reduces Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2021;128(4):474-491.
[52] LECCE L, XU Y, V’GANGULA B, et al. Histone deacetylase 9 promotes endothelial-mesenchymal transition and an unfavorable atherosclerotic plaque phenotype. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(15):e131178.
[53] QIN J, GUO N, TONG J, et al. Function of histone methylation and acetylation modifiers in cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021;159:120-129.
[54] MORIN S, CHARRON F, ROBITAILLE L, et al. GATA-dependent recruitment of MEF2 proteins to target promoters. EMBO J. 2000;19(9):2046-2055.
[55] ZHANG CL, MCKINSEY TA, CHANG S, et al. Class II histone deacetylases act as signal-responsive repressors of cardiac hypertrophy. Cell. 2002;110(4):479-488.
[56] VEGA RB, HARRISON BC, MEADOWS E, et al. Protein kinases C and D mediate agonist-dependent cardiac hypertrophy through nuclear export of histone deacetylase 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(19):8374-8385.
[57] ZHANG J, LIANG Y, HUANG X, et al. STAT3-induced upregulation of lncRNA MEG3 regulates the growth of cardiac hypertrophy through miR-361-5p/HDAC9 axis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):460.
[58] HU T, SCHREITER FC, BAGCHI RA, et al. HDAC5 catalytic activity suppresses cardiomyocyte oxidative stress and NRF2 target gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(21):8640-8652.
[59] ZHAO X, STERNSDORF T, BOLGER TA, et al. Regulation of MEF2 by histone deacetylase 4- and SIRT1 deacetylase-mediated lysine modifications. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(19):8456-8464.
[60] SONG T, GUAN X, WANG X, et al. Dynamic modulation of gut microbiota improves post-myocardial infarct tissue repair in rats via butyric acid-mediated histone deacetylase inhibition. FASEB J. 2021;35(3):e21385.
[61] LI D, YANG Y, WANG S, et al. Role of acetylation in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Redox Biol. 2021;46:102089.
[62] WU L, ZHANG Y, REN J. Epigenetic modification in alcohol use disorder and alcoholic cardiomyopathy: From pathophysiology to therapeutic opportunities. Metabolism. 2021;125:154909.
[63] XU Z, SUN J, TONG Q, et al. The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2001.
[64] LI S J, KAO Y H, CHUNG C C, et al. HDAC I inhibitor regulates RUNX2 transactivation through canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling in aortic valvular interstitial cells. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(2):744-754.
|