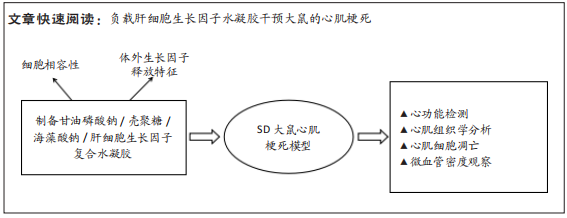
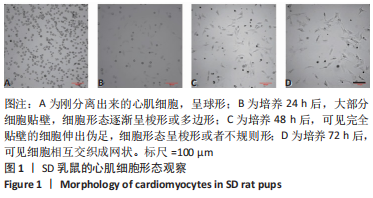
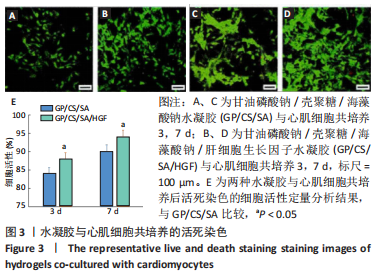
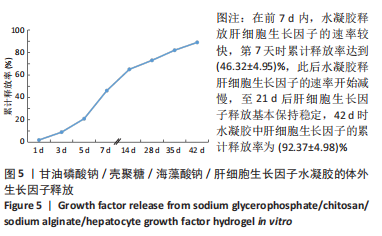
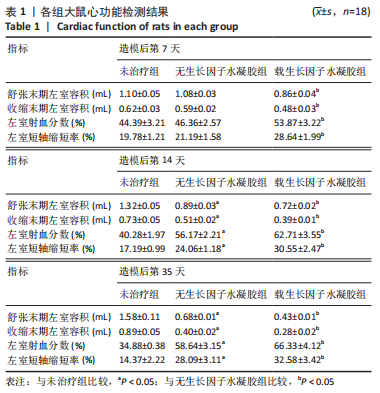
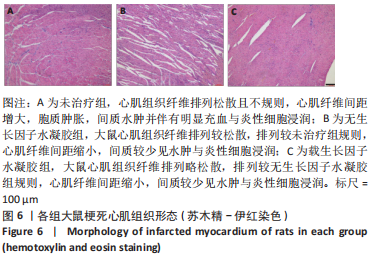
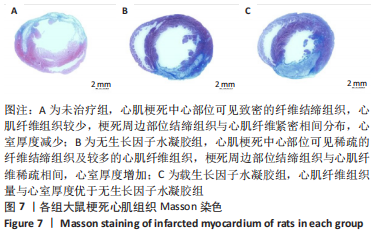
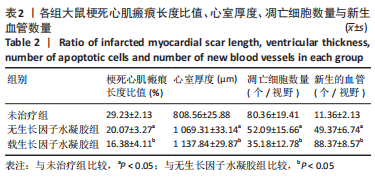
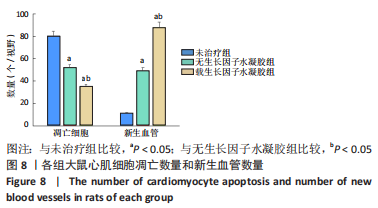
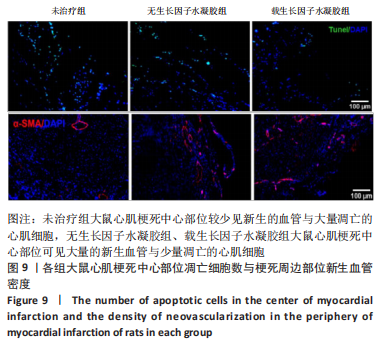
[1] SAITO Y, TANAKA A, NODE K, et al. Uric acid and cardiovascular disease: A clinical review. J Cardiol. 2021;78(1):51-57.
[2] SOPPERT J, LEHRKE M, MARX N, et al. Lipoproteins and lipids in cardiovascular disease: from mechanistic insights to therapeutic targeting. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;159:4-33.
[3] KAPUR NK, THAYER KL, ZWECK E. Cardiogenic Shock in the Setting of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2020;16(1):16-21.
[4] MITSIS A, GRAGNANO F. Myocardial Infarction with and without ST-segment Elevation: a Contemporary Reappraisal of Similarities and Differences. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2021;17(4):e230421189013.
[5] SUN J, SHEN H, SHAO L, et al. HIF-1α overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mediates cardioprotection in myocardial infarction by enhanced angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1): 373.
[6] YAO X, YANG W, REN Z, et al. Neuroprotective and Angiogenesis Effects of Levetiracetam Following Ischemic Stroke in Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:638209.
[7] LIANG C, ZHANG T, SHI XL, et al. Modified Renshen Yangrong decoction enhances angiogenesis in ischemic stroke through promotion of MicroRNA-210 expression by regulating the HIF/VEGF/Notch signaling pathway. Brain Behav. 2021;11(8):e2295.
[8] DIKICI S, BULLOCK AJ, YAR M, et al. 2-deoxy-d-ribose (2dDR) upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and stimulates angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 2020;131:104035.
[9] QAYYUM AA, JOSHI FR, LUND LD, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in ischaemic heart disease. Ugeskr Laeger. 2020;182(44): V05200344.
[10] JEONG HM, WEON KY, SHIN BS, et al. 3D-Printed Gastroretentive Sustained Release Drug Delivery System by Applying Design of Experiment Approach. Molecules. 2020;25(10):2330.
[11] KAMAL MM, AKTER S, AL HAGBANI T, et al. Sustained release of curcumin self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) from solvent-cast Soluplus® films. Pharm Dev Technol. 2021;26(10):1102-1109.
[12] QIU S, GAO J, LIU J, et al. Study on Novel Nanoparticle Slow-Release Drugs for Moyamoya Disease. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021;21(2): 1008-1017.
[13] MONTAGNAT OD, WEBSTER GR, BULITTA JB, et al. Lessons learned in the development of sustained release penicillin drug delivery systems for the prophylactic treatment of rheumatic heart disease (RHD). Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018;8(3):729-739.
[14] MADONNA R, ROKOSH G, DE CATERINA R, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor/Met gene transfer in cardiac stem cells--potential for cardiac repair. Basic Res Cardiol. 2010;105(4):443-452.
[15] O’NEILL HS, O’SULLIVAN J, PORTEOUS N, et al. A collagen cardiac patch incorporating alginate microparticles permits the controlled release of hepatocyte growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 to enhance cardiac stem cell migration and proliferation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):e384-e394.
[16] ZHANG Z, LONG C, GUAN Y, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor intervention to reduce myocardial injury and improve cardiac function on diabetic myocardial infarction rats. Eur J Histochem. 2020;64(s2):3142.
[17] 陈慧敏,宋婷婷,吴齐越,等.海藻酸钠壳聚糖支架复合成骨细胞特异性多肽修复兔颅骨缺损[J].安徽医科大学学报,2017,52(4): 504-507
[18] LV K, LI Q, ZHANG L, et al. Incorporation of small extracellular vesicles in sodium alginate hydrogel as a novel therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2019;9(24):7403-7416.
[19] LI Y, CHEN X, JIN R, et al. Injectable hydrogel with MSNs/microRNA-21-5p delivery enables both immunomodification and enhanced angiogenesis for myocardial infarction therapy in pigs. Sci Adv. 2021; 7(9):eabd6740.
[20] CHEN R, ZHU C, XU L, et al. An injectable peptide hydrogel with excellent self-healing ability to continuously release salvianolic acid B for myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120855.
[21] RUVINOV E, COHEN S. Alginate biomaterial for the treatment of myocardial infarction: Progress, translational strategies, and clinical outlook: From ocean algae to patient bedside. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;96:54-76.
[22] LLC BB. IK-5001 for the prevention of remodeling of the ventricle and congestive heart failure after acute myocardial infarction(PRESERVATION 1). Study NCT012265 63 Available at: http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov 2010 (Accessed July 16, 2015).
[23] MCCARTHY PC, ZHANG Y, ABEBE F. Recent Applications of Dual-Stimuli Responsive Chitosan Hydrogel Nanocomposites as Drug Delivery Tools. Molecules. 2021;26(16):4735.
[24] ERICKSON CB, NEWSOM JP, FLETCHER NA, et al. In vivo degradation rate of alginate-chitosan hydrogels influences tissue repair following physeal injury. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(6): 2484-2494.
[25] 王晓,郝新青,王小萌,等.壳聚糖/海藻酸钠水凝胶顺序释放BMP/WNT信号通路激活剂促成骨细胞分化的体外实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,31(1):9-15
[26] GHOLAMI M, GILANPOUR H, SADEGHINEZHAD J, et al. Facile fabrication of an erythropoietin-alginate/chitosan hydrogel and evaluation of its local therapeutic effects on spinal cord injury in rats. Daru. 2021; 29(2):255-265.
[27] 王秀力,姜世强,刘颖,等.慢病毒介导Wnt蛋白5a基因过表达对骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死大鼠的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(9):1720-1723
[28] 刘化进,马江伟,乔增勇,等.血清VEGF、HGF在AMI阿托伐他汀强化治疗干预时的变化及对AMI预后的预测[J].贵州医药,2018, 42(11):1389-1391
[29] KAMBE Y, YAMAOKA T. Biodegradation of injectable silk fibroin hydrogel prevents negative left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10):4153-4165.
[30] GUO W, FENG W, HUANG J, et al. Supramolecular Self-Assembled Nanofibers Efficiently Activate the Precursor of Hepatocyte Growth Factor for Angiogenesis in Myocardial Infarction Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(19):22131-22141.
[31] SALA V, GALLO S, GATTI S, et al. Cardiac concentric hypertrophy promoted by activated Met receptor is mitigated in vivo by inhibition of Erk1,2 signalling with Pimasertib. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;93:84-97.
[32] WANG Z, FEI S, SUO C, et al. Antifibrotic Effects of Hepatocyte Growth Factor on Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Transforming Growth Factor-Beta1 (TGF-β1)/Smad and Akt/mTOR/P70S6K Signaling Pathways. Ann Transplant. 2018;23:1-10. |