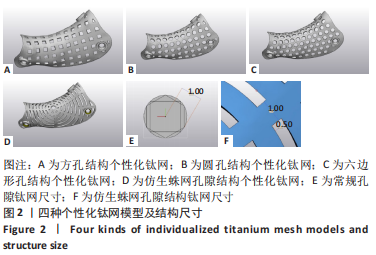
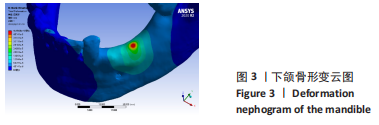
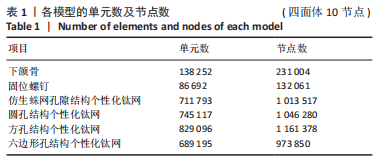
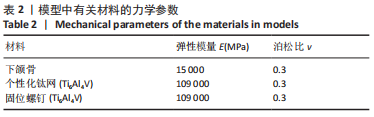
[1] CHA HS, KIM JW, HWANG JH, et al. Frequency of bone graft in implant surgery. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;38(1):19.
[2] BRIGUGLIO F, FALCOMATÀ D, MARCONCINI S, et al. The Use of Titanium Mesh in Guided Bone Regeneration: A Systematic Review. Int J Dent. 2019;2019:9065423.
[3] TOLSTUNOV L, HAMRICK JFE, BROUMAND V, et al. Bone Augmentation Techniques for Horizontal and Vertical Alveolar Ridge Deficiency in Oral Implantology. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2019;31(2):163-191.
[4] RA G, WO Q. Bone regeneration in dentistry: an overview. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021;35(1 Suppl.1):37-46.
[5] CHIAPASCO M, ZANIBONI M, BOISCO M. Augmentation procedures for the rehabilitation of deficient edentulous ridges with oral implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17 Suppl 2:136-159.
[6] CUCCHI A, VIGNUDELLI E, FIORINO A, et al. Vertical ridge augmentation (VRA) with Ti-reinforced d-PTFE membranes or Ti meshes and collagen membranes: 1-year results of a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2021;32(1):1-14.
[7] NAENNI N, STUCKI L, HÜSLER J, et al. Implants sites with concomitant bone regeneration using a resorbable or non-resorbable membrane result in stable marginal bone levels and similar profilometric outcomes over 5 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2021;32(8):893-904.
[8] CUCCHI A, VIGNUDELLI E, NAPOLITANO A, et al. Evaluation of complication rates and vertical bone gain after guided bone regeneration with non-resorbable membranes versus titanium meshes and resorbable membranes. A randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(5):821-832.
[9] GU C, XU L, SHI A, et al. Titanium Mesh Exposure in Guided Bone Regeneration Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2022;37(1):e29-e40.
[10] MAIORANA C, FONTANA F, DAL POLO MR, et al. Dense Polytetrafluoroethylene Membrane versus Titanium Mesh in Vertical Ridge Augmentation: Clinical and Histological Results of a Split-mouth Prospective Study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021;22(5):465-472.
[11] 郭雪琪,陈韵欣,杨岚,等.3D打印个性化钛网修复严重牙槽骨缺损的短期效果观察[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2021,26(6):368-375.
[12] HARTMANN A, SEILER M. Minimizing risk of customized titanium mesh exposures - a retrospective analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):36.
[13] LIZIO G, PELLEGRINO G, CORINALDESI G, et al. Guided bone regeneration using titanium mesh to augment 3-dimensional alveolar defects prior to implant placement. A pilot study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(6):607-621.
[14] PENG WM, LIU YF, JIANG XF, et al. Bionic mechanical design and 3D printing of novel porous Ti6Al4V implants for biomedical applications. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019;20(8):647-659.
[15] KAEWUNRUEN S, NGAMKHANONG C, XU S. Large amplitude vibrations of imperfect spider web structures. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19161.
[16] 邓欢,田茂欢.集中荷载与风载作用下蜘蛛网变形行为研究[J].湖北大学学报(自然科学版),2018,40(5):496-500+506.
[17] SU I, NARAYANAN N, LOGRONO MA, et al. In situ three-dimensional spider web construction and mechanics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(33):e2101296118.
[18] 王心彧,张亮,韩泽奎,等.用于牙槽骨增量的钛网的设计及制作方法,CN113520638A[P/OL]. 2021-06-18. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/patent/CN202110676172.0
[19] BAI L, JI P, LI X, et al. Mechanical Characterization of 3D-Printed Individualized Ti-Mesh (Membrane) for Alveolar Bone Defects. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:4231872.
[20] SARRAFPOUR B, SWAIN M, LI Q, et al. Tooth eruption results from bone remodelling driven by bite forces sensed by soft tissue dental follicles: a finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58803.
[21] CHIAPASCO M, CASENTINI P, TOMMASATO G, et al. Customized CAD/CAM titanium meshes for the guided bone regeneration of severe alveolar ridge defects: Preliminary results of a retrospective clinical study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2021;32(4):498-510.
[22] LI S, ZHANG T, ZHOU M, et al. A novel digital and visualized guided bone regeneration procedure and digital precise bone augmentation: A case series. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2021;23(1):19-30.
[23] SUMIDA T, OTAWA N, KAMATA YU, et al. Custom-made titanium devices as membranes for bone augmentation in implant treatment: Clinical application and the comparison with conventional titanium mesh. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43(10):2183-2188.
[24] SAGHEB K, SCHIEGNITZ E, MOERGEL M, et al. Clinical outcome of alveolar ridge augmentation with individualized CAD-CAM-produced titanium mesh. Int J Implant Dent. 2017;3(1):36.
[25] SOLDATOS NK, STYLIANOU P, KOIDOU VP, et al. Limitations and options using resorbable versus nonresorbable membranes for successful guided bone regeneration. Quintessence Int. 2017;48(2):131-147.
[26] CUCCHI A, BIANCHI A, CALAMAI P, et al. Clinical and volumetric outcomes after vertical ridge augmentation using computer-aided-design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) customized titanium meshes: a pilot study. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):219.
[27] SEILER M, KÄMMERER PW, PEETZ M, et al. Customized lattice structure in reconstruction of three-dimensional alveolar defects. Int J Comput Dent. 2018;21(3):261-267.
[28] SUMIDA T, OTAWA N, KAMATA YU, et al. Custom-made titanium devices as membranes for bone augmentation in implant treatment: Clinical application and the comparison with conventional titanium mesh. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43(10):2183-2188.
[29] 孟文侠,胡亚利.个性化钛网联合屏障膜在引导骨再生修复牙槽骨缺损中的应用效果[J].医学临床研究,2022,39(6):862-865.
[30] 王献利,王国庆,赵西博,等.钛网在上前牙唇侧重度骨缺损种植中的临床研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2021,19(1):26-30.
[31] XIE Y, LI S, ZHANG T, et al. Titanium mesh for bone augmentation in oral implantology: current application and progress. Int J Oral Sci. 2020; 12(1):37.
[32] 白丽云.用于牙槽骨增量的3D打印个性化钛网的生物力学研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2019.
[33] RAKHMATIA YD, AYUKAWA Y, JINNO Y, et al. Micro-computed tomography analysis of early stage bone healing using micro-porous titanium mesh for guided bone regeneration: preliminary experiment in a canine model. Odontology. 2017;105(4):408-417.
[34] GUTTA R, BAKER RA, BARTOLUCCI AA, et al. Barrier membranes used for ridge augmentation: is there an optimal pore size? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67:1218-1225.
[35] SENOO M, HASUIKE A, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Comparison of Macro-and Micro-porosity of a Titanium Mesh for Guided Bone Regeneration: An In Vivo Experimental Study. In Vivo. 2022;36(1):76-85.
[36] DELLAVIA C, CANCIANI E, PELLEGRINI G, et al. Histological assessment of mandibular bone tissue after guided bone regeneration with customized computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacture titanium mesh in humans: A cohort study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2021;23(4):600-611.
[37] HER S, KANG T, FIEN MJ. Titanium mesh as an alternative to a membrane for ridge augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70: 803-810.
[38] TAMADDON M, SAMIZADEH S, WANG L, et al. Intrinsic Osteoinductivity of Porous Titanium Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Biomater. 2017;2017:5093063.
[39] 吴文孟,张倩,宁宝麟,等.3D打印Ti-6Al-4V合金机械性能研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2016,3(10): 93-95.
[40] 程康杰.修复下颌骨缺损的复合结构植入体优化设计及制备研究[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2020.
[41] YAN W, DING M, KONG B, et al. Lightweight Splint Design for Individualized Treatment of Distal Radius Fracture. J Med Syst. 2019; 43(8):284.
[42] QIN Z, COMPTON BG, LEWIS JA, et al. Structural optimization of 3D-printed synthetic spider webs for high strength. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7038.
[43] 张世梁.基于蜘蛛网结构的伞状可展机构设计与分析[D].长春:长春工业大学,2019.
[44] AOYANAGI Y, OKUMURA K. Simple model for the mechanics of spider webs [published correction appears in Phys Rev Lett. 2015;115(3):039903]. Phys Rev Lett. 2010;104(3):038102.
|