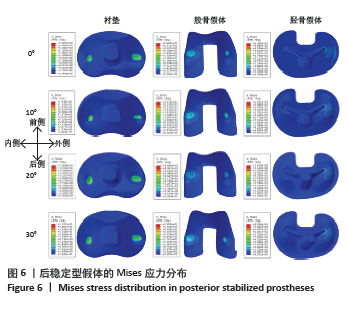
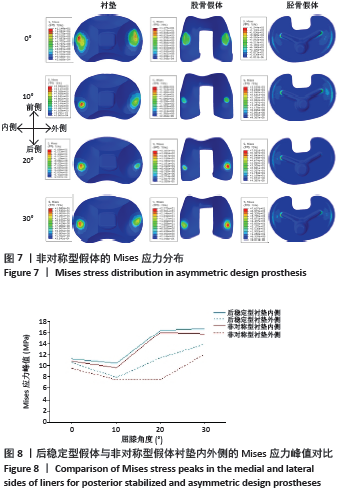
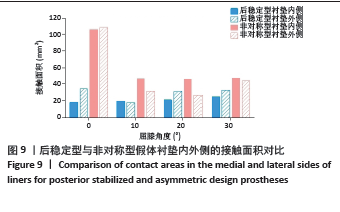
[1] 刘超.胫骨平台后倾角在全膝关节置换术中不同截骨方案的差异分析[D].新乡:新乡医学院,2022.
[2] BISTOLFI A, GIUSTRA F, BOSCO F, et al. Comparable results between crosslinked polyethylene and conventional ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene implanted in total knee arthroplasty: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(9):3120-3130.
[3] HODGES NA, SUSSMAN EM, STEGEMANN JP. Aseptic and septic prosthetic joint loosening: Impact of biomaterial wear on immune cell function, inflammation, and infection. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121127.
[4] KUO AW, CHEN DB, WOOD J, et al. Modern total knee arthroplasty designs do not reliably replicate anterior femoral morphology. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28:2808-2815.
[5] SONG YD, NAKAMURA S, KURIYAMA S, et al. How does asymmetric tibial insert affect tibiofemoral kinematics and contact stresses in total knee Arthroplasty? Knee. 2022;39:185-196.
[6] ROSSI SMP, SANGALETTI R, JANNELLI E, et al. PCL preservation or sacrifice does not influence clinical outcomes and survivorship at mid-term follow-up of a J-curve CR total knee replacement with a medial congruent liner and a functional coronal alignment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024;144(1):307-313.
[7] KOHN MD, SASSOON AA, FERNANDO ND. Classifications in brief: Kellgren-Lawrence classification of osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474: 1886-1893.
[8] 张震,董跃福,陈秋平,等.基于CT和MRI影像数据融合构建个体化OA膝关节三维解剖模型[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(12):1241-1244.
[9] 张震,董跃福,苏宏飞,等.轻度OA膝关节有限元解剖模型的构建及其力学分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(5):439-443.
[10] 张震.基于有限元法的OA膝关节生物力学研究[D].上海:上海工程技术大学,2020.
[11] 张吉超.OA膝关节在TKA手术前后不同角度下的数值仿真研究[D].上海:上海工程技术大学,2022.
[12] PINSKEROVA V, JOHAL P, NAKAGAWA S, et al. Does the femur roll-back with flexion? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(6):925-931.
[13] DONAHUE TL, HULL ML, RASHID MM, et al. A finite element model of the human knee joint for the study of tibio-femoral contact. J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(3):273-280.
[14] 樊瑜波,王丽珍.骨肌系统生物力学建模与仿真[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2018.
[15] VAUGHAN CL, DAVIS BL, O’CONNOR JC. Dynamics of Human Gait. Cape Town, South Africa: Kiboho Publishers, 1992:8-12.
[16] ASTM F3141-17a. Standard Guide for Total Knee Replacement Loading Profiles. USA: ASTM International. 2017.
[17] 李君芳.人工韧带重建与膝关节前交叉韧带的运动损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(12):2221-2224.
[18] 赵鸣昕.单髁置换人工膝关节生物力学研究[D].太原:太原理工大学, 2022.
[19] MONONEN ME, JURVELIN JS, KORHONEN RK. Implementation of a gait cycle loading into healthy and meniscectomised knee joint models with fibril-reinforced articular cartilage. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2015;18(1-4):141-152.
[20] HALONEN KS, MONONEN ME, JURVELIN JS, et al. Deformation of articular cartilage during static loading of a knee joint – Experimental and finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2014;47(10):2467-2474.
[21] 张吉超,董跃福,牟志芳,等.骨关节炎患者在不同步态角度下膝关节内部生物力学变化的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(9):1357-1361.
[22] PAZ A, OROZCO GA, KORHONEN RK, et al. Expediting finite element analyses for subject-specific studies of knee osteoarthritis: a literature review. Appl Sci. 2021;11(23):11440.
[23] POPESCU R, HARITINIAN EG, CRISTEA S. Relevance of Finite Element in Total Knee ArthroplastyLiterature Review. Chirurgia. 2019;114(4):437-442.
[24] EIDEL B, GOTE A, FRITZEN CP, et al. Tibial implant fixation in TKA worth a revision? how to avoid stress-shielding even for stiff metallic implants. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;24(3):320-332.
[25] INNOCENTI B, BELLEMANS J, CATANI F. Deviations From Optimal Alignment in TKA: Is There a Biomechanical Difference Between Femoral or Tibial Component Alignment? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1):295-301.
[26] SHARMA A, KOMISTEK RD, RANAWAT CS, et al. In Vivo Contact Pressures in Total Knee Arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(3):404-416.
[27] 张素红,许悦,胡晓然.人工关节置换术护理特点的探讨[C].全国第10届骨科护理学术交流暨专题讲座会议论文汇编,2008.
[28] DENNIS DA, KOMISTEK RD, MAHFOUZ MR, et al. Conventry Award Paper: Multicenter Determination of In Vivo Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;416:37-57.
[29] CASTELLARIN G, PIANIGIANI S, INNOCENTI B. Asymmetric polyethylene inserts promote favorable kinematics and better clinical outcome compared to symmetric inserts in a mobile bearing total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27:1096-1105.
[30] KANG KT, SON J, KWON SK, et al. Finite element analysis for the biomechanical effect of tibial insert materials in total knee arthroplasty. Compos Struct. 2018;201:141-150.
[31] BHANDARKAR S, DHATRAK P. Optimization of a knee implant with different biomaterials using finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2022;59:459-467.
[32] DONAHUE TLH, HULL ML, RASHID MM, et al. How the stiffness of meniscal attachments and meniscal material properties affect tibio-femoral contact pressure computed using a validated finite element model of the human knee joint. J Biomech. 2003;36(1):19-34.
[33] ZENG YM, YAN MN, LI HW, et al. Does mobile-bearing have better flexion and axial rotation than fixed-bearing in total knee arthroplasty? A randomised controlled study based on gait. J Orthop Translat. 2020;20:86-93. |