[1] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;136:104745.
[2] WANG W, BARAN GR, BETZ RR, et al. The Use of Finite Element Models to Assist Understanding and Treatment For Scoliosis: A Review Paper. Spine Deform. 2014;2(1):10-27.
[3] NAOUM S, VASILIADIS AV, KOUTSERIMPAS C, et al. Finite Element Method for the Evaluation of the Human Spine: A Literature Overview. J Funct Biomater. 2021;12(3):43.
[4] CAI XY, SANG D, YUCHI CX, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020;116:103519.
[5] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[6] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5): 301-317.
[7] KIM HJ, CHUN HJ, KANG KT, et al. A validated finite element analysis of nerve root stress in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47(6):599-605.
[8] WEI W, ZHANG T, YANG J, et al. Material sensitivity of patient-specific finite element models in the brace treatment of scoliosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1111449.
[9] WANG R, WU Z. Recent advancement in finite element analysis of spinal interbody cages: A review. FrFront Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1041973.
[10] SAKTI YM, SARASWATY RW, PRATAMA BY, et al. Functional outcomes following surgical treatment in patient with primary degenerative adult scoliosis. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;84:106095.
[11] ZHANG H, YU H, ZHANG M, et al. Selection of spinal surgery and hip replacement sequence in patients with both degenerative scoliosis and hip disease. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(12):300060520959224.
[12] CHEN K, ZHAO J, YANG Y, et al. Global research trends of adult degenerative scoliosis in this decade (2010-2019): a bibliometric study. Eur Spine J. 2020; 29(12):2970-2979.
[13] SUN W, GAO J, ZHU L, et al. Effect of spinal manipulation on degenerative scoliosis. J Tradit Chin Med. 2020;40(6):1033-1040.
[14] DIEBO BG, SHAH NV, BOACHIE-ADJEI O, et al. Adult spinal deformity. Lancet. 2019;394(10193):160-172.
[15] DIEBO BG, LAVIAN JD, MURRAY DP, et al. The Impact of Comorbid Mental Health Disorders on Complications Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery With Minimum 2-Year Surveillance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018; 43(17):1176-1183.
[16] DIEBO BG, CHERKALIN D, JALAI CM, et al. Comparing psychological burden of orthopaedic diseases against medical conditions: Investigation on hospital course of hip, knee, and spine surgery patients. J Orthop. 2018;15(2): 297-301.
[17] PETROSYAN E, FARES J, LESNIAK MS, et al. Biological principles of adult degenerative scoliosis. Trends Mol Med. 2023;29(9):740-752.
[18] LI LG, GAO JH, GAO CY, et al. [Clinical observation of chiropractic manipulation in the treatment of degenerative scoliosis]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022;35(5):442-447.
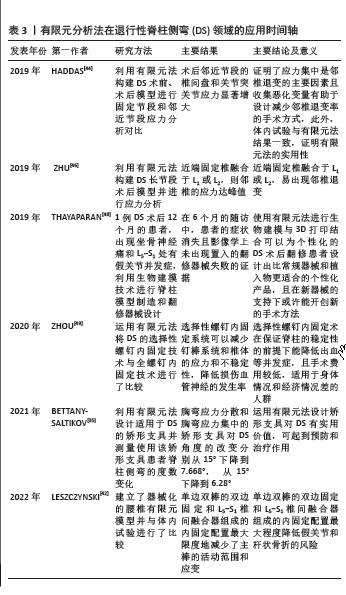
[19] HADDAS R, VILLARREAL J, LIEBERMAN IH. Kinematic comparison of the use of walking sticks versus a rolling walker during gait in adult degenerative scoliosis patients. Spine Deform. 2020;8(4):717-723.
[20] DONG J, LI W, JIANG Y, et al. [Selection of upper instrumented vertebra for long-segment fixation in adult degenerative scoliosis]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;36(10):1305-1311.
[21] SONG Z, ZHANG Z, YANG X, et al. Mid- and Long-Term Comparison Analysis of Two Approaches for the Treatment of Level III or Higher Lenke-Silva Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: Radical or Limited Surgery? Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2006-2015.
[22] CRISTANTE AF, SILVA RTE, COSTA G, et al. Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021;56(1):1-8.
[23] BALDAIRON F, CHARLES YP, EICHLER D, et al. Analysis of factors associated with sagittal alignment deterioration after correction of degenerative scoliosis by in situ contouring. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(7):103023.
[24] SHAHRESTANI S, BROWN NJ, ACHARYA N, et al. A case report of robotic-guided prone transpsoas lumbar fusion in a patient with lumbar pseudarthrosis, adjacent segment disease, and degenerative scoliosis. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022;94:106999.
[25] LI B, MENG X, ZHANG X, et al. Frailty as a risk factor for postoperative complications in adult patients with degenerative scoliosis administered posterior single approach, long-segment corrective surgery: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):333.
[26] FAN ZQ, YAN XA, LI BF, et al. Prevalence of osteoporosis in spinal surgery patients older than 50 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2023;18(5):e0286110.
[27] XU M, YANG J, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite element method-based study for effect of adult degenerative scoliosis on the spinal vibration characteristics. Comput Biol Med. 2017;84:53-58.
[28] ZHENG J, YANG Y, CHENG B, et al. Exploring the pathological role of intervertebral disc and facet joint in the development of degenerative scoliosis by biomechanical methods. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2019;70: 83-88.
[29] WANG L, ZHANG B, CHEN S, et al. A Validated Finite Element Analysis of Facet Joint Stress in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. World Neurosurg. 2016;95:126-133.
[30] 郑杰, 杨永宏, 楼肃亮, 等. 退变性脊柱侧弯的生物力学有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(30):5490-5496.
[31] 郑杰, 杨永宏. 椎间盘和关节突关节在退变性脊柱侧凸发生发展中的作用[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(9):826-831.
[32] HOMMINGA J, LEHR AM, MEIJER GJ, et al. Posteriorly directed shear loads and disc degeneration affect the torsional stiffness of spinal motion segments: a biomechanical modeling study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(21):E1313-1319.
[33] 周仕炼, 胡星新, 杨曦, 等.退变性腰椎侧凸六种工况运动下的生物力学的有限元分析[J]. 华西医学,2018,33(9):1099-1105.
[34] 黄平. 退变性腰椎侧凸演变过程及相关生物力学机制的有限元分析[D]. 上海:第二军医大学,2013.
[35] BETTANY-SALTIKOV J, PARK A, LING J. The experiences and effectiveness of the Spinecor brace on older adults with degenerative scoliosis: a mixed methods pilot study. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2021;280:294-295.
[36] KARIMI MT, EBRAHIMI MH, MOHAMMADI A, et al. Evaluation of the influences of various force magnitudes and configurations on scoliotic curve correction using finite element analysis. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2017;40(1):231-236.
[37] 郑杰, 何敏娟, 王大伟, 等. 退变性脊柱侧弯3D打印个性化减压融合[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(15):1364-1368.
[38] 赵迪. 成人退变性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的建立及后路三维矫形生物力学研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2010.
[39] 郑杰, 杨永宏, 张冬生, 等. 退变性脊柱侧凸不同方式长节段固定融合术后邻近节段生物力学变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(9):769-773.
[40] 马超. 长/短节段固定治疗成人退变性脊柱侧凸的临床研究及有限元分析[D]. 北京:中国人民解放军医学院, 2016.
[41] CHO KJ, KIM YT, SHIN SH, et al. Surgical treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(3):371-381.
[42] LESZCZYNSKI A, MEYER F, CHARLES YP, et al. Development of a flexible instrumented lumbar spine finite element model and comparison with in-vitro experiments. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022; 25(2):221-237.
[43] HA KY, KIM YH, AHN JH. Is it real adjacent segment pathology by stress concentration after limited fusion in degenerative lumbar scoliosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(13):1059-1066.
[44] HADDAS R, XU M, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite Element Based-Analysis for Pre and Post Lumbar Fusion of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis Patients. Spine Deform. 2019;7(4):543-552.
[45] FRADET L, WANG X, CRANDALL D, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Acute Proximal Junctional Failure After Surgical Instrumentation of Adult Spinal Deformity: The Impact of Proximal Implant Type, Osteotomy Procedures, and Lumbar Lordosis Restoration. Spine Deform. 2018;6(5):483-491.
[46] ZHU WY, ZANG L, LI J, et al. A biomechanical study on proximal junctional kyphosis following long-segment posterior spinal fusion. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52(5):e7748.
[47] BARI TJ, KARSTENSEN S, SøRENSEN MD, et al. Revision surgery and mortality following complex spine surgery: 2-year follow-up in a prospective cohort of 679 patients using the Spine AdVerse Event Severity (SAVES) system. Spine Deform. 2020;8(6):1341-1351.
[48] THAYAPARAN GK, OWBRIDGE MG, THOMPSON RG, et al. Designing patient-specific solutions using biomodelling and 3D-printing for revision lumbar spine surgery. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(Suppl 2):18-24.
[49] ZHOU Y, XIN D, LEI Z, et al. Comparative Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of 4 Kinds of Pedicle Screw Schemes for Treatment of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e922050.
[50] FASSER MR, GERBER G, PASSAPLAN C, et al. Computational model predicts risk of spinal screw loosening in patients. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(10): 2639-2649.
[51] DRISCOLL M, MAC-THIONG JM, LABELLE H, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of 2 Different Pedicle Screw Systems During the Surgical Correction of Adult Spinal Deformities. Spine Deform. 2015;3(2):114-121.
[52] SUN XY, KONG C, ZHANG TT, et al. Correlation between multifidus muscle atrophy, spinopelvic parameters, and severity of deformity in patients with adult degenerative scoliosis: the parallelogram effect of LMA on the diagonal through the apical vertebra. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):276.
[53] TANG Y, YANG S, CHEN C, et al. Assessment of the association between paraspinal muscle degeneration and quality of life in patients with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(1):505-511.
[54] TIAN L, GUO Y, GUO Z. Association between serum β-oestradiol and health-related quality of life in postmenopausal women with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2023;98(1):91-97.
|